|
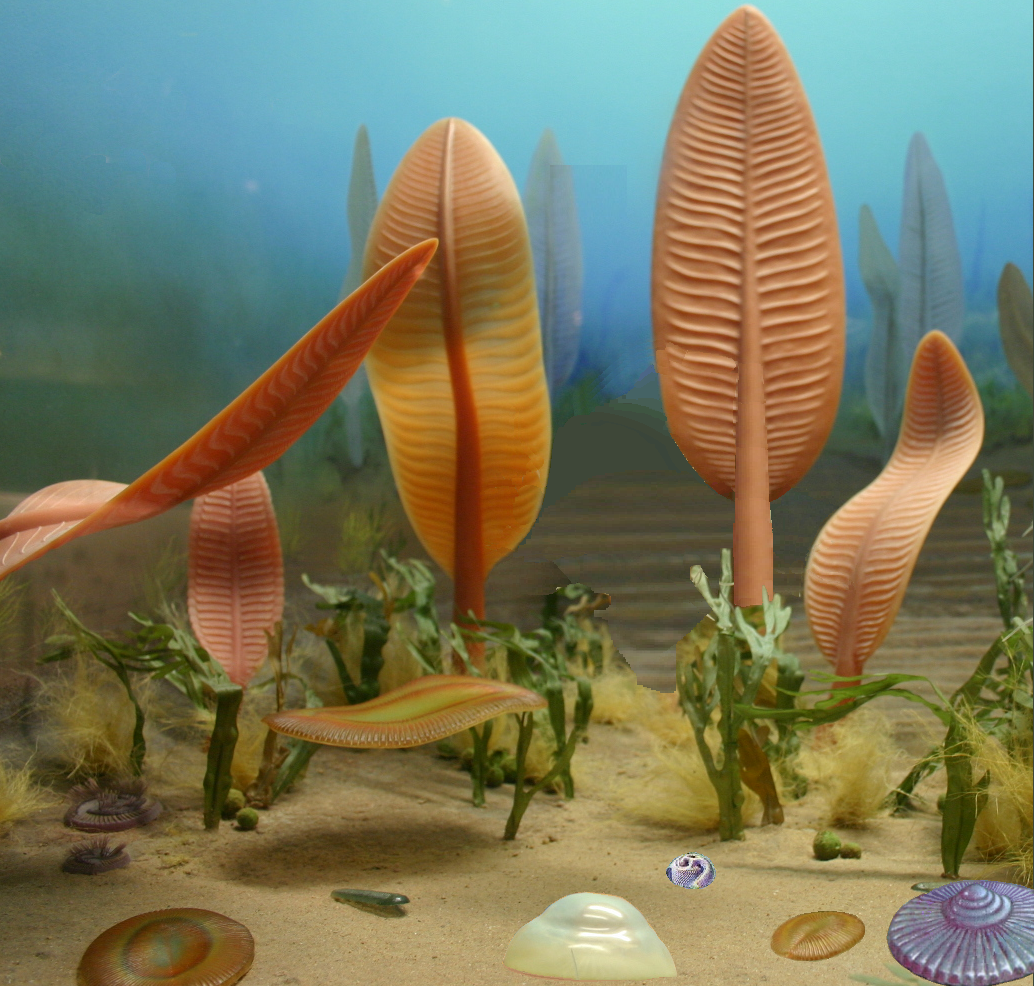
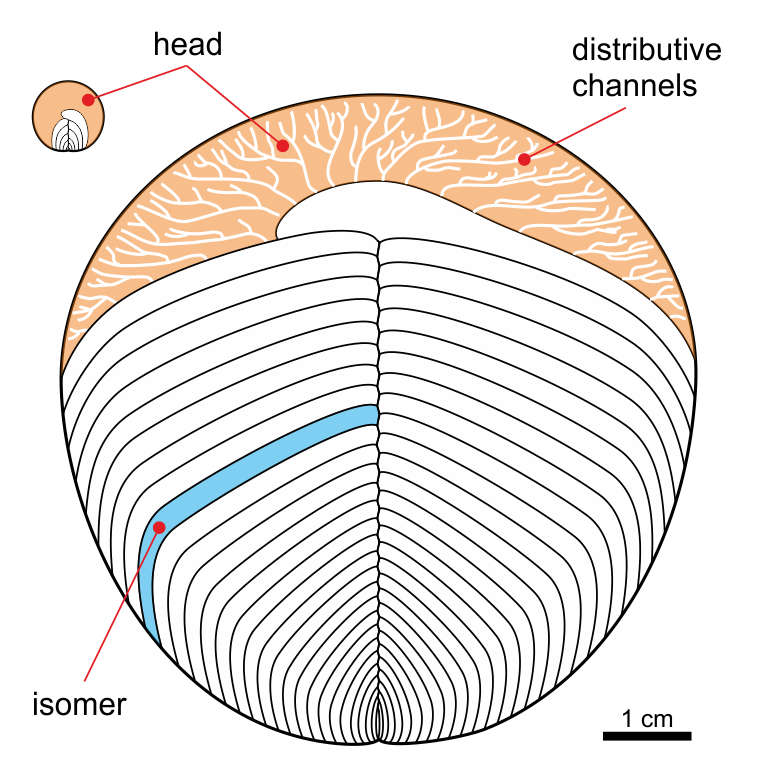
Yorgia
''Yorgia waggoneri'' is a discoid Ediacaran organism. It has a low, segmented body consisting of a short wide "head", no appendages, and a long body region, reaching a maximum length of . It is classified within the extinct animal phylum Proarticulata. Etymology The generic name ''Yorgia'' comes from the Yorga river on the Zimnii Bereg (Winter Coast) of the White Sea, where the first specimens were found. The specific name ''Yorgia waggoneri'' honors the American paleontologist Ben Waggoner, who found the first specimen. Morphology The body plan of the ''Yorgia'' and other proarticulates is unusual for solitary (non-colonial) metazoans. These bilateral organisms have segmented metameric bodies, but left and right transverse elements (isomers) are organized in an alternating pattern relatively to the axis of the body – they are not direct mirror images. This phenomenon is described as the symmetry of glide reflection, which is a characteristic also found in the similar ''Spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, near-bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as ''Dickinsonia'', '' Vendia'', '' Cephalonega'', '' Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer (Proarticulata)
Isomer (Greek ''isos'' = "equal", ''méros'' = "part") is an element of transverse body articulation of the bilateral fossil animals of the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran (Vendian) period. This term has been proposed by Andrey Yu. Ivantsov, a Russian paleontologist from the Laboratory of the Precambrian organisms, Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences. Morphology Proarticulatan isomers are distinct from the segments of the Annelida and Panarthropoda, as each of these elements occupies only half of width of a body and are organized in an alternating pattern relatively to the axis of the body. In other words, although proarticulatans are bilaterally symmetrical, one side is not the direct mirror image of its opposite. Opposite isomers of left and right side are located with displacement of half of its width. This phenomenon is described as the symmetry of gliding reflection.M. A. Fedonkin (1985). "Systematic Description of Vendian Metazoa". In Sokolov, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalozoa
Cephalozoa are an extinct class (biology), class of primitive segmented marine organisms within the Phylum (biology), Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran period. They possessed bilateral symmetry and were characterized by a thin, rounded body. Description Unlike the other classes of proarticulata, proarticulates, the segmentation of the body is not complete and shows a "head" with fine distribution channels. Some species of the Yorgiidae family also show some asymmetry. They were discovered in Russia near the White Sea in the Arkhangelsk region, where they lived during the Ediacaran, approximately 635 to 540 myr, Ma (millions of years ago). Taxonomy Cephalozoa includes the families Yorgiidae and Sprigginidae: Yorgiidae *† ''Archaeaspinus'' Ivantsov, 2007 (synonym of ''Archaeaspis'') **† ''Archaeaspinus fedonkini'' Ivantsov, 2001 *† ''Yorgia'' Ivantsov, 1999 **† ''Yorgia waggoneri'' Ivantsov, 1999 Sprigginidae *† ''Spriggina'' Glaessner, 1958 **† ''Spriggina fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacara Biota
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The term "Ediacara biota" has received criticism from some scientists due to its alleged inconsistency, arbitrary exclusion of certain fossils, and inability to be precisely defined. The Ediacaran biota may have undergone evolutionary radiation in a proposed event called the Avalon explosion, . This was after the Earth had thawed from the Cryogenian period's extensive glaciation. This biota largely disappeared with the rapid increase in biodiversity known as the Cambrian explosion. Most of the currently existing body plans of animals first appeared in the fossil record of the Cambrian rather than the Ediacara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran Life
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The term "Ediacara biota" has received criticism from some scientists due to its alleged inconsistency, arbitrary exclusion of certain fossils, and inability to be precisely defined. The Ediacaran biota may have undergone evolutionary radiation in a proposed event called the Avalon explosion, . This was after the Earth had thawed from the Cryogenian period's extensive glaciation. This biota largely disappeared with the rapid increase in biodiversity known as the Cambrian explosion. Most of the currently existing body plans of animals first appeared in the fossil record of the Cambrian rather than the Ediacaran. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epibaion
''Epibaion'' is a trace fossil imprint of the Ediacaran animals of the phylum Proarticulata, which became extinct in the Precambrian. Imprints often occurring in chains, that is interpreted as a feeding trace; some chains terminate in a body fossil, allowing their maker to be identified. Several specimens are known; ''E. waggoneris'' was produced by '' Yorgia waggoneri''; ''E. costatus'' by ''Dickinsonia costata'', and ''E. axiferus'', the type species, has as yet not been found with a trace-maker. It is proposed that the Australian fossil '' Phyllozoon'' is also a feeding trace of Proarticulata. See also * List of Ediacaran genera The existence of life, especially that of animals, before the Cambrian had long been the subject of debate in paleontology. The apparent suddenness of the Cambrian explosion had no firm explanation, and Charles Darwin himself recognized the chal ... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q5382415 Proarticulata Fossil taxa described in 2002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeaspinus
''Archaeaspinus fedonkini'' is an extinct proarticulatan organism from the Late Ediacaran period. Background ''Archaeaspinus'' was discovered in Zimnii Bereg, the Winter Coast of the White Sea in Russia, by A. Yu. Ivantsov in 2001. Since then, numerous additional fossils have been attributed to the genus, mostly from that same type locality, but a small number from Flinders Ranges in South Australia South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ... as well. Originally called '' Archaeaspis''—a name already applied to a redlichiid trilobite—in 2001 by Ivantsov, it was later recombined under its current name in 2007 by the same author. The type species, ''A. fedonkini'', is the only species known in this genus. It appears in the fossil record between 571-551Ma. Descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalonega
''Cephalonega stepanovi'' is a fossil organism from Ediacaran deposits of the Arkhangelsk Region, Russia. It was described by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1976 Name Its original genus name ''Onega'' comes from the Onega Peninsula of the White Sea, where the first fossils were found. The species name was given to honour V.A. Stepanov, who discovered the Ediacaran fossil site on the Letniy Bereg (" Summer Coast") in 1972, on the Onega Peninsula, the first Proterozoic site found in the Arkhangelsk Oblast. The original generic name is previously occupied by the hemipteran genus ''Onega'' Distant (1908). Ivantsov ''et al.'' (2019) coined a replacement generic name ''Cephalonega''. Morphology The small fossils, which range up to long, have oval outlines and low bodies with an articulated central zone built of isomers encircled by an undivided zone. The surface of the undivided region of ''Cephalonega'' is covered with small tubercles. ''Cephalonega'' was originally described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last period of the Proterozoic geologic eon, Eon as well as the last of the so-called "Precambrian supereon", before the beginning of the subsequent Cambrian Period marks the start of the Phanerozoic Eon, where recognizable fossil evidence of life becomes common. The Ediacaran Period is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia, where trace fossils of a diverse community of previously unrecognized lifeforms (later named the Ediacaran biota) were first discovered by geologist Reg Sprigg in 1946. Its status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period took namesake from the Ediacara Hills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ediacaran Genera
The existence of life, especially that of animals, before the Cambrian had long been the subject of debate in paleontology. The apparent suddenness of the Cambrian explosion had no firm explanation, and Charles Darwin himself recognized the challenge it posed for his theory of evolution. While reports of Precambrian organisms have been made since Alexander Murray's 1868 discovery of ''Aspidella'', it wasn't until the discovery of ''Charnia'' in 1956 that considerable evidence of Precambrian life had been presented. The period immediately preceding the Cambrian, the Ediacaran, is now widely accepted of containing animal life. It spans from 635 to 540 million years ago, and covers approximately 2% of Earth's history. Taxonomists have purported a total of 245 described genera from the Ediacaran, 162 of which are accepted as valid. Key * Valid genus - Genera that are accepted by the scientific community * Synonym (taxonomy), Junior synonym - Alternative name for an already existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |