|
Zaum
() are the linguistic experiments in sound symbolism and language creation of Russian Cubo-Futurist poets such as Velimir Khlebnikov and Aleksei Kruchenykh. Zaum is a non-referential phonetic entity with its own ontology. The language consists of neologisms that mean nothing. Zaum is a language organized through phonetic analogy and rhythm. Zaum literature cannot contain any onomatopoeia or psychopathological states. Usage Aleksei Kruchenykh created Zaum in order to show that language was indefinite and indeterminate. Kruchenykh stated that when creating Zaum, he decided to forgo grammar and syntax rules. He wanted to convey the disorder of life by introducing disorder into the language. Kruchenykh considered Zaum to be the manifestation of a spontaneous non-codified language. Khlebnikov believed that the purpose of Zaum was to find the essential meaning of word roots in consonantal sounds. He believed such knowledge could help create a new universal language based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyr Bul Shchyl
(Zaum: , ) is the earliest and most famous zaum/transrational poem by Aleksei Kruchenykh, written using the Zaum language, which, according to the author, is "more Russian national, than in all of Pushkin's poetry". The poem was written in December 1912. This date the author then called "the time of occurrence of the phenomenon of Zaum language (i.e. the language that has no utility value), in which are written the whole independent works, and not just parts thereof (as the chorus, sound decoration, etc.)". Initiator of the creation of the work of the "unknown words" was David Burliuk. "Dyr bul shchyl" was published in January 1913 in a series of "three poems" in Kruchenykh's book (). According to Kruchenykh, this poem was to become much more known than him. Prefacing the poems, he also stated that "its words do not have/a definite meaning". The poem, in Marjorie Perloff, Majorie Perloff's English transliteration, runs: References {{Futurism, state=expanded 1912 poe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victory Over The Sun
__NOTOC__ ''Victory over the Sun'' (, ''Pobeda nad Solntsem'') is a Russian Futurist opera premiered in 1913 at the Luna Park in Saint Petersburg. The libretto written in '' zaum'' language was contributed by Aleksei Kruchonykh, the music was written by Mikhail Matyushin, the prologue was added by Velimir Khlebnikov, and the stage designer was Kazimir Malevich. The opera has become notable as the event where Malevich made his first Black Square, as part of a design for a curtain. The first performance was organised by the artistic group Soyuz Molodyozhi. Plot and reception The plot concerns a group of protagonists who want to destroy reason, by disposing of time and capturing the Sun. The opera was intended to underline parallels between literary text, musical score, and the art of painting, and featured a cast of such extravagant characters as ''Nero and Caligula in the Same Person'', ''Traveller through All the Ages'', ''Telephone Talker'', ''The New Ones'', etc. The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksei Kruchenykh
Aleksei Yeliseyevich Kruchyonykh (; 9 February 1886 – 17 June 1968). Original name at birth ( Ukrainian: Олексій Єлисейович Кручений) also romanized Kruchenykh due to confusion about , was a poet, artist, and theorist, perhaps one of the most radical poets of Russian Futurism, a movement that included Vladimir Mayakovsky, David Burliuk and others. Born in 1886, he lived in the time of the Russian Silver Age of literature, and together with Velimir Khlebnikov, another Russian Futurist, Kruchenykh is considered the inventor of ''zaum'', a poetry style utilising nonsense words. Kruchonykh wrote the libretto for the Futurist opera '' Victory Over the Sun'', with sets provided by Kazimir Malevich. In 1912, he wrote the poem '' Dyr bul shchyl''; four years later, in 1916, he created his most famous book, '' Universal War''. He is also known for his ''Declaration of the Word as Such'' (1913): "The worn-out, violated word "lily" is devoid of all express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velimir Khlebnikov
Viktor Vladimirovich Khlebnikov, better known by the pen name ( rus, Велими́р Хле́бников, p=vʲɪlʲɪˈmʲir ˈxlʲɛbnʲɪkəf; – 28 June 1922), was a Russian poet and playwright, a central part of the Russian Futurist movement, but his work and influence stretch far beyond it. Influential linguist Roman Jakobson hailed Khlebnikov as "the greatest world poet of our century". Biography Viktor Vladimirovich Khlebnikov was born in 1885 in Malye Derbety, Astrakhan Governorate, Russian Empire (in present-day Kalmykia). He was of Russian, Armenian and Zaporozhian Cossack descent.James R. Russell, "The Black Dervish of Armenian Futurism," ''Journal of Armenian Studies'', 10 His younger sister, Vera Khlebnikova, was an artist. He moved to Kazan, where he attended school. He then attended school in Saint Petersburg. He eventually quit school to become a full-time writer. His earliest works are from 1908. In 1909-10, he met the to-be Russian Futurists Vasil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Of The Gods
Divine language, the language of the gods, or, in monotheism, the language of God (or angels), is the concept of a mystical or divine proto-language, which predates and supersedes human speech. Abrahamic traditions In Judaism and Christianity, it is unclear whether the language used by God to address Adam was the language of Adam, who as name-giver (Genesis 2:19) used it to name all living things, or if it was a different divine language. In Islam, Arabic is the language in which God revealed the final revelation. Some Christians see the languages written on the INRI cross (Aramaic-Hebrew, Greek and Latin) as God's languages. Indian traditions In Hinduism, "speech" Vāc, i.e. the language of liturgy, now known as Sanskrit, is considered the language of the gods called "Devavani" (speech (vani) of Devas). Later Hindu scholarship, in particular the Mīmāṃsā school of Vedic hermeneutics, distinguished ''Vāc'' from ''Śábda'', a distinction comparable to the Saussurian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zangezi
Zangezi (), or Zangezi: A Supersaga in 20 Planes, is a futurist poem-play by Soviet, poet, writer and scholar Velimir Khlebnikov. Title and history Zangezi is the name of a prophet in the work, the name being composed from Kalmyk word 'zyange', that in Kalmyk language means "messenger". The name Zangezi had different variants in Velimir Khlebnikov's draft book (which he was ironically calling in German fashion 'Großbuch'): Zengezi, Mangezi, Changezi, Changili (Зенгези, Мангези, Чангези, Чангили). Some critics said the name Zangezi associated with famous rivers Ganges and Zambezi. Other pointed out that Zangezi is name composed from Kalmyk word 'zyange', that in Kalmyk language means 'the messenger'. Velimir Khlebnikov wrote to his friend, fellow futurist poet Vasily Kamensky in 1909, that he had wanted to create a work in which 'every chapter must not have a likeness of another' ('...каждая глава не должна походить на д� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Symbolism
In linguistics, sound symbolism is the perceptual similarity between speech sounds and concept meanings. It is a form of linguistic iconicity. For example, the English word ''ding'' may sound similar to the actual sound of a bell. Linguistic sound may be perceived as similar to not only sounds, but also to other sensory properties, such as size, vision, touch, or smell, or abstract domains, such as emotion or value judgment. Such correspondence between linguistic sound and meaning may significantly affect the form of spoken languages. History Plato and the Cratylus Dialogue In '' Cratylus'', Plato has Socrates commenting on the origins and correctness of various names and words. When Hermogenes asks if he can provide another hypothesis on how signs come into being (his own is simply 'convention'), Socrates initially suggests that they fit their referents in virtue of the sounds they are made of: However, faced by an overwhelming number of counterexamples given by Hermog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serge Segay
Serge Segay (real name Sergey Vsevolodovich Sigov , 19 March 1947 - 21 September 2014), also known as Sergej Sigej, was a Russian artist, poet, writer as well as specialist in Russian Futurism. Many of his artworks are in private and public collections throughout the world. He was an important figure in Transfurism movement as an artist, poet, writer, as well as a prominent figure in Mail art history. He was also key member of "Uktuss School" and "Anarfut" art movements. Early life Segay was born in Murmansk, Russia on 19 March 1947. His father was a dean of Taganrog university and communist "aparatchik". After school he got a place in Taganrog university, studying Russian literature, with multiple private tutors being paid by his father. Arrangement did not last however, as there was a row between Serge Segay and his father about abstract art, which at that point was deemed as contradicting party guidelines. Row was very bad: Serge Segay run away from home (apparently also in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimeograph
A mimeograph machine (often abbreviated to mimeo, sometimes called a stencil duplicator or stencil machine) is a low-cost duplicating machine that works by forcing ink through a stencil onto paper. The process is called mimeography, and a copy made by the process is a mimeograph. Mimeographs, along with spirit duplicators and hectographs, were common technologies for printing small quantities of a document, as in office work, classroom materials, and church bulletins. For even smaller quantities, up to about five, a typist would use carbon paper. Early fanzines were printed by mimeograph because the machines and supplies were widely available and inexpensive. Beginning in the late 1960s and continuing into the 1970s, photocopying gradually displaced mimeographs, spirit duplicators, and hectographs. Origins Use of stencils is an ancient art, butthrough chemistry, papers, and pressestechniques advanced rapidly in the late nineteenth century: Papyrograph A description of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamphlet
A pamphlet is an unbound book (that is, without a Hardcover, hard cover or Bookbinding, binding). Pamphlets may consist of a single sheet of paper that is printed on both sides and folded in half, in thirds, or in fourths, called a ''leaflet'' or it may consist of a few pages that are folded in half and Saddle stitch stapler, saddle stapled at the crease to make a simple book. In the "International Standardization of Statistics Relating to Book Production and Periodicals", UNESCO defines a pamphlet as "a non-periodical printed publication of 5 to 48 pages, excluding covers, published in a specific country and available to the public," while a book is "a non-periodical printed publication of at least 49 pages, excluding covers." These definitions are intended solely for UNESCO's book production statistics. Etymology The word ''pamphlet'' for a small work (''opuscule'') issued by itself without covers came into Middle English as or , generalized from a twelfth-century Elegiac c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
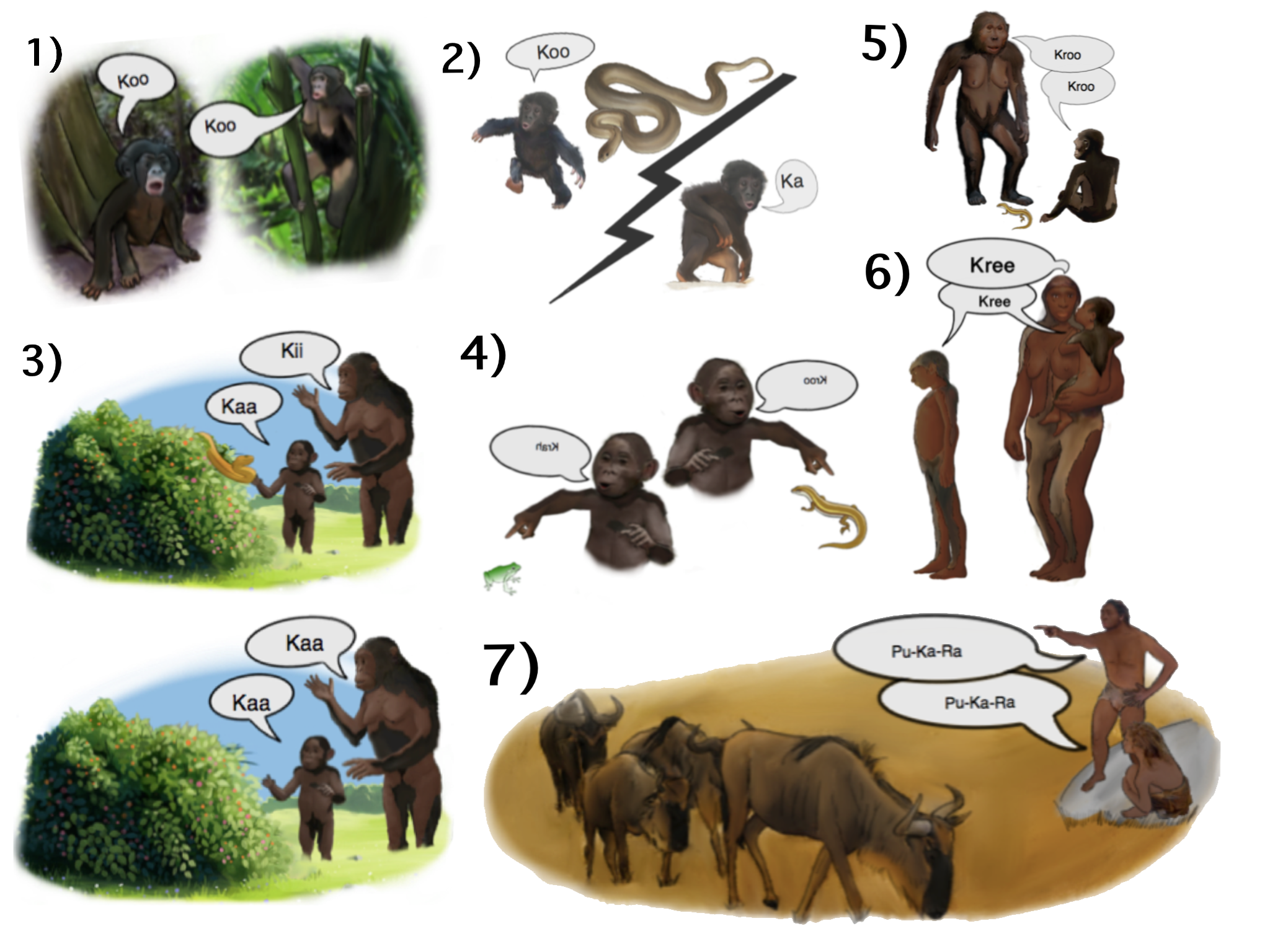
Glottogony
The origin of language, its relationship with human evolution, and its consequences have been subjects of study for centuries. Scholars wishing to study the origins of language draw inferences from evidence such as the fossil record, archaeological evidence, and contemporary language diversity. They may also study language acquisition as well as comparisons between human language and systems of animal communication (particularly other primates). Many argue for the close relation between the origins of language and the origins of modern human behavior, but there is little agreement about the facts and implications of this connection. The shortage of direct, empirical evidence has caused many scholars to regard the entire topic as unsuitable for serious study; in 1866, the Linguistic Society of Paris banned any existing or future debates on the subject, a prohibition which remained influential across much of the Western world until the late twentieth century. Various hypotheses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dadaism
Dada () or Dadaism was an anti-establishment art movement that developed in 1915 in the context of the Great War and the earlier anti-art movement. Early centers for dadaism included Zürich and Berlin. Within a few years, the movement had spread to New York City and a variety of artistic centers in Europe and Asia. Within the umbrella of the movement, people used a wide variety of artistic forms to protest the logic, reason, and aestheticism of modern capitalism and modern war. To develop their protest, artists tended to make use of nonsense, irrationality, and an anti-bourgeois sensibility. The art of the movement began primarily as performance art, but eventually spanned visual, literary, and sound media, including collage, sound poetry, cut-up technique, cut-up writing, and sculpture. Dadaist artists expressed their discontent toward violence, war, and nationalism and maintained political affinities with radical politics on the left-wing and far-left politics. The movem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |