|
Zaniolepis Frenata
''Zaniolepis frenata'', the shortspine combfish, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Zaniolepididae.The species occurs in the eastern Pacific Ocean. Taxonomy ''Zaniolepis frenata'' was first formally description in 1889 by the American ichthyologists Carl H. Eigenmann and Rosa Smith Eigenmann with its type locality given as Cortes Bank off San Diego, California. The specific name, ''frenata'', means "bridled". The Eigenmanns did not explain this allusion but they were probably referring the diagonal dark band running through the eye. Description ''Zaniolepis frenata'' has an elongated, slender and compressed body. The background color is tan or pink on the upper body broken by with darker, rather ill-defined markings, fading to white on the underside. In life they have a row of dark saddle-like markings along the back and a variety of blotches and spots on the flanks with a diagonal fark bar through the eye. They have a long anal fin which has a broad dark st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl H
Carl may refer to: *Carl, Georgia, city in USA *Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name *Carl², a TV series * "Carl", an episode of television series ''Aqua Teen Hunger Force'' * An informal nickname for a student or alum of Carleton College CARL may refer to: *Canadian Association of Research Libraries *Colorado Alliance of Research Libraries See also *Carle (other) *Charles *Carle, a surname *Karl (other) *Karle (other) Karle may refer to: Places * Karle (Svitavy District), a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Karli, India, a town in Maharashtra, India ** Karla Caves, a complex of Buddhist cave shrines * Karle, Belgaum, a settlement in Belgaum ... {{disambig ja:カール zh:卡尔 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies. These data are used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fisheries biology. Overall length * Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. Simply put, this measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. * Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini ( hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys), and (usually) Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays), as well as some other fishes. Total leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haliotrema Parahaliotremata
''Haliotrema'' is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Ancyrocephalidae. The species of this genus are found in Pacific Ocean and America. Species: *''Haliotrema abaddon'' *''Haliotrema acanthuri'' *''Haliotrema alatum'' *'' Haliotrema allornata'' *'' Haliotrema amanses'' *'' Haliotrema amplimacrohamus'' *''Haliotrema ampliocuspidis'' *''Haliotrema angelopterum'' *''Haliotrema angulocirrus'' *''Haliotrema arsiosa'' *''Haliotrema auribaculum'' *''Haliotrema aurigae'' *''Haliotrema aurigae'' *'' Haliotrema australe'' *'' Haliotrema balisticus'' *'' Haliotrema banana'' *''Haliotrema bifurcocirrus'' *''Haliotrema bihamulatum'' *''Haliotrema bilobatum'' *''Haliotrema bisegmentatum'' *''Haliotrema bodiani'' *''Haliotrema breve'' *''Haliotrema brevicirrus'' *''Haliotrema brevicornigerum'' *''Haliotrema brevispirocirrus'' *''Haliotrema brotulae'' *''Haliotrema caballeroi'' *''Haliotrema caesiopercae'' *''Haliotrema canescens'' *''Haliotrema caraiben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamaticolax Prolixus
''Hamaticolax'' is a genus of parasitic copepods belonging to the family Bomolochidae. Its members can only be distinguished from the closely related genus '' Acantholochus'' by the presence of an accessory process on the claw of the maxillipeds. It includes the following species: *'' Hamaticolax attenuatus'' (C. B. Wilson, 1913) *'' Hamaticolax embiotocae'' (Hanan, 1976) *'' Hamaticolax galeichthyos'' (Luque & Bruno, 1990) *'' Hamaticolax maleus'' (Oldewage, 1994) *'' Hamaticolax occultus'' (Kabata, 1971) *'' Hamaticolax paralabracis'' (Luque & Bruno, 1990) *'' Hamaticolax prolixus'' (Cressey, 1969) *'' Hamaticolax scutigerulus'' (C. B. Wilson, 1935) *''Hamaticolax spinulus ''Hamaticolax'' is a genus of parasitic copepods belonging to the family Bomolochidae. Its members can only be distinguished from the closely related genus ''Acantholochus'' by the presence of an accessory process on the claw of the maxillipeds. ...'' (Cressey, 1969) *'' Hamaticolax unisagittatus'' (Tavar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Lion
Sea lions are pinnipeds characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they make up the family Otariidae, eared seals. The sea lions have six extant and one extinct species (the Japanese sea lion) in five genera. Their range extends from the subarctic to tropical waters of the global ocean in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, with the notable exception of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They have an average lifespan of 20–30 years. A male California sea lion weighs on average about and is about long, while the female sea lion weighs and is long. The largest sea lions are Steller's sea lions, which can weigh and grow to a length of . Sea lions consume large quantities of food at a time and are known to eat about 5–8% of their body weight (about ) at a single feeding. Sea lions can move around in water and at their fastest they can r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same environmental problems and feeding niches have resulted in similar adaptations. The first seabirds evolved in the Cretaceous period, and modern seabird families emerged in the Paleogene. In general, seabirds live longer, breed later and have fewer young than other birds do, but they invest a great deal of time in their young. Most species nest in colonies, which can vary in size from a few dozen birds to millions. Many species are famous for undertaking long annual migrations, crossing the equator or circumnavigating the Earth in some cases. They feed both at the ocean's surface and below it, and even feed on each other. Seabirds can be highly pelagic, coastal, or in some cases spend a part of the year away from the sea entirely. Seabirds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
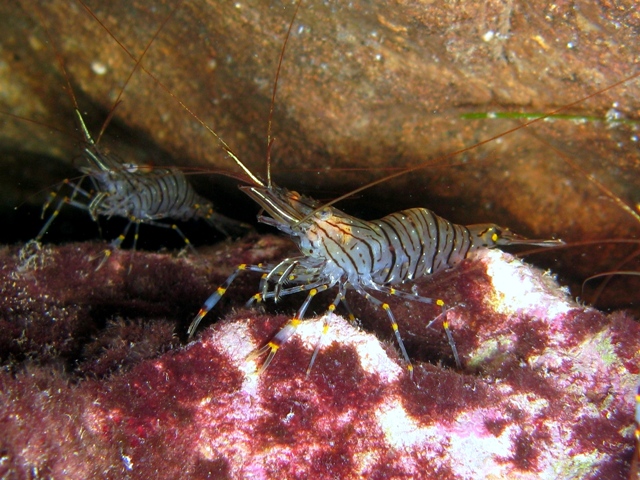
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referred to as "shrimp". More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either group or to only the marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails ( abdomens), long whiskers ( antennae), and slender legs. Any small crustacean which resembles a shrimp tends to be called one. They swim forward by paddling with swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks with the tail driving them backwards very quickly. Crabs and lobsters have strong walking legs, whereas shrimp have thin, fragile legs which they use primarily for perching.Rudloe & Rudloe (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the sandworm or clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepest known spot in the Earth's oceans. Only 168 species (less than 2% of all polychaetes) are known from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopoda
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are grazers, or filter feeders, a few are predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or bottom of freshwater bodies of water, but some taxa can swim for a short distance. Terrestrial forms move around by crawling and tend to be found in cool, moist places. Some species are able to roll themselves into a ball as a defense mechanism or to conserve moisture. There are over 10,000 identified species of isopod worldwide, with around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
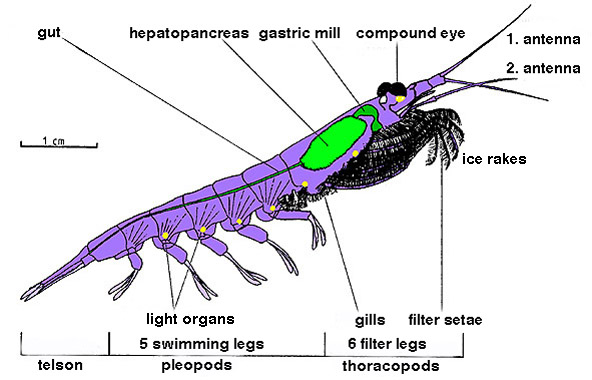
Krill
Krill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection – near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and (to a lesser extent) zooplankton, yet also are the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, ''Euphausia superba'', makes up an estimated biomass of around 379,000,000 tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, seals, penguins, seabirds, squid, and fish each year. Most krill species display large daily vertical migrations, thus providing food for predators near the surface at night and in deeper waters during the day. Krill are fished commercially in the Southern Ocean and in the waters around Japa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult and then, after more molts, achieves adult development. The nauplius form is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)