|
Yokosuka E5Y
The Yokosuka E5Y (long designation: Yokosuka Navy Type 90-3 Reconnaissance Seaplane) was a single-engine Japanese seaplane used for reconnaissance. The E5Y was also built by Kawanishi as the E5K (long designation: Kawanishi Navy Type 90-3 Reconnaissance Seaplane) Development The Yokosuka Type 90-3 (E5Y1) was a second-generation seaplane with a engine based on an updated Yokosuka E1Y, developed at the Yokosuka Naval Arsenal in Kanagawa Prefecture, featuring two externally mounted floats. The Japanese Navy initially designated it as the Yokosuka Navy Type 14-2 Kai-1 Reconnaissance Seaplane, but production was undertaken by Kawanishi as the Kawanishi Navy Type 90-3 Reconnaissance Seaplane. By 1932, the Aichi AB-6 was under development to replace the E5Y / E5K seaplanes. Kawanishi E5K The Kawanishi E5K1 or Kawanishi Type G was a large 1930s Japanese three-seat reconnaissance floatplane. The E5K1, a radial-engined twin-float seaplane, first flew in October 1931, but due to probl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
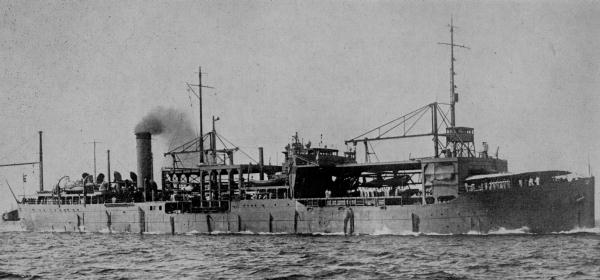
Japanese Seaplane Tender Kamoi
was an Replenishment oiler, oiler/seaplane tender/flying boat tender of the Imperial Japanese Navy, serving from the 1920s through World War II. She was initially planned in 1920 as one of six of the oilers under the Eight-eight fleet final plan. Service ''Kamoi'' was completed 12 September 1922, and classified as a special service ship (Replenishment oiler, Oiler). On 27 September she sailed to Yokosuka, Kanagawa, Yokosuka, from where she sailed to the Japanese mainland and back no fewer than 25 times. Somewhere around the end of 1932, she was converted to seaplane tender for January 28 Incident at Uraga Dock Company, an overhaul that was finished in February 1933. Upon completion of this evolution, she was assigned to the Combined Fleet. On 1 June 1934, ''Kamoi'' was reclassified as a warship (seaplane tender). On 1 June 1936, she was assigned to the Third Carrier Division. While on this assignment, during July 1937, she was assigned to search for downed American aviator Ameli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biplanes
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While a biplane wing structure has a structural advantage over a monoplane, it produces more drag (aerodynamics), drag than a monoplane wing. Improved structural techniques, better materials and higher speeds made the biplane configuration obsolete for most purposes by the late 1930s. Biplanes offer several advantages over conventional cantilever monoplane designs: they permit lighter wing structures, low wing loading and smaller span for a given wing area. However, interference between the airflow over each wing increases drag substantially, and biplanes generally need extensive bracing, which causes additional drag. Biplanes are distinguished from tandem wing arrangements, where the wings are placed forward and aft, instead of above and below. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawanishi Aircraft
Kawanishi may refer to: Places * Kawanishi, Hyōgo 270px, Lake Chimyo 270px, Aerial view of Kawanishi city center 270px, Tada-in is a city located in Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 155,165 and a population density of 2900 persons per km². The total area of ... * Kawanishi, Nara * Kawanishi, Yamagata * Kawanishi, Niigata – now merged into Tōkamachi People with the surname *, Japanese painter *, Japanese swimmer *, Japanese idol Other uses * Kawanishi Aircraft Company, a former Japanese aircraft manufacturer {{Disambig, geo, surname Japanese-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokosuka Aircraft
is a city in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. , the city has a population of 373,797, and a population density of . The total area is . Yokosuka is the 11th-most populous city in the Greater Tokyo Area, and the 12th in the Kantō region. The city is home to United States Fleet Activities Yokosuka. Geography Yokosuka occupies most of Miura Peninsula, and is bordered by the mouth of Tokyo Bay to the east and Sagami Bay on the Pacific Ocean on the west. Surrounding municipalities * Hayama * Kanazawa-ku, Yokohama * Miura * Zushi History Pre-modern period The area around present-day Yokosuka City has been inhabited for thousands of years. Archaeologists have found stone tools and shell middens from the Japanese Paleolithic period and ceramic shards from the Jōmon and Kofun periods at numerous locations in the area. During the Heian period, local warlord Muraoka Tamemichi established Kinugasa Castle in 1063. He became the ancestor of the Miura clan, which subsequently dominate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floatplanes
A floatplane is a type of seaplane with one or more slender floats mounted under the fuselage to provide buoyancy. By contrast, a flying boat uses its fuselage for buoyancy. Either type of seaplane may also have landing gear suitable for land, making the vehicle an amphibious aircraft. British usage is to call floatplanes "seaplanes" rather than use the term "seaplane" to refer to both floatplanes and flying boats. Use Since World War II and the advent of helicopters, advanced aircraft carriers and land-based aircraft, military seaplanes have stopped being used. This, coupled with the increased availability of civilian airstrips, has greatly reduced the number of flying boats being built. However, many modern civilian aircraft have floatplane variants, most offered as third-party modifications under a supplemental type certificate (STC), although there are several aircraft manufacturers that build floatplanes from scratch. These floatplanes have found their niche as one type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Flying Boats And Floatplanes
The following is a list of seaplanes, which includes floatplanes and flying boats. A seaplane is any airplane that has the capability of landing and taking off from water, while an amphibian is a seaplane which can also operate from land. (They do not include rotorcraft, or ground-effect vehicles which can only skim along close to the water) A flying boat relies on its main hull for buoyancy, while a floatplane has a conventional aircraft fuselage fitted with external floats. In some locales, the term "seaplane" is used as a synonym for floatplane. List A small number of seaplanes have retractable beaching gear, which is not capable of being used for landings and takeoffs, but these remain flying boats or floatplanes and are not amphibians. Many floatplanes, especially those since 1945, can have either conventional floats for operating just from water, or amphibious floats, which have retractable undercarriage built into them. Some experimental flying boats have used skis or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Military Aircraft Of Japan
This list of military aircraft of Japan includes project, prototype, pre-production, and operational types, regardless of era. This includes both domestically developed Japanese designs, licensed variants of foreign designs, and foreign-produced aircraft that served in the military of Japan. Japanese names are used here; World War II Allied reporting names are mentioned where available. The prefix "Ki" in this list is an abbreviation of "Kitai", meaning "airframe", and was used only by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force. "Ki" should be read as one word. For clarification on other designations, particularly those used by the Navy, see Japanese military aircraft designation systems. ''(Note: " - " indicates information is unknown or not applicable.)'' Pre-1945 Post-1945 See also * List of aircraft of Japan, World War II References Citations Bibliography * External links * picture of Kawasaki Ki-66 {{DEFAULTSORT:Military Aircraft Of Japan * Aircraft An ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 89 Machine-guns
Type 89 refers to two unrelated Imperial Japanese Army aircraft machine guns. Its Imperial Japanese Navy counterparts are the Type 97 machine gun (fixed), and Type 92 machine gun. Type 89 fixed The first machine gun is a recoil-operated, licensed copy of the Vickers Class E machine gun re-chambered to 7.7x58mmSR Type 89 cartridge, it is referred to as the "fixed type". It was used in synchronized applications in fighter cowls and in wing gun applications. It was belt-fed, using a steel link disintegrating belt. The fixed Type 89 was used in the Nakajima Ki-27, Ki-43, early Ki-44 fighters, the Mitsubishi Ki-30 and Ki-51 light bombers, the Kawasaki Ki-32 light bomber and various others. Communist forces used some ex-Japanese Type 89s during the Korean War. Indonesian Republican forces also used them for ground use during the Indonesian National Revolution. Type 89 flexible type The second machine gun is gas-operated, it consists of two modified Type 11 machine guns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiro Type 91 520 Hp Water-cooled W-12
The Hiro Type 91, (full designation Hiro Type 91 520 hp water-cooled W-12), was a 12-cylinder, water-cooled, W engine developed for aircraft use by the Imperial Japanese Navy in the mid-1930s. Power was in the 450 kW (600 hp) range. Its design was derived from the Hiro Type 90. An enlarged more powerful engine, the Hiro Type 90 600 hp water-cooled W-12 had also been developed, producing 600 hp. Applications * Aichi E10A * Aichi E11A * Hiro H4H * Kawanishi E7K * Mitsubishi Ka-9 Specifications (Type 91 500hp-1) See also References * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hiro Type 91 (Engine) 1930s aircraft piston engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine 12E Courlis
The Lorraine 12E Courlis was a W-12 (broad arrow) aero engine produced by the French company Lorraine-Dietrich during the 1920s and 1930s. Variants ;12E: ;12Eb: ;12Ebr: ;12Ed: ;12Edr: ;12Ee: ;12Ew: The standard Eb fitted with a supplementary supercharger. ;Elizalde A: The 12E built under licence in Spain by Elizalde S.A. ;12E: Made under licence by the Polish Skoda Works (PZS) Applications Aircraft Other applications * Argentine Nahuel tank The Nahuel DL-43 tank was a medium tank developed in Argentina during World War II. It was the Argentine equivalent of the M4 Sherman and the M3 Grant American medium tanks. Design The designer was Lt. Colonel Alfredo Baisi. The word ''Nahuel' ... Specifications (12Ed) See also References Notes Bibliography * Gunston, Bill. ''World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines''. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 1989. {{Lorraine aeroengines 12E 1920s aircraft piston engines W engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Jupiter VIII
The Bristol Jupiter is a British nine-cylinder single-row piston radial engine that was built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. Originally designed late in World War I and known as the Cosmos Jupiter, a lengthy series of upgrades and developments turned it into one of the finest engines of its era. The Jupiter was widely used on many aircraft designs during the 1920s and 1930s. Thousands of Jupiters of all versions were produced, both by Bristol and abroad under licence. A turbo-supercharged version of the Jupiter known as the Orion suffered development problems and only a small number were produced. The "Orion" name was later re-used by Bristol for an unrelated turboprop engine. The Bristol Jupiter was licensed by the Soviet Union as the Shvetsov M-22. Design and development The Jupiter was designed during World War I by Roy Fedden of Brazil Straker and later Cosmos Engineering. The first Jupiter was completed by Brazil Straker in 1918 and featured three carburettors, ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |