|
Yves Roberge
Yves Roberge is professor of linguistics in the French Department at the University of Toronto. He received a BA in French Studies in 1981 and an MA in linguistics in 1983, both from the University of Sherbrooke, and a PhD in Linguistics from the University of British Columbia in 1986. Roberge served as Principal of New College from 2010 through 2017. Roberge researches the syntax and semantics of French and other Romance languages, especially Canadian French, as well as dialectal variation, first language acquisition, and the syntax-morphology interface. He is well known for his work on implicit (or silent) arguments, which he has studied from both a theoretical perspective and an acquisition perspective, and which is the subject of his book ''The Syntactic Recoverability of Null Arguments'', published in 1990. In 2015, Roberge received the National Achievement Award presented by the Canadian Linguistic Association The Canadian Linguistic Association (CLA; French: Associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Toronto
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguists From Canada
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Linguistic Association
The Canadian Linguistic Association (CLA; French: Association canadienne de linguistique, ACL) is the principal professional organization of linguists in Canada. Yearly meetings are held, usually at the end of May, in which members present scholarly research on any area of Linguistics. Every year since 2011, a new exhibit of the Canadian Language Museum has also opened at the annual meeting. The CLA also publishes the '' Canadian Journal of Linguistics'', which is published quarterly. The association was founded in 1954. The Canadian Linguistic Association also awards an annual National Achievement Award, which has been presented to * J. K. Chambers (2010) * Yves Charles-Morin and Shana Poplack (2011) * Keren Rice Keren Rice (born 1949) is a Canadian linguist. She is a professor of linguistics and serves as the Director of the Centre for Aboriginal Initiatives at the University of Toronto. Education and career Rice earned her PhD in 1976 from the Univ ... (2013) * J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Acquisition
Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the capacity to perceive and comprehend language (in other words, gain the ability to be aware of language and to understand it), as well as to produce and use words and sentences to communicate. Language acquisition involves structures, rules and representation. The capacity to use language successfully requires one to acquire a range of tools including phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and an extensive vocabulary. Language can be vocalized as in speech, or manual as in sign. Human language capacity is represented in the brain. Even though human language capacity is finite, one can say and understand an infinite number of sentences, which is based on a syntactic principle called recursion. Evidence suggests that every individual has three recursive mechanisms that allow sentences to go indeterminately. These three mechanisms are: ''relativization'', ''complementation'' and ''coordination''. There are tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
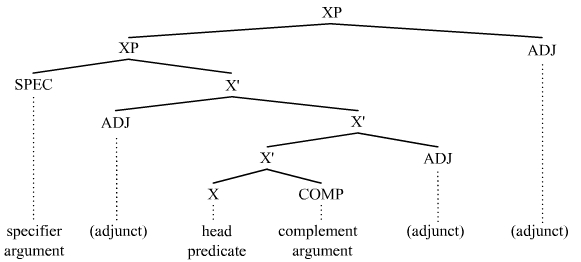
Argument (linguistics)
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the '' complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Language Acquisition
Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the capacity to perceive and comprehend language (in other words, gain the ability to be aware of language and to understand it), as well as to produce and use words and sentences to communicate. Language acquisition involves structures, rules and representation. The capacity to use language successfully requires one to acquire a range of tools including phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and an extensive vocabulary. Language can be vocalized as in speech, or manual as in sign. Human language capacity is represented in the brain. Even though human language capacity is finite, one can say and understand an infinite number of sentences, which is based on a syntactic principle called recursion. Evidence suggests that every individual has three recursive mechanisms that allow sentences to go indeterminately. These three mechanisms are: ''relativization'', ''complementation'' and ''coordination''. There are two ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena: One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. Under this definition, the dialects or varieties of a particular language are closely related and, despite their differences, are most often largely mutually intelligible, especially if close to one another on the dialect continuum. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors, such as social class or ethnicity. A dialect that is associated with a particular social class can be termed a sociolect, a dialect that is associated with a particular ethnic group can be termed an ethnolect, and a geographical/regional dialect may be termed a regiolectWolfram, Walt and Schilling, Natalie. 2016. ''American Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |