|
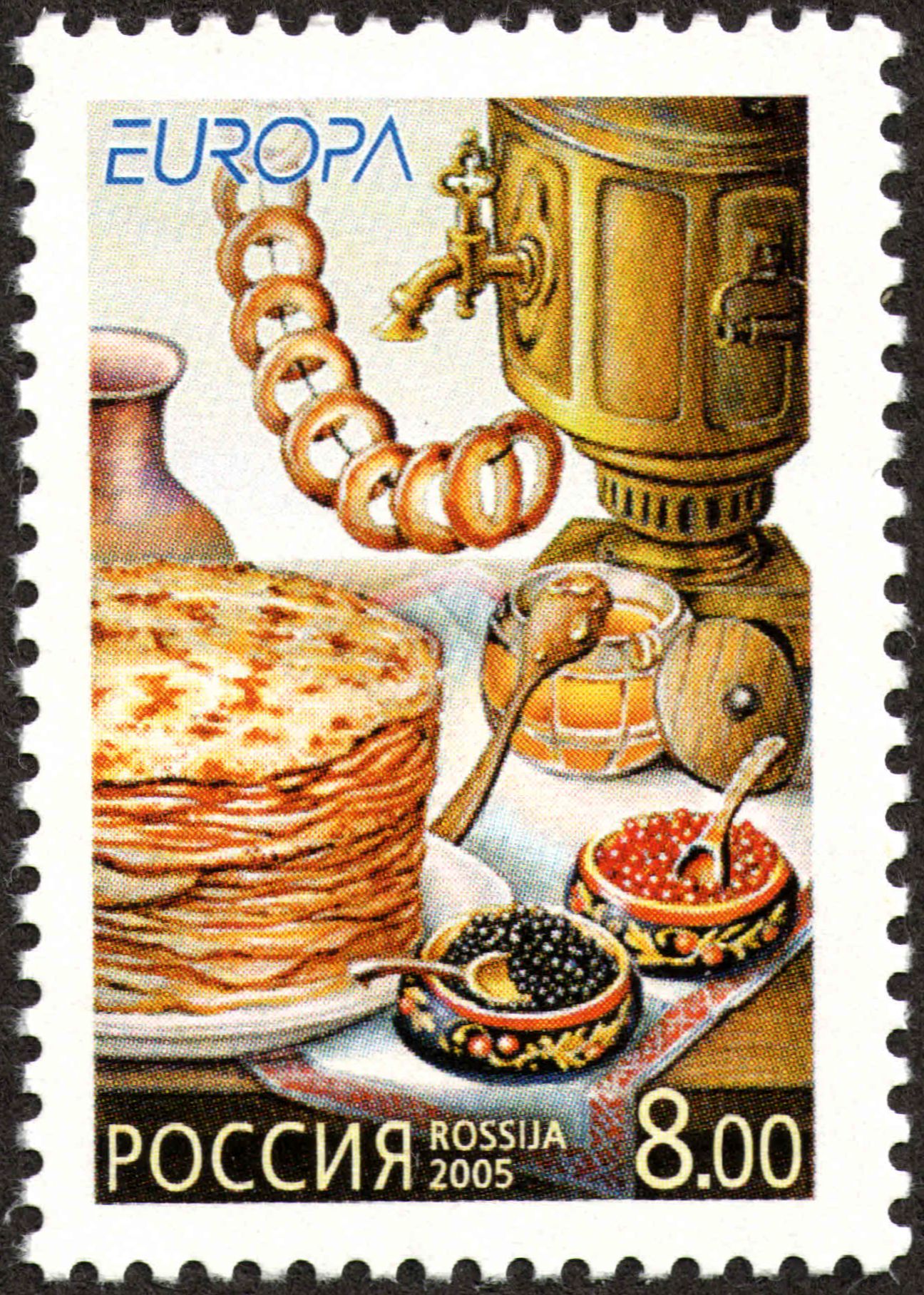
Zakuski
''Zakuski'' (, ; ) is the term for an assortment of cold hors d'oeuvres, entrées and snacks in Russian food culture. They are considered to be an integral part of any Russian festive meal, as well as often everyday meals. Terminology Originally, the term referred to pies and other sweet delicacies served after a main meal, but now can refer to a light meal before a main meal or a snack, which may also be eaten at a stand-up bar known as ''zakusochnaya''. It is served as a course on its own or "intended to follow each shot of vodka or another alcoholic drink". The word literally means 'little bites'. History The tradition of ''zakuski'' is linked to the Swedish and Finnish '' brännvinsbord'', which was also the ancestor of modern smörgåsbord, and to '' meze'' of the Ottoman Empire and other Middle Eastern cultures. Its origin is generally attributed to Peter I of Russia (), who absorbed many foreign customs during his travels to Western Europe. ''Zakuski'' are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Cuisine
Russian cuisine is a collection of the different dishes and cooking traditions of the Russians, Russian people as well as a list of culinary products popular in Russia, with most names being known since pre-Soviet times, coming from all kinds of social circles. History The history of Russian cuisine was divided in four groups: Old Russian cuisine (9th to 16th century), Old Moscow cuisine (17th century), the cuisine that existed during the ruling of Peter the Great, Peter and Catherine the Great (18th century), and finally Petersburg cuisine, which took place from the end of the 18th century to the 1860s. In the Old Russian period, the main food groups were bread, grains, and other foods that contained starch. Women baked pies with many different fillings, such as mushrooms or berries. During gatherings, a loaf of bread and salt was always present. Kasha, such as buckwheat and oats, were represented as wellbeing to the household. Many Russians used honey and berries and mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vodka
Vodka ( ; is a clear distilled beverage, distilled alcoholic beverage. Its varieties originated in Poland and Russia. Vodka is composed mainly of water and ethanol but sometimes with traces of impurities and flavourings. Traditionally, it is made by distilling liquid from Fermentation in food processing, fermented cereal, cereal grains and potatoes since the latter was introduced in Europe in the 18th century. Some modern brands use maize, Sugarcane, sugar cane, fruits, fruit, honey, and Maple syrup, maple sap as the base. Since the 1890s, standard vodkas have been 40% alcohol by volume (ABV) (80 U.S. proof). The European Union has established a minimum alcohol content of 37.5% for vodka. Vodka in the United States must have a minimum alcohol content of 40%. Vodka is traditionally drunk "Bartending terminology, neat" (not mixed with water, ice, or other Mixer drink, mixers), and it is often served freezer chilled in the Alcohol belts of Europe#Vodka belt, vodka belt of Belaru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beet
The beetroot (British English) or beet (North American English) is the taproot portion of a '' Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' plant in the Conditiva Group. The plant is a root vegetable also known as the table beet, garden beet, dinner beet, or else categorized by color: red beet or golden beet. It is also a leaf vegetable called beet greens. Beetroot can be eaten raw, roasted, steamed, or boiled. Beetroot can also be canned, either whole or cut up, and often are pickled, spiced, or served in a sweet-and-sour sauce. It is one of several cultivated varieties of ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' grown for their edible taproots or leaves, classified as belonging to the Conditiva Group. Other cultivars of the same subspecies include the sugar beet, the leaf vegetable known as spinach beet (Swiss chard), and the fodder crop mangelwurzel. Etymology ''Beta'' is the ancient Latin name for beetroot,Gledhill, David (2008). "The Names of Plants". Cambridge University Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirog
Pirog ( rus, пиро́г, p=pʲɪˈrok, a=Ru-пирог.ogg, links=yes; , , ; ; ; , ; , ; ; ) is a baked case of dough with either sweet or savory filling.Darra Goldstein. ''A Taste of Russia: A Cookbook of Russian Hospitality'', "Russian pies", p.54. Russian Information Service, 1999, Вильям Похлебкин. ''Кулинарный словарь''Пироги Москва: Центрполиграф, 2007, ( William Pokhlyobkin. ''The Culinary Dictionary'', "Pirogi". Moscow: Centrpoligraph, 2007; in Russian) The dish is common in Eastern European cuisines. The name is derived from the ancient Proto-Slavic word ''pir'', meaning "banquet" or " festivity".Вильям Похлебкин. ''Большая энциклопедия кулинарного искусства''Пироги русские Москва: Центрполиграф, 2010, ( William Pokhlyobkin. ''The Great Encyclopedia of Culinary Art'', "Russian pirogi". Moscow: Centrpoligraph, 2010; in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salad
A salad is a dish consisting of mixed ingredients, frequently vegetables. They are typically served chilled or at room temperature, though some can be served warm. Condiments called '' salad dressings'', which exist in a variety of flavors, are usually used to make a salad. Garden salads have a base of raw leafy greens (sometimes young "baby" greens) such as lettuce, arugula (rocket), kale or spinach; they are common enough that the word ''salad'' alone often refers specifically to garden salads. Other types of salad include bean salad, tuna salad, bread salads (such as fattoush, panzanella), vegetable salads without leafy greens (such as Greek salad, potato salad, coleslaw), rice-, pasta- and noodle-based salads, fruit salads and dessert salads. Salads may be served at any point during a meal: * Appetizer salads – light, smaller-portion salads served as the first course of the meal * Side salads – to accompany the main course as a side dish; examples inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Cuts
Lunch meats—also known as cold cuts, luncheon meats, cooked meats, sliced meats, cold meats, sandwich meats, delicatessens, and deli meats—are precooked or cured meats that are sliced and served cold or hot. They are typically served in sandwiches or on a tray. They can be purchased canned, pre-sliced (usually in vacuum packs), or they can be sliced to order, most often in delicatessens and charcuteries. Lunch meats are processed meats designed for convenience. The preservatives added to extend the shelf life have been increasingly scrutinized due to potential links to certain diseases. In the US, ''Listeria'' infection is possible and has resulted in additional guidelines from the CDC for the elderly. Types * Bresaola * Chicken breast * Chicken loaf (also known as chicken roll) * Corned beef * Cotechino * Dutch loaf * Ham ** Baked ** Boiled ** Chipped chopped ** Cooked ** ''Éisleker'' ** '' Jamón'': ''serrano'' or ''ibérico'' ** Presunto ** Prosciut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Soviet States
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they existed as Republics of the Soviet Union, Union Republics, which were the top-level constituents of the Soviet Union. There are 15 post-Soviet states in total: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Estonia, Georgia (country), Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. Each of these countries succeeded their respective Union Republics: the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, Armenian SSR, the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, Azerbaijan SSR, the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR, the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic, Estonian SSR, the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, Georgian SSR, the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, Kazakh SSR, the Kirghiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Cuisine
Soviet cuisine, the common cuisine of the Soviet Union, was formed by the integration of the various national cuisines of the Soviet Union, in the course of the formation of the Soviet people. It is characterized by a limited number of ingredients and simplified cooking. This type of cuisine was prevalent in canteens everywhere in the Soviet Union. It became an integral part of household cuisine and was used in parallel with national dishes, particularly in large cities. Generally, Soviet cuisine was shaped by Soviet eating habits and a very limited availability of ingredients in most parts of the USSR. Most dishes were simplifications of French, Russian, Austro- Hungarian cuisines, and cuisines from other Eastern Bloc nations. Caucasian cuisines, particularly Georgian cuisine, contributed as well. To a significant extent it was reflected in and formed by '' The Book of Tasty and Healthy Food'', first printed in 1939, following the directions of Anastas Mikoyan. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Nobility
The Russian nobility or ''dvoryanstvo'' () arose in the Middle Ages. In 1914, it consisted of approximately 1,900,000 members, out of a total population of 138,200,000. Up until the February Revolution of 1917, the Russian noble estates staffed most of the Russian government and possessed a self-governing body, the Assembly of the Nobility. The Russian language, Russian word for nobility, ''dvoryanstvo'' derives from Slavonic ''dvor'' (двор), meaning the noble court, court of a prince or duke (''knyaz''), and later, of the tsar or emperor. Here, ''dvor'' originally referred to servants at the estate of an aristocrat. In the late 16th and early 17th centuries, the system of hierarchy was a system of seniority known as ''mestnichestvo''. The word ''dvoryane'' described the highest rank of gentry, who performed duties at the royal court, lived in it (''Moskovskie zhiltsy'', "Moscow dwellers"), or were candidates to it, as for many boyar scions (''dvorovye deti boyarskie'', ''v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter I Of Russia
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman and Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a significant portion of the eastern Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a tsardom to an empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist and medieval social and political systems with ones that were modern, scientific, Westernized, and based on radical Enlightenment. In December 1699, he introduced the Julian calendar, and in 1703, he introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |