|
Yent Mound
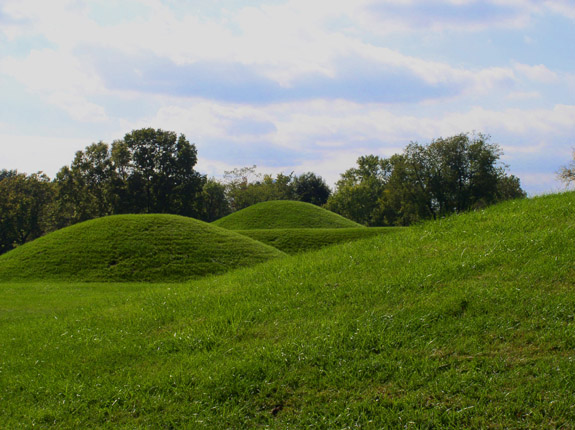
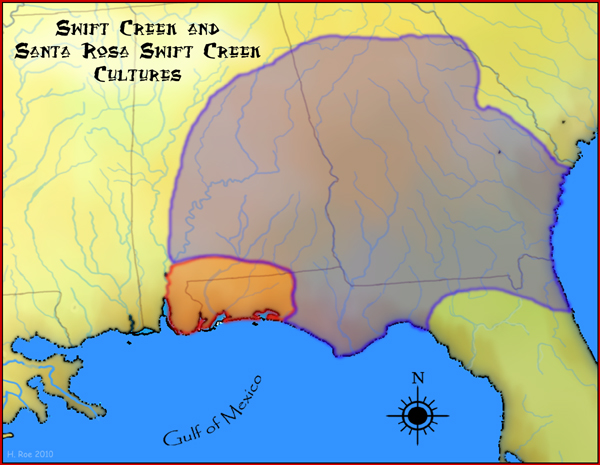
The Yent Mound ( 8FR5) is a Santa Rosa-Swift Creek culture archaeological site located on Alligator Harbor west of St. Teresa, Florida. It is on the east side of County Road 370, approximately 2.5 miles from the junction of U.S. Route 98. On May 24, 1973, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. The Yent Mound was constructed by people of the Deptford culture around the beginning of the Current Era. William Sears defined the archaeological Yent complex based on artifacts found in the Yent Mound, Pierce Mound and Crystal River Mounds. The Yent complex was related to the Hopewell tradition, and some of the artifacts were trade items from the Hopewell area. See also * List of burial mounds in the United States This is a list of notable burial mounds in the United States built by Native Americans. Burial mounds were built by many different cultural groups over a span of many thousands of years, beginning in the Late Archaic period and continuing throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin County, Florida
Franklin County is a county along the Gulf of Mexico in the panhandle of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,451, making it the third-least populous county in Florida. The county seat is Apalachicola. The county includes several large preserved areas and rivers and has been home to commercial timber and fishing industry. More recently it has become popular for tourism and retirement. It includes several rivers, state parks, and islands. History Franklin County was founded in 1832. It was named for Benjamin Franklin. The second largest town in Franklin County is Carrabelle, 25 miles east of Apalachicola on the Carrabelle River. Camp Gordon Johnston During World War II most of Franklin County was used by the U.S. Army for amphibious and jungle training, for which the beaches and islands were ideal. When the war ended and the military left, Lanark Village was established from the remaining officer's quarters. Geography According to the U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierce Site
The Pierce Site (also known as Pierce Mounds and Middens and 8FR14, and other numbers) is a Pre-Columbian archaeological site in Apalachicola, Florida. It is located approximately 1 mile northwest of Apalachicola on 12th Street. On January 11, 1974, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic .... It was occupied during the Middle Woodland Period, which includes ceramics of early Weeden Island and Swift Creek types. It also was occupied during the late prehistoric Fort Walton Period. References External links Franklin County listingsaNational Register of Historic PlacesFranklin County listingsaFlorida's Office of Cultural and Historical Programs Swift Creek culture Mounds in Florida Native American histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites On The National Register Of Historic Places In Florida
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Franklin County, Florida
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. It can be characterized as a chronological and cultural manifestation without any massive changes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
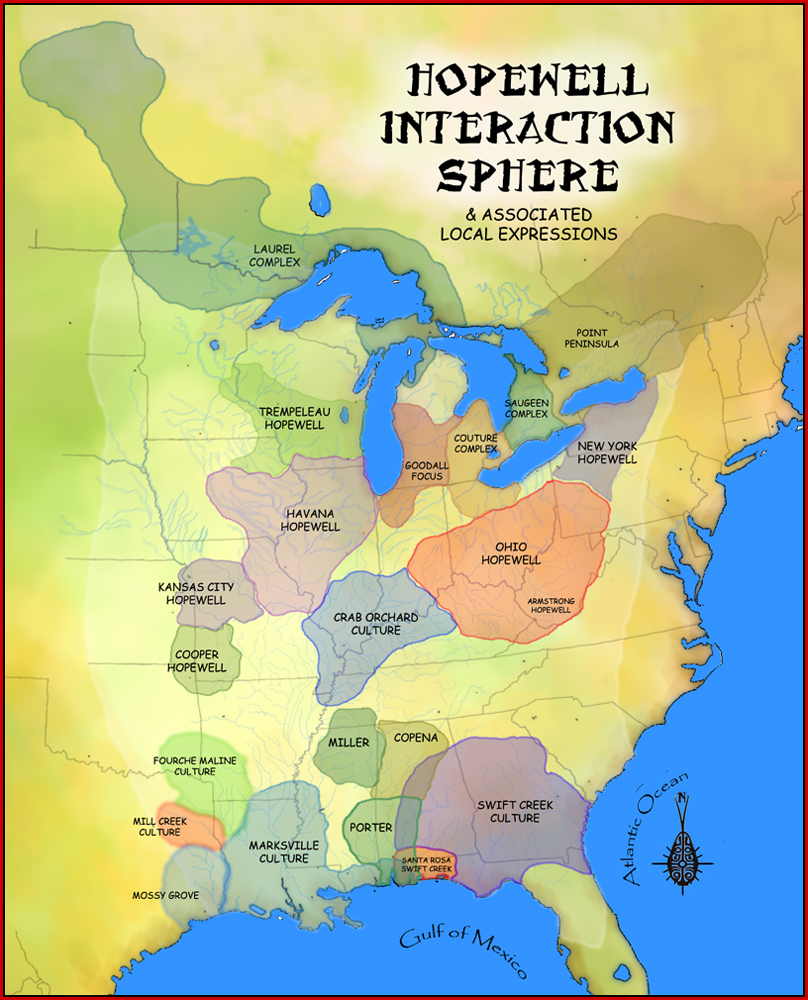
Swift Creek Culture
The Swift Creek culture was a Middle Woodland period archaeological culture in the Southeastern Woodlands of North America, dating to around 100-800 CE. It occupied the areas now part of Georgia, Alabama, Florida, South Carolina, and Tennessee. In Florida, Swift Creek ceremonial practices and burial complexes are referred to technically as the Yent-Green Point complex. The Swift Creek culture was contemporaneous with and interacted with the Hopewell culture; Swift Creek is often described as "Hopewellian." The type site for the Swift Creek culture was the Swift Creek mound site, which was located in Bibb County, Georgia. The Leake Mounds are another significant Swift Creek Culture site in Georgia. Swift Creek peoples practiced mound-building but were generally non- sedentary. Their sustenance resulted from hunting, gathering/collecting, and fishing. Swift Creek are characterized by earthenware pottery with complicated stamped designs, involving mostly curvilinear elements. Exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Burial Mounds In The United States
This is a list of notable burial mounds in the United States built by Native Americans. Burial mounds were built by many different cultural groups over a span of many thousands of years, beginning in the Late Archaic period and continuing through the Woodland period In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeo ... up to the time of European contact. Adena and Hopewell culture burial mounds Mississippian culture burial mounds See also * List of Adena culture sites * List of Hopewell sites * List of Mississippian sites * List of the oldest buildings in the United States References External links International Architecture: database website {{Prehistoric technology Mounds in the United States, Archaeology-related lists, Buria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopewell Tradition
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from 100 BCE to 500 CE, in the Middle Woodland period. The Hopewell tradition was not a single culture or society but a widely dispersed set of populations connected by a common network of trade routes. At its greatest extent, the Hopewell exchange system ran from the northern shores of Lake Ontario south to the Crystal River Indian Mounds in modern-day Florida. Within this area, societies exchanged goods and ideas, with the highest amount of activity along waterways, which were the main transportation routes. Peoples within the Hopewell exchange system received materials from all over the territory of what now comprises the mainland United States. Most of the items traded were exotic materials; they were delivered to peoples living in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal River Archaeological State Park
Crystal River State Archaeological Site is a Florida State Park located on the Crystal River and within the Crystal River Preserve State Park. The park is located two miles (3 km) northwest of the city of Crystal River, on Museum Point off U.S. 19/ 98. Under the title of Crystal River Indian Mounds, it is also a U.S. National Historic Landmark (designated as such on September 29, 1970). History The park contains a six-mound complex, occupied from the Deptford period through Santa Rosa-Swift Creek culture and up to the Late Fort Walton period. This timespan makes it one of the longest continually occupied sites in Florida, believed to have been occupied for 1,600 years. Native Americans traveled long distances to the complex to bury their dead and to engage in trading activities. An estimated 7,500 people may have visited the complex annually when it was occupied. The complex contains burial mounds, temple/platform mounds, a plaza area, and a midden. The earliest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as "Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida and Cuba; it is the only state that borders both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Spanning , Florida ranks 22nd in area among the 50 states, and with a population of over 21 million, it is the third-most populous. The state capital is Tallahassee, and the most populous city is Jacksonville. The Miami metropolitan area, with a population of almost 6.2 million, is the most populous urban area in Florida and the ninth-most populous in the United States; other urban conurbations with over one million people are Tampa Bay, Orlando, and Jacksonville. Various Native American groups have inhabited Florida for at least 14,000 years. In 1513, Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León became th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deptford Culture
The Deptford culture (800 BCE—700 CE) was an archaeological culture in southeastern North America characterized by the appearance of elaborate ceremonial complexes, increasing social and political complexity, mound burial, permanent settlements, population growth, and an increasing reliance on cultigens. Definition and range Deptford is named for the Deptford area near Savannah, Georgia. The culture is defined by the presence of sand- tempered pottery decorated with the impressions of carved wooden paddles that were pressed against the vessels before they were fired. The sand-tempering distinguishes Deptford ceramics from the fiber-tempered ceramics of the late-Archaic Stallings Island/St. Simons, Orange, and Norwood cultures that preceded it. Other contemporary cultures of the southeastern United States also produced paddle decorated ceramics. The Deptford culture was oriented to the coast. From northern Georgia it spread along the Atlantic coast, reaching Cape Fear, North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)