|
Yessotoxin
Yessotoxins are a group of lipophilic, sulfur bearing polyether toxins that are related to ciguatoxins. They are produced by a variety of dinoflagellates, most notably '' Lingulodinium polyedrum'' and '' Gonyaulax spinifera''. When the environmental conditions encourage the growth of YTX producing dinoflagellates, the toxin(s) bioaccumulate in edible tissues of bivalve molluscs, including mussels, scallops, and clams, thus allowing entry of YTX into the food chain. History The first YTX analog discovered, yessotoxin, was initially found in the scallop species '' Patinopecten yessoensis'' in the 1960s. Since then, numerous yessotoxin analogs have been isolated from shellfish and marine algae (including 45-hydroxyyessotoxin and carboxyyessotoxin). Initially, scientists wrongly classified YTXs in the group of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins along the lines of okadaic acid and azaspiracids. These type of toxins can cause extreme gastrointestinal upset and acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingulodinium Polyedrum
''Lingulodinium polyedra'' is a species of motile photosynthetic dinoflagellates. ''L. polyedra'' are often the cause of red tides in southern California, leading to bioluminescent displays on beaches at night. Life cycle As part of its life cycle, this species produces a resting stage, a dinoflagellate cyst called '' Lingulodinium machaerophorum'' (synonym '' Hystrichosphaeridium machaerophorum''). This cyst was first described by Deflandre and Cookson in 1955 from the Miocene of Balcombe Bay, Victoria, Australia as: "Shell globular, subsphaerical or ellipsoidal with a rigid membrane, more brittle than deformable, covered with numerous long, stiff, conical, pointed processes resembling the blade of a dagger. Surface of shell granular or punctate." Its stratigraphic range is the Upper Paleocene of eastern USA and Denmark till Recent. Organic-walled dinocyst morphology is shown to be controlled by changes in salinity and temperature in some species, more particularly process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellates
The dinoflagellates ( Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey ( phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, '' Oodinium'' and '' Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipophilic
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipophilic (translated as "fat-loving" or "fat-liking"), and the axiom that "like dissolves like" generally holds true. Thus lipophilic substances tend to dissolve in other lipophilic substances, but hydrophilic ("water-loving") substances tend to dissolve in water and other hydrophilic substances. Lipophilicity, hydrophobicity, and non-polarity may describe the same tendency towards participation in the London dispersion force, as the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the terms "lipophilic" and "hydrophobic" are not synonymous, as can be seen with silicones and fluorocarbons, which are hydrophobic but not lipophilic. __TOC__ Surfactants Hydrocarbon-based surfactants are compounds that are amphiphilic (or amphipathic), hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
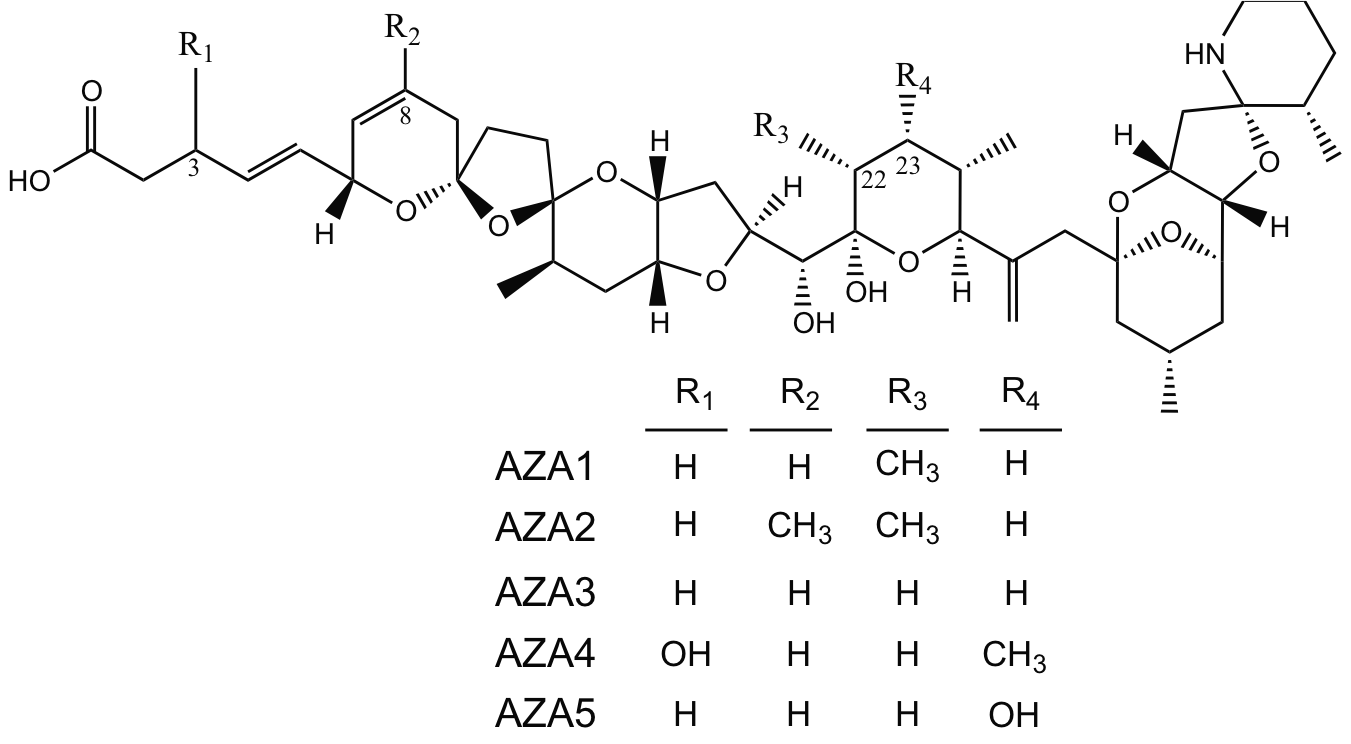
Azaspiracid
Azaspiracids (AZA) are a group of polycyclic ether marine algal toxins produced by the small dinoflagellate ''Azadinium spinosum'' that can accumulate in shellfish and thereby cause illness in humans. Azaspiracid was first identified in the 1990s following an outbreak of human illness in the Netherlands that was associated with ingestion of contaminated shellfish originating from Killary Harbour, Ireland. To date, over 20 AZA analogues have been identified in phytoplankton and shellfish. Over the last 15 years, AZAs have been reported in shellfish from many coastal regions of western Europe, Northern Africa, South America, and North America. In addition, AZAs have been found in Japanese sponges and Scandinavian crabs. Not surprisingly, the global distribution of AZAs appears to correspond to the apparent wide spread occurrence of ''Azadinium''. Empirical evidence is now available that unambiguously demonstrates the accumulation of AZAs in shellfish via direct feeding on AZA-produci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
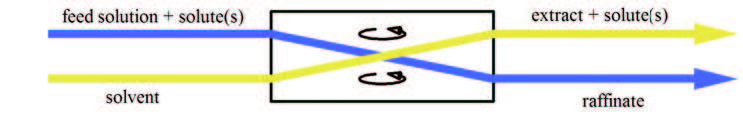
Liquid–liquid Extraction
Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE), also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes, based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water (polar) and an organic solvent (non-polar). There is a net transfer of one or more species from one liquid into another liquid phase, generally from aqueous to organic. The transfer is driven by chemical potential, i.e. once the transfer is complete, the overall system of chemical components that make up the solutes and the solvents are in a more stable configuration (lower free energy). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called the raffinate. LLE is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment called as mixer settlers. This type of process is commonly performed after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity And Specificity
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Selectivity
Functional selectivity (or “agonist trafficking”, “biased agonism”, “biased signaling”, "ligand bias" and “differential engagement”) is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways relative to a reference ligand (often the endogenous hormone or peptide) at the same receptor. Functional selectivity can be present when a receptor has several possible signal transduction pathways. To which degree each pathway is activated thus depends on which ligand binds to the receptor. Functional selectivity, or biased signaling, is most extensively characterized at G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). A number of biased agonists, such as those at muscarinic M2 receptors tested as analgesics or antiproliferative drugs, or those at opioid receptors that mediate pain, show potential at various receptor families to increase beneficial properties while reducing side effects. For example, pre-clinical studies with G protein biased agonists at the μ-opioid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body of about 32,000 European civil servants. The Commission is divided into departments known as Directorates-General (DGs) that can be likened to departments or ministries each headed by a Director-General who is responsible to a Commissioner. There is one member per member state, but members are bound by their oath of office to represent the general interest of the EU as a whole rather than their home state. The Commission President (currently Ursula von der Leyen) is proposed by the European Council (the 27 heads of state/governments) and elected by the European Parliament. The Council of the European Union then nominates the other members of the Commission in agreement with the nominated President, and the 27 members as a team are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919) and is derived from the word toxic. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. Toxins vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Toxins are largely secondary metabolites, which are organic compounds that are not directly involved in an organism's growth, development, or reproduction, instead often aiding it in matters of defense. Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium and calcium ions, as well as that of the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in the optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms: it is thought to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specifically, a neurotoxin or neurotoxicant– alters the normal activity of the nervous system in such a way as to cause permanent or reversible damage to nervous tissue. This can eventually disrupt or even kill neurons, which are cells that transmit and process signals in the brain and other parts of the nervous system. Neurotoxicity can result from organ transplants, radiation treatment, certain drug therapies, recreational drug use, and exposure to heavy metals, bites from certain species of venomous snakes, pesticides, certain industrial cleaning solvents, fuels and certain naturally occurring substances. Symptoms may appear immediately after exposure or be delayed. They may include limb weakness or numbness, loss of memory, vision, and/o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |