|
Yelpidifor Anempodistovich Kirillov
Yelpidifor Anempodistovich Kirillov (8 October 1883 – 27 November 1964) was a Soviet physicist, doctor of physical-mathematical sciences, the founder of the Odessa scientific school in the field of photography. Biography Yelpidifor Kirillov was born in Shipka. He graduated from the Mathematics Department of Physics and Mathematics of the Novorossiysk University in 1907 with a first degree and was kept at the department of physics in preparation for an academic career. From 1908 to 1915, he worked as an assistant at the University for Women, also worked part-time observer of the magnetic-meteorological observatory, and then in the Department of Physics and Mathematics Department of Physics University of Novorossiysk on the assistant position again. In 1915 Kirillov was promoted to master's degree, and was elected assistant professor in the Department of Physics. From 1921 he headed the department of experimental physics. In 1926 joined as Director of Institute of Physics at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thesis
A thesis (: theses), or dissertation (abbreviated diss.), is a document submitted in support of candidature for an academic degree or professional qualification presenting the author's research and findings.International Standard ISO 7144: Documentation�Presentation of theses and similar documents International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, 1986. In some contexts, the word ''thesis'' or a cognate is used for part of a bachelor's or master's course, while ''dissertation'' is normally applied to a doctorate. This is the typical arrangement in American English. In other contexts, such as within most institutions of the United Kingdom, South Africa, the Commonwealth Countries, and Brazil, the reverse is true. The term graduate thesis is sometimes used to refer to both master's theses and doctoral dissertations. The required complexity or quality of research of a thesis or dissertation can vary by country, university, or program, and the required minimum study period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1964 Deaths
Events January * January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved. * January 5 – In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch Athenagoras I of Constantinople meet in Jerusalem. * January 6 – A British firm, the Leyland Motor Corp., announces the sale of 450 buses to the Cuban government, challenging the United States blockade of Cuba. * January 9 – ''Martyrs' Day (Panama), Martyrs' Day'': Armed clashes between United States troops and Panamanian civilians in the Panama Canal Zone precipitate a major international crisis, resulting in the deaths of 21 Panamanians and 4 U.S. soldiers. * January 11 – United States Surgeon General Luther Terry reports that smoking may be hazardous to one's health (the first such statement from the U.S. government). * January 22 – Kenneth Kaunda is inaugurated as the first Prime Minister of Northern Rhodesia. * January ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1883 Births
Events January * January 4 – ''Life (magazine), Life'' magazine is founded in Los Angeles, California, United States. * January 10 – A Newhall House Hotel Fire, fire at the Newhall Hotel in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States, kills 73 people. * January 16 – The Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act, establishing the United States civil service, is passed. * January 19 – The first electric lighting system employing overhead wires begins service in Roselle, New Jersey, United States, installed by Thomas Edison. February * February 15 – Tokyo Electrical Lightning Grid, predecessor of Tokyo Electrical Power (TEPCO), one of the largest electrical grids in Asia and the world, is founded in Japan. * February 16 – The ''Ladies' Home Journal'' is published for the first time, in the United States. * February 23 – Alabama becomes the first U.S. state to enact an Competition law, antitrust law. * February 28 – The first vaudeville th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain, and predict List of natural phenomena, natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guido Beck
Guido Beck (29 August 1903 – 21 October 1988) was an Argentine physicist of German Bohemian origin, who was born in Liberec and died in Rio de Janeiro. He discovered all cylindrically symmetric nonrotating vacuum solutions in general relativity, which is the first instance of exactly solved gravitational waves. Biography Beck studied physics in Vienna and received his doctorate in 1925, under Hans Thirring. He worked in Leipzig in 1928 as an assistant to Werner Heisenberg. A combination of the troubled political climate of Europe in the 1930s, his own restlessness, and the Nazi persecutions in Germany, made the Jewish-born Beck a traveler in those years. Until 1935 he worked in Cambridge with Ernest Rutherford, Copenhagen, Prague, United States and Japan. In 1935, Beck was invited to work in the Soviet Union by Head of the Institute of Physics, Odessa University Yelpidifor Anempodistovich Kirillov. At the Odessa University Beck was head of the Department of Theoretical Physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, implemented in 1949 following the end of World War II, defines a German as a German nationality law, German citizen. During the 19th and much of the 20th century, discussions on German identity were dominated by concepts of a common language, culture, descent, and history.. "German identity developed through a long historical process that led, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, to the definition of the German nation as both a community of descent (Volksgemeinschaft) and shared culture and experience. Today, the German language is the primary though not exclusive criterion of German identity." Today, the German language is widely seen as the primary, though not exclusive, criterion of German identity. Estimates on the total number of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR State Prize
The USSR State Prize () was one of the Soviet Union’s highest civilian honours, awarded from its establishment in September 1966 until the dissolution of the USSR in 1991. It recognised outstanding contributions in the fields of science, mathematics, literature, the arts, and architecture. History State Stalin Prize (1941–1956) The award traces its origins to the State Stalin Prize (), commonly known as the Stalin Prize, which was established in 1941. It honoured achievements in science, technology, literature, and the arts deemed vital to the Soviet war effort and postwar reconstruction.Volkov, Solomon; Bouis, Antonina W., trans. 2004. ''Shostakovich and Stalin: The Extraordinary Relationship Between the Great Composer and the Brutal Dictator''. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-375-41082-1. Ceremonies were suspended during 1944–45 and then held twice in 1946 (January for works from 1943–44; June for 1945 works). USSR State Prize (1966–1991) By 1966, the Stalin Prize h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Photoelectric Effect
Negative may refer to: Science and mathematics * Negative number * Minus sign (−), the mathematical symbol * Negative mass * Negative energy * Negative charge, one of the two types of electric charge * Negative (electrical polarity), in electric circuits * Negative result (other) * Negative lens, in optics Photography * Negative (photography), an image with inverted luminance or a strip of film with such an image * Original camera negative, the film in a motion picture camera which captures the original image * Paper negative, a negative image printed on paper used to create the final print of a photograph Linguistics * A negative answer, commonly expressed with the word ''no'' * A type of grammatical construction; see affirmative and negative *A double negative is a construction occurring when two forms of grammatical negation are used in the same sentence. Music * Negative (Finnish band), a Finnish band established in 1997 * Negative (Serbian band), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
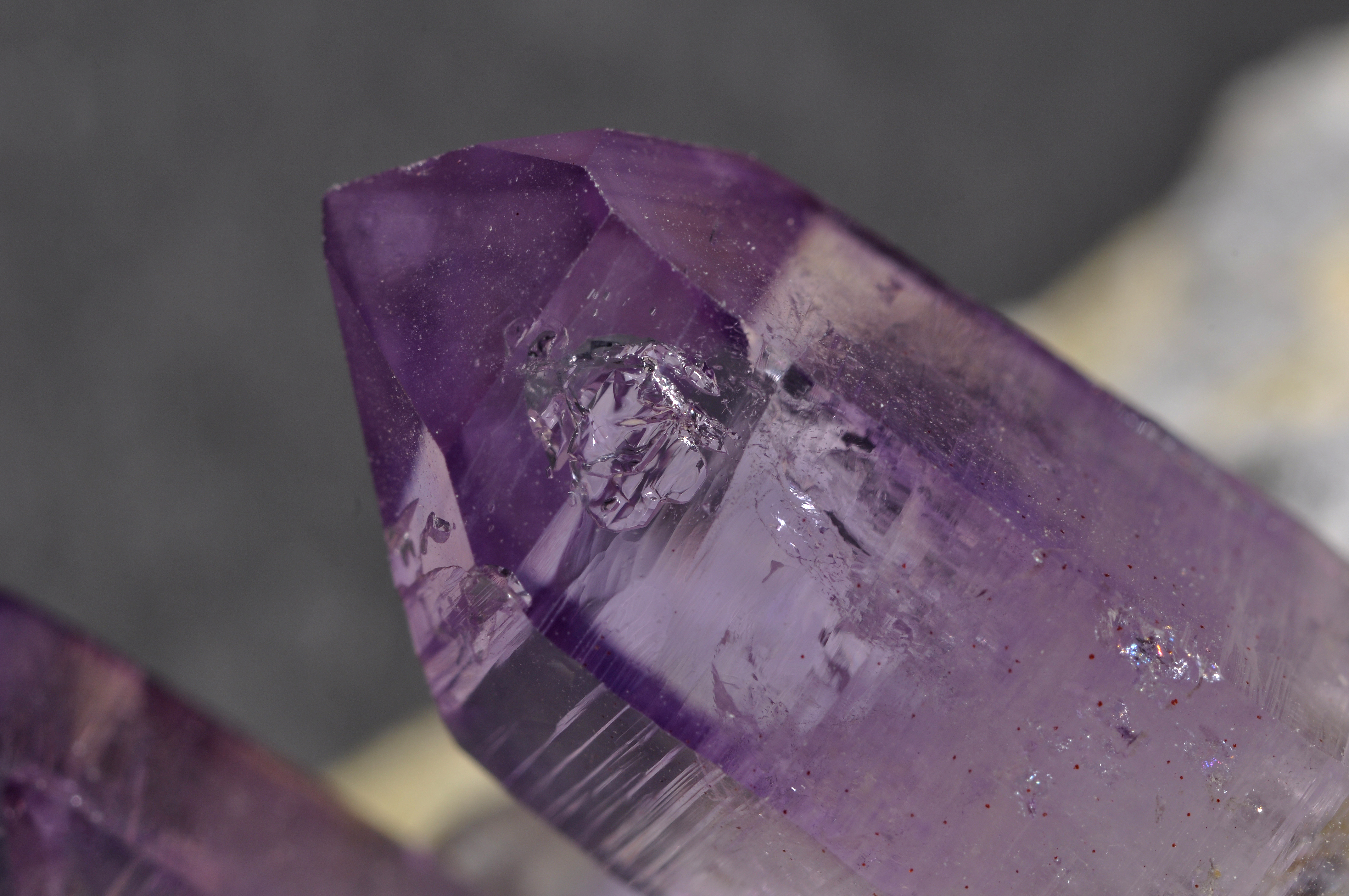
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Photoelectric Effect
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and measurement applications, or for the generation of electrical power in solar cells. Photodiodes are used in a wide range of applications throughout the electromagnetic spectrum from visible light photocells to gamma ray spectrometers. Principle of operation A photodiode is a PIN structure or p–n junction. When a photon of sufficient energy strikes the diode, it creates an electron–hole pair. This mechanism is also known as the inner photoelectric effect. If the absorption occurs in the junction's depletion region, or one diffusion length away from it, these carriers are swept from the junction by the built-in electric field of the depletion region. Thus holes move toward the anode, and electrons toward the cathode, and a photocurrent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |