|
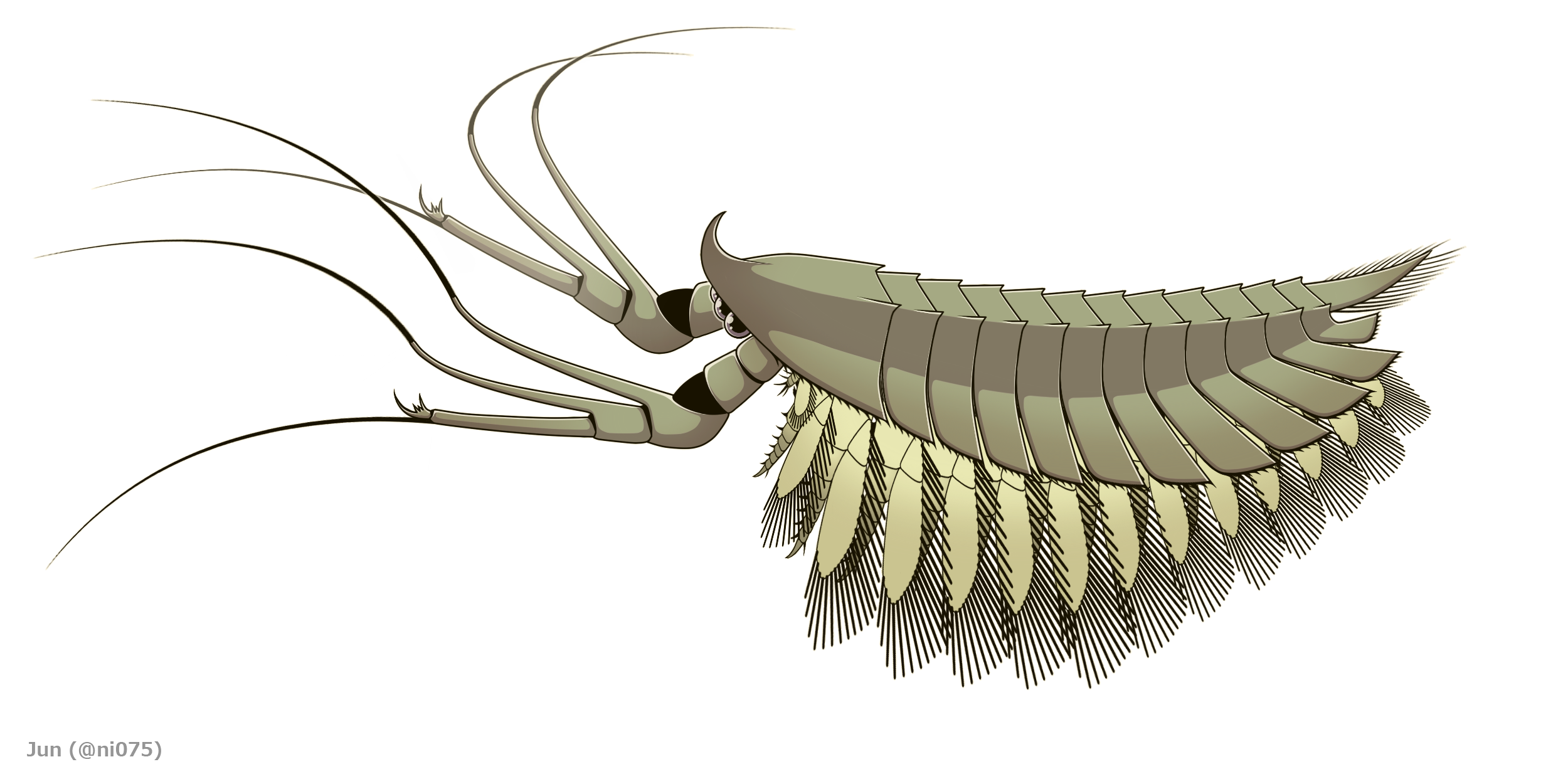
Yohoia
''Yohoia'' is an extinct genus of megacheiran arthropod from the Cambrian period that has been found as fossils in the Burgess Shale formation of British Columbia, Canada. The type species, ''Yohoia tenuis'', was described in 1912 by Walcott, who considered it an anostracan crustacean. 711 specimens of ''Yohoia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 1.35% of the community. In 2015, Conway Morris ''et al.'' reported another species, ''Y. utahana'', from the Marjum Formation, Utah. Description Fossil specimens of ''Yohoia'' range in size from 7 to 23 mm, they have a head shield which is followed by 13 trunk tergites, or plates. On both sides, the bottom side of the first 10 of these ended in backward-pointing, triangular points or projections. The last three plates were complete tubes, circling the entire trunk. At the end of the trunk was a paddle-like tail. There were also a pair of large extensions at the front of the head shield. They had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Appendage
Megacheira ("great hands", also historically great appendage arthropods) is an extinct class of predatory arthropods defined by their possession of spined "great appendages". Their taxonomic position is controversial, with studies either considering them stem-group euarthropods, or stem-group chelicerates. The homology of the great appendages to the cephalic appendages of other arthropods is also controversial. Uncontested members of the group were present in marine environments worldwide from the lower Cambrian to the upper Ordovician. Morphology Megacheirans are defined by their possession of uniramous "great appendages", which are their first pair of head appendages. The first one or two proximalmost segments/ podomeres are spineless (it has been argued that the supposed first of the two proximal podomeres is actually an arthrodial membrane), while the remaining 3–4 more distal podomeres each typically bear a single upward pointing spine attached towards the distal en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess Shale Fossils
The fossils of the Burgess Shale, like the Burgess Shale itself, are fossils that formed around 505 million years ago in the mid-Cambrian, Cambrian period. They were discovered in Canada in 1886, and Charles Doolittle Walcott collected over 65,000 specimens in a series of field trips up to the alpine site from 1909 to 1924. After a period of neglect from the 1930s to the early 1960s, new excavations and re-examinations of Walcott's collection continue to reveal new species, and statistical analysis suggests that additional discoveries will continue for the foreseeable future. Stephen Jay Gould's 1989 book ''Wonderful Life (book), Wonderful Life'' describes the history of discovery up to the early 1980s, although his analysis of the implications for evolution has been contested. The fossil beds are in a series of shale layers, averaging and totalling about in thickness. These layers were deposited against the face of a high undersea limestone cliff. All these features were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleobiota Of The Burgess Shale
This is a list of the Biota (ecology), biota of the Burgess Shale, a Cambrian lagerstätte located in Yoho National Park in Canada. The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At 508 million years old (Wuliuan, middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints. During the Cambrian, the ecosystem of the Burgess Shale sat under 100 to 300 metres (330 to 1000 feet) of water at the base of a submarine canyon known as the Cathedral escarpment, Cathedral Escarpment, which today is a part of the Canadian Rockies. The ecosystem would have sat in dimly lit water, most likely at the edge, or in the Mesopelagic zone. The ecosystem was preserved by rapid mudslides that quickly buried organisms near, or on the seafloor, which helps explain the rarity of nektonic organisms at the site. The shale would have supported uniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alalcomenaeus
''Alalcomenaeus'' is one of the most widespread and longest-surviving arthropod genera of the Early and Middle Cambrian. Known from over 300 specimens in the Burgess Shale and the Chengjiang biota. It is a member of the family Leanchoiliidae in the group Megacheira. Morphology ''Alalcomenaeus'' had three median eyes; two stalked, more lateral eyes; a triflagellate great appendage; and two more head appendages posterior to that. Like its body appendages, these were biramous—their inner branch was spiny, segmented, flexible and leg-like, while the outer portion had a large surface area and resembled a flap. ''Alalcomenaeus'' reached about 6 cm in length, although many smaller specimens are known. Its head was covered with a shield, and its eleven body segments were also covered with an exoskeleton. Its body terminated with a paddle-like telson ("tail") which probably helped to propel the organism; this ended with long flat spikes in the plane of the tail fin. Ecology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leanchoilia
''Leanchoilia'' is a megacheiran marine arthropod known from Cambrian deposits of the Burgess Shale in Canada and the Chengjiang biota of China. Description ''L. superlata'' was about long and had long, whip-like flagellae extending from its great appendages. Its internal organs are occasionally preserved within the substrate in three dimensions. Their two pairs of eyes are protected and covered by their exterior head shields, with two eyes being located on each side. Species Seven species are tentatively accepted today: ''L. superlata'' (the type species), ''L. persephone'' and ''L. protogonia'' from the Burgess Shale, ''L. illecebrosa'' and ''L. obesa'' from the Chengjiang biota, 'L. robisoni'' from Kaili, and ''L.''? ''hanceyi'' from the Spence Shale. ''L. superlata'' and ''L. persephone'' may however be examples of sexual dimorphism. Distribution 55 specimens of ''Leanchoilia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.1% of the community. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiodonta
Radiodonta is an extinct Order (biology), order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and were used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts were among the earliest large predators, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris, Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia, Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', ''Titanokorys gainesii, Titanokorys gainesi, Cambroraster, Cambroraster falcatus'' and ''Amplectobelua, Amplectobelua symbrachiata''. The later surviving members include the subfamily Aegirocassisinae from the Early Ordovician of Morocco and the Early Devonian member ''Schinderhannes bartelsi'' from Germany. Etymology The name Radiodonta (Latin for ''radius'' "spoke of a wheel" and Greek for ''odoús'' "tooth") refers to the radial arrang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Arthropods
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa, Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new Convergent boundary, convergent plate boundaries and Volcanic arc, continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in Life, life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, Unicellular organism, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Charles Doolittle Walcott
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess Shale Animals
Burgess may refer to: People and fictional characters * Burgess (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * Burgess (given name), a list of people Places Canada * Mount Burgess, a mountain in Yoho National Park, British Columbia England * Burgess Park, a park in London * Burgess Field, a nature reserve in Oxford *Burgess Hill, a town and parish in West Sussex United States * Burgess, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Burgess, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Burgess, South Carolina, an unincorporated community * Burgess, Virginia, an unincorporated community * Burgess Township, Bond County, Illinois, a township * Burgess Branch, a tributary of the Missisquoi River in Vermont Other uses *Burgess (title), a political official or representative *Burgess Company, an American airplane manufacturer * Burgess GAA, an athletic club in Ireland See also * Burgess House (other), several buildings named * Burgess model, or Concentric zone model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Arthropod Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schinderhannes Bartelsi
''Schinderhannes bartelsi'' is a fossil species of hurdiid radiodont (anomalocaridid), known from a single specimen from the Lower Devonian Hunsrück Slate in Germany. Its discovery expanded the known range of radiodonts, the latest members of which were previously known only from the Early Ordovician, at least 66 million years earlier than ''Schinderhannes bartelsi''. Discovery The single specimen was discovered in the Eschenbach-Bocksberg Quarry in Bundenbach, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, and is named after the outlaw Schinderhannes who frequented the area. Its specific epithet ''bartelsi'' honours Christoph Bartels, a Hunsrück Slate expert. The specimen is now housed in the Naturhistorisches Museum in Mainz. Morphology ''Schinderhannes'' is about long in full body length ( long excluding telsonDryad Data ). Like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |