|
Yucca Sterilis
''Yucca sterilis'' is a species in the family Asparagaceae, native to the Uintah Basin region in Duchesne and Uintah Counties, Utah. It is closely related to '' Y. harrimaniae'' Trel. ''Yucca sterilis'' is an acaulescent (trunkless) species spreading by underground rhizomes. The inflorescence is up to 40 cm tall, with flowers white or sometimes tinged with violet along the edges of the tepals A tepal is one of the outer parts of a flower (collectively the perianth). The term is used when these parts cannot easily be classified as either sepals or petals. This may be because the parts of the perianth are undifferentiated (i.e. of very ....Neese & Welsh, Great Basin Naturalist 45(4):789-790 (1985) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q16760375 sterilis Plants described in 2008 Flora of Utah Flora without expected TNC conservation status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparagaceae
Asparagaceae, known as the asparagus family, is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. The family name is based on the edible garden asparagus, '' Asparagus officinalis''. Those who live in the temperate climates may be surprised to learn that this family includes both common garden plants as well as common houseplants. The garden plants include asparagus, yucca, bluebell, and hosta, and the houseplants include snake plant, corn cane, spider plant and plumosus fern. Taxonomy In earlier classification systems, the species involved were often treated as belonging to the family Liliaceae. The APG II system of 2003 allowed two options as to the circumscription of the family: either Asparagaceae ''sensu lato'' ("in the wider sense") combining seven previously recognized families, or Asparagaceae ''sensu stricto'' ("in the strict sense") consisting of very few genera (notably '' Asparagus'', also '' Hemiphylacus''), but nevertheless to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
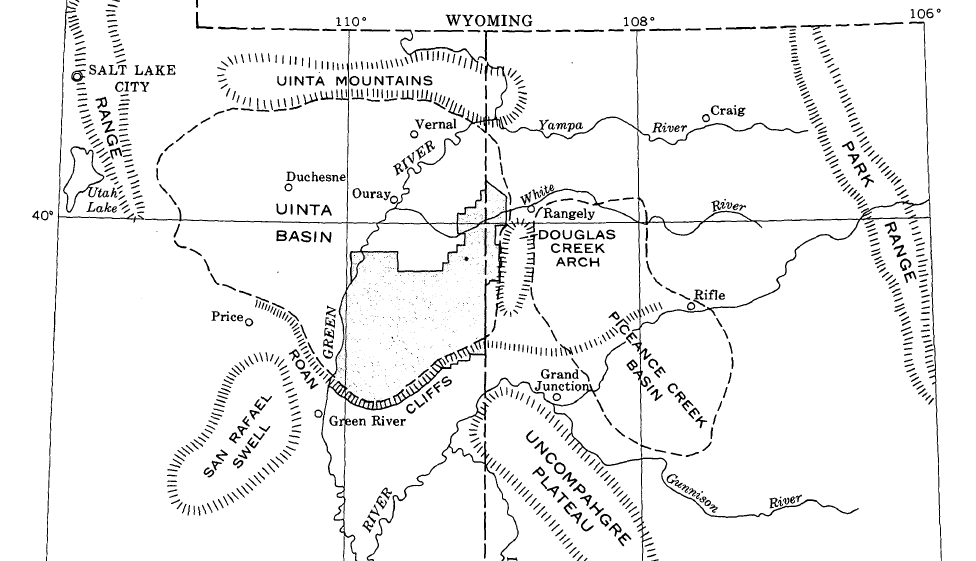
Uintah Basin
The Uinta Basin (also known as the Uintah Basin) is a physiographic section of the larger Colorado Plateaus province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is also a geologic structural basin in eastern Utah, east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains. The Uinta Basin is fed by creeks and rivers flowing south from the Uinta Mountains. Many of the principal rivers (Strawberry River, Currant Creek, Rock Creek, Lake Fork River, and Uintah River) flow into the Duchesne River which feeds the Green River—a tributary of the Colorado River. The Uinta Mountains forms the northern border of the Uinta Basin. They contain the highest point in Utah, Kings Peak, with a summit 13,528 feet (4123 metres) above sea level. The climate of the Uinta Basin is semi-arid, with occasionally severe winter cold. History Father Escalante's expedition visited the Uinta Basin in September 1776. 1822–1840 French Canadian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchesne County, Utah
Duchesne County ( ) is a county in the northeast part of the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 18,607. Its county seat is Duchesne, and the largest city is Roosevelt. History Much of Duchesne County was part of the Uintah Reservation, created 1861 by US President Abraham Lincoln as a permanent home of the Uintah and White River Utes. Later the Uncompahgre Utes were moved to the Uintah and newly created Uncompahgre Indian reservations from western Colorado. At the turn of the century, under the Dawes Act, both Indian reservations were thrown open to homesteaders. This was done after allotments of land were made to Indians of the three tribes. The homesteading process was opened on the Uintah on August 27, 1905. Unlike much of the rest of Utah Territory, settlement of the future Duchesne County area did not occur due to LDS Church pressures. It was settled by individuals who obtained 160 acres under the federal Homestead Act. Homestead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uintah County, Utah
Uintah County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2020 United States Census the population was 35,620. Its county seat and largest city is Vernal. The county was named for the portion of the Ute Indian tribe that lived in the basin. Uintah County is the largest natural gas producer in Utah, with 272 billion cubic feet produced in 2008. The Vernal, UT Micropolitan Statistical Area includes all of Uintah County. History Archeological evidence suggests that portions of the Uinta Basin have been inhabited by Archaic peoples and Fremont peoples. By the time of recorded history, its inhabitants were the Ute people. The first known traverse by non-Indians was made by Fathers Domínguez and Escalante (1776), as they sought to establish a land route between California and Spanish America. The region was claimed by the Spanish Empire as the Alta California division of New Spain (1521-1821) and was later under Mexican control (1821-1848). By the early nine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca Harrimaniae
''Yucca harrimaniae'' Trel., the Spanish bayonet, is a species in the family Asparagaceae Asparagaceae, known as the asparagus family, is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. The family name is based on the edible garden asparagus, ''Asparagus officinalis''. Those who live in the temperate c ..., native to Utah, Nevada, Colorado, northeastern Arizona and northern New Mexico, at elevations from 1000 m to 2700 m. ''Yucca harrimaniae'' is a small, acaulescent (stemless) species forming clumps of rosettes. Flowers are nodding (hanging downward), partly greenish-white, partly purplish. The species is closely related to '' Y. sterilis'' (Neese & S.L.Welsh) S.L.Welsh & L.C.Higgins.. The overall species is relatively common and widespread. Two varieties, var. ''nana'' and var. ''sterilis'', have very small and restricted ranges. References harrimaniae Plants described in 1902 Flora of the Southwestern United States Taxa na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acaulescent
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. A B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizomes
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome (; , ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally. The rhizome also retains the ability to allow new shoots to grow upwards. A rhizome is the main stem of the plant that runs underground horizontally. A stolon is similar to a rhizome, but a stolon sprouts from an existing stem, has long internodes, and generates new shoots at the end, such as in the strawberry plant. In general, rhizomes have short internodes, send out roots from the bottom of the nodes, and generate new upward-growing shoots from the top of the nodes. A stem tuber is a thickened part of a rhizome or stolon that has been enlarged for use as a storage organ. In general, a tuber is high in starch, e.g. the potato, which is a modified stolon. The term "tuber" is often used imprecisely and is sometimes applied to pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tepals
A tepal is one of the outer parts of a flower (collectively the perianth). The term is used when these parts cannot easily be classified as either sepals or petals. This may be because the parts of the perianth are undifferentiated (i.e. of very similar appearance), as in '' Magnolia'', or because, although it is possible to distinguish an outer whorl of sepals from an inner whorl of petals, the sepals and petals have similar appearance to one another (as in '' Lilium''). The term was first proposed by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1827 and was constructed by analogy with the terms "petal" and "sepal". (De Candolle used the term ''perigonium'' or ''perigone'' for the tepals collectively; today, this term is used as a synonym for ''perianth''.) p. 39. Origin Undifferentiated tepals are believed to be the ancestral condition in flowering plants. For example, '' Amborella'', which is thought to have separated earliest in the evolution of flowering plants, has flowers with und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial shrubs and trees in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped leaves and large terminal panicles of white or whitish flowers. They are native to the hot and dry (arid) parts of the Americas and the Caribbean. Early reports of the species were confused with the cassava (''Manihot esculenta''). Consequently, Linnaeus mistakenly derived the generic name from the Taíno word for the latter, ''yuca''. The Aztecs living in Mexico since before the Spanish arrival, in Nahuatl, call the local yucca species ('' Yucca gigantea'') , which gave the Spanish . is also used for '' Yucca filifera''. Distribution The natural distribution range of the genus ''Yucca'' (49 species and 24 subspecies) covers a vast area of the Americas. The genus is represented throughout Mexico and extends into Guatemala ('' Yucca guatemalensis''). It also extends to the north throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Described In 2008
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ability t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Utah
This is a list of flora of Utah, a state in the western United States, listed alphabetically by family. , there are 3,930 species of plants in Utah, with 3,128 of those being indigenous and 792 being introduced through various means. Plants sorted by family Each entry lists the scientific name first (sorted alphabetically), then one or more common names for the plant (if any). Flora that have been introduced to the state are indicated with an † at the right of the scientific name. Entries are otherwise native. Entries marked with ‡ are considered invasive or noxious per the official list of noxious weeds maintained by the Utah Department of Agriculture and Food, though nine of those are not known to exist in Utah and have therefore not been included here. Amaranthaceae *'' Allenrolfea occidentalis'' – iodine bush *'' Atriplex argentea'' – silverscale saltbush, silver orache *'' Atriplex canescens'' – chamiso, chamiza, four-wing saltbush *'' Atriplex confertifolia'' � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |