|
Yi Kwal
Yi Kwal (; 1562 – 14 February 1624) was a general during the Joseon Dynasty, Korea, known for the failed Yi Kwal's Rebellion. His family belonged to the Goseong Lee clan, Goseong Yi clan. He rebelled against Injo of Joseon, King Injo in 1624, but failed. Yi Kwal was then killed by his own troops. Yi Kwal's rebellion put Korea into a state of chaos before it was invaded by the Manchu Qing dynasty. Background In 1622, he joined the Injo revolution, which was a movement in Korea to get rid of the government of King Gwanghaegun, who advocated evenhanded diplomacy between the Ming Dynasty, Ming and the Qing Dynasty, Qing. At that time, the Han (people), Han Ming Dynasty had recently fallen to the invading Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jurchen, who had renamed themselves the Manchu. Historically, Korea was in a long time conflict with the Jurchen tribes, who inhabited the wide plains of Manchuria. The Jurchen took Liaoning during the late Ming and established the Qing Dynasty, Later Jin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseon Dynasty
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom was founded following the aftermath of the overthrow of Goryeo in what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul. The kingdom's northernmost borders were expanded to the natural boundaries at the rivers of Yalu River, Amnok and Tumen River, Tuman through the subjugation of the Jurchen people, Jurchens. During its 500-year duration, Joseon encouraged the entrenchment of Korean Confucianism, Confucian ideals and doctrines in Korean society. Neo-Confucianism was installed as the new state's ideology. Korean Buddhism, Buddhism was accordingly discouraged, and occasionally Buddhists faced persecution. Joseon consolidated its effective rule over the Korean peninsula and saw the he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taejo Of Joseon
Taejo (; 4 November 1335 – 27 June 1408), personal name Yi Seong-gye (), later Yi Dan (), was the founder and first monarch of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. After overthrowing the Goryeo dynasty, he ascended to the throne in 1392 and abdicated six years later during a strife between his sons. He was honored as Emperor Go () following the establishment of the Korean Empire. Taejo emphasized continuity over change. No new institutions were created, and no massive purges occurred during his reign. His new dynasty was largely dominated by the same ruling families and officials that had served the previous regime. He re-established amicable ties with Japan and improved relations with Ming dynasty, Ming China. Biography Early life The future King Taejo was born in Ssangseong Prefecture on the frontiers of the Yuan dynasty. Taejo's father was Yi Cha-ch'un, an official of Korean ethnicity serving the Mongols, Mongol-led Yuan. His mother, Queen Uihye, Lady Ch'oe, came from a famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Korea
The Lower Paleolithic era on the Korean Peninsula and in Manchuria began roughly half a million years ago. Christopher J. Norton, "The Current State of Korean Paleoanthropology", (2000), ''Journal of Human Evolution'', 38: 803–825. The earliest known Korean pottery dates to around 8000 BC and the Neolithic period began thereafter, followed by the Bronze Age by 2000 BC, Jong Chan Kim, Christopher J Bae, "Radiocarbon Dates Documenting The Neolithic-Bronze Age Transition in Korea" , (2010), ''Radiocarbon'', 52: 2, pp. 483–492. and the around 700 BC. The |
Yi Eung-tae
Yi or YI may refer to: Philosophic principle * Yi (philosophy) (义; 義, righteousness, justice) among the Three Fundamental Bonds and Five Constant Virtues Ethnic groups * Dongyi, the Eastern Yi, or Tung-yi (Chinese: , ''Yí''), ancient peoples who lived east of the Zhongguo in ancient China * Yi people (Chinese: , ''Yí''; Vietnamese: ''Lô Lô''), an ethnic group in modern China, Vietnam, and Thailand Language * Yi (Cyrillic), the letter of the Ukrainian alphabet written "Ї" and "ї" * Yi language or the Nuosu language spoken by the Yi people of China * Yi script, either of two scripts used to write the Yi languages * Yiddish (ISO 639-1 language code: yi), the historical language of the Ashkenazi Jews * Yi, an obsolete Japanese kana Mythology and religion * Yi the Archer or Houyi, a heroic archer and hunter in Chinese mythology * Yi (husbandman), also known as Boyi or Bo Yi, a heroic user of fire and government minister in Chinese mythology People Surname * Yi ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Manchu Invasion Of Korea
The Later Jin invasion of Joseon occurred in early 1627 when the Later Jin prince Amin led an invasion of the Joseon dynasty. The war ended after three months with the Later Jin establishing itself as sovereign tributary overlord over Joseon. However Joseon continued its relationship with the Ming dynasty and showed defiance in solidifying its tributary relationship with the Later Jin. It was followed by the Qing invasion of Joseon in 1636. Background The kingdom of Joseon had previously sent 10,069 musketeers and 3,000 archers to aid the Ming dynasty in attacking the Later Jin in 1619, which culminated in an allied defeat at the Battle of Sarhū. The Joseon general Gang Hong-rip surrendered with his remaining forces and insisted that Joseon did not hold anything against the Jurchens, having only sent reinforcements to repay an obligation to Ming. In 1623, a faction at the Joseon court known as the Westerners deposed King Gwanghaegun (Hangul: 광해군, Hanja: 光海君) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Myeong-ryun
Han may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * "Han", a fifth season episode of ''The West Wing'' * Han (musician), born Han Ji-sung, a South Korean singer-songwriter, rapper, and record producer, member of Stray Kids * Han Lue, a character in the ''Fast & Furious'' franchise * Han Solo, a character in the ''Star Wars'' franchise Education * Han school, Japan, Edo period * HAN University of Applied Sciences, in the Netherlands People Ethnic groups * Han Chinese, or Han people (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group ** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese people who are fully or partially of Han Chinese descent * Han Minjok, or Han people (): the Korean native name referring to Koreans * Hän: one of the First Nations peoples of Canada Names * Han (name), a given name and surname ** Han (Chinese surname), also Haan, Hahn or Hann, the Romanized spelling of many Chinese family name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
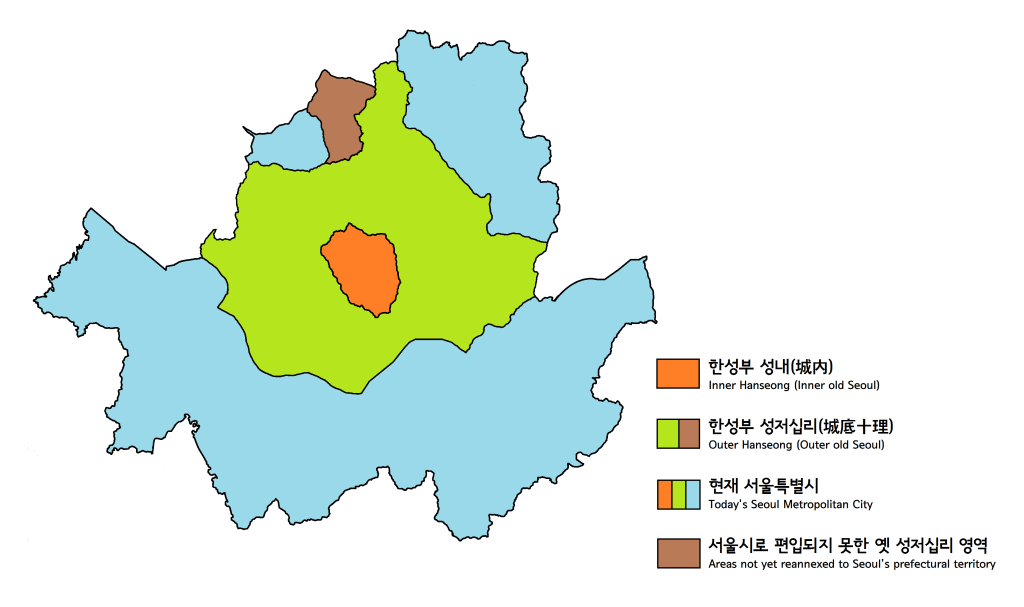
Hanseong
The region now corresponding to Seoul, South Korea has been inhabited since the Paleolithic Age. It has been the capital of a number of kingdoms since it was established. Prehistoric It is believed that humans were living in the area that is now Seoul along the lower reaches of the Han River during the Paleolithic Age and archaeological research shows that people began to lead settled lives starting in the Neolithic Age. Prehistoric remains that are unearthed in the , located in Gangdong District, date back to about 3,000 to 7,000 years ago. With the introduction of bronze ware from about 700 BC, settlements gradually began to spread from the river basin toward inland areas. Three Kingdoms and Unified Silla period In 18 BC, the kingdom of Baekje founded its capital city, Wiryeseong, which is believed to be inside modern-day Seoul. Baekje subsequently developed from a member state of the Mahan confederacy into one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. There are several city wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamgyong Province
Hamgyong Province (; ) was one of the Eight Provinces of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. Hamgyong was located in the northeast of Korea. The provincial capital was Hamhung. Names The province was first established as Yŏnggil () in 1413. It was renamed Hamgil () three years later. In 1470, it was renamed Yŏngan (). In 1509, it was renamed Hamgyŏng after its two principal cities, Hamhung and Kyongsong. In the 18th century, this was transcribed via Chinese as Kyen-king and glossed as meaning "the Happy". In the 19th century, it was transcribed as Ham-kieng. Within Korea, the province was also referred to as "Dongbuk" ("Northeast"). The southern half of the province was also referred as "Kwannam", and the northern half of the province was also referred as "Kwanbuk". History Korea's northeastern frontier was first organized into the province of Yonggil in 1413. In 1895, the province was replaced by the districts () of Kyongsong in the northeast, Kapsan in the northwest, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southerners (Korean Political Faction)
The Southerners () were a political faction of the Joseon Dynasty. The faction was created after the split of the Easterners in 1591 by Yi Sanhae's opponents. Its leader was Yu Sŏngnyong, who died in 1607. Leader Heo Mok was Left Prime Minister from 1675 to 1678. Leader Yun Hyu was executed in 1680. They supported Jang Huibin, queen consort of Sukjong of Joseon from 1688 to 1694. The faction continued to exist until the 18th century. See also, Noron, and for the role of private Confucian academies (together with their shrines), in strife between the factions, see seowon. Members * Yu Sŏngnyong * Yun Seon-do *Yun Hyu * Heo Mok *Heo Jeok * Jang Huibin *Jeong Yak-yong Jeong (the Revised Romanization spelling of ) may refer to: *Jeong (surname) *Jeong (given name) Jeong, also spelled Jung or Jong, Chung, Chong is a single-syllable Korean given name, and an element in many two-syllable Korean given names. Its ... {{Sasaek Dangpa Political factions in Joseon 16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northerners (Korean Political Faction)
The Northerners () were a political faction of the Joseon Dynasty. It was created after the split of the Easterners in 1591 by Yi Sanhae and his supporters. In 1606, during the reign of Queen Inmok, the Northerners divided into Greater Northerners (led by Heo Gyun Heo is a family name in Korea. It is also often spelled as Huh or Hur, or less commonly as Her or Hue. In South Korea in 1985, out of a population of between roughly 40 and 45 million, there were approximately 264,000 people surnamed Heo. The na ...) and Smaller Northerners. In 1613, the Greater Northerners split further into Flesh Northerners, Bone Northerners and Middle Northerners. The Smaller Northerners allied with the Westerners and Southerners. Members * Yi Sanhae * Chung In-hong *Nam Yi-gong *Yi Yicheom References Political factions in Joseon {{Asia-poli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerners (Korean Political Faction)
The Westerners () was a political faction that dominated Korea in the 17th century. In 1575, the Sarim split into the Easterners (Korean political faction), Easterners and Westerners. The Westerners remained the main contender of the Easterners in the Seonjo of Joseon, Seonjo age. The Westerners lost power in the later years of the Seonjo age. The Easterners and the factions that split from the Easterners had power throughout the last decade of the Seonjo age and the entirety of the Gwanghaegun age. However, the Westerners ousted Gwanghaegun from power in 1623, making Prince Neungyang king and causing the Westerners to regain power, which they had lost for a generation. The Westerners had power for half a century, from 1623 to 1674, in which they were relatively unified. The era also led to the appearance of powerful Westerner politicians such as Song Si-yeol, Song Jun-gil, and Kim Su-hang, of which Song Si-yeol was the most influential. the Yesong debate of the Hyeonjong of Joseo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easterners (Korean Political Faction)
The Easterners () were a Political factions in Joseon Dynasty, political faction of the Joseon dynasty. This faction appeared during the reign of Seonjo of Joseon in sixteenth-century Korea, in 1575. Originating from friends of Gim Hyowon, they soon encompassed most of the disciples of Jo Sik and Yi Hwang, conflicting with Yi I and his followers, who formed the core of the Westerners (Korean political faction), Westerners. Though emerging as the dominant faction in the 1580s, it nearly collapsed at the suicide of Jeong Yeo-rip and the 1589 rebellion of Jeong Yeo-rip, succeeding bloodshed in 1589. After Westerner Jeong Cheol was exiled for attempting to make Gwanghaegun of Joseon, Prince Gwanghae the Crown Prince, the Easterners divided into Northerners (Korean political faction), Northerners and Southerners (Korean political faction), Southerners. History Division from Sarim After the death of Queen Dowager Queen Munjeong, Munjeong and her brother Yun Won-hyeong in the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |