|
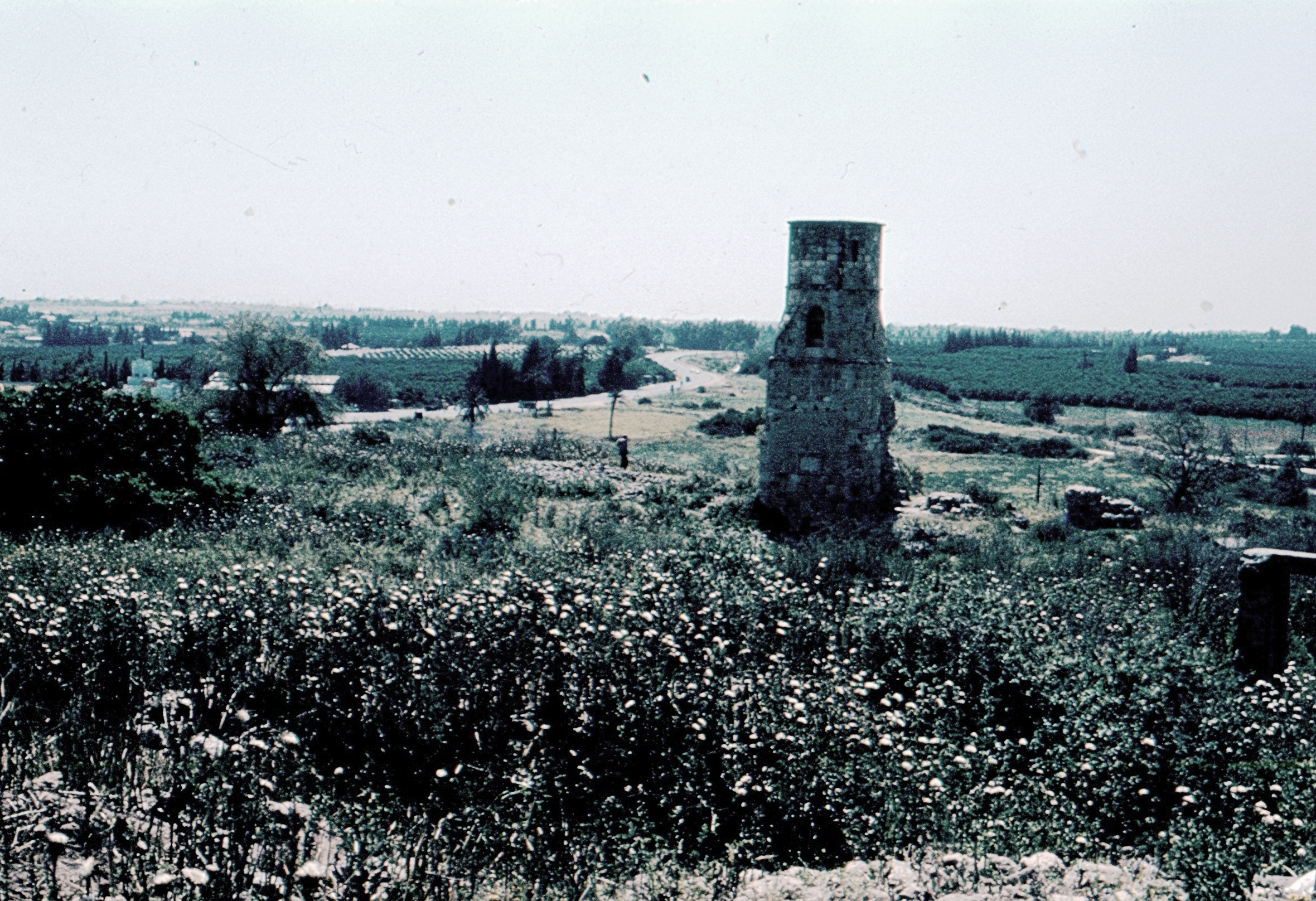
Yebna
Yibna ( ar, يبنى; ''Jabneh'' or ''Jabneel'' in Biblical times; ''Jamnia'' in Roman empire, Roman times; ''Lordship of Ibelin, Ibelin'' to the Crusades, Crusaders), or Tel Yavne is an archaeological site and depopulated Palestinian people, Palestinian town. The ruins are located immediately southeast of the modern Israeli city of Yavne. The town had a population of 5,420 in 1948, located 15 kilometers southwest of Ramla.Khalidi, 1992, p.421 Yibna was taken by Israeli forces on 4 June 1948, and was depopulated during the military assault and expulsion. It is a significant site for post-biblical Jewish history, as it was the location of the Council of Jamnia, considered the birthplace of modern Rabbinic Judaism. It is also significant in the history of the Crusades, as the location of the House of Ibelin. Name In many English translations of the Bible, it is known as Yavne or Jabneh . During Greco-Roman times, it was known as Jamnia ( grc, Ἰαμνία ''Iamníā''; la, Iamni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and French Third Republic, France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Jamnia
The Council of Jamnia (presumably Yavneh in the Holy Land) was a council purportedly held late in the 1st century CE to finalize the canon of the Hebrew Bible. It has also been hypothesized to be the occasion when the Jewish authorities decided to exclude believers in Jesus as the Messiah from synagogue attendance, as referenced by interpretations of in the New Testament. The writing of the Birkat haMinim benediction is attributed to Shmuel ha-Katan at the supposed Council of Jamnia. The theory of a council of Jamnia that finalized the canon, first proposed by Heinrich Graetz in 1871, was popular for much of the 20th century. However, it was increasingly questioned from the 1960s onward, and the theory has been largely discredited. Background The Talmud relates that some time before the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 AD, Rabbi Yohanan ben Zakkai relocated to the city of Yavneh, where he received permission from the Romans to found a school of ''halakha'' (Jewish re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the '' Pax Romana'' or ''Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the " Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salome I
Salome I (ca. 65 BCE – ca. 10 CE) was the sister of Herod the Great and the mother of Berenice by her husband Costobarus, governor of Idumea. She was a nominal queen regnant of the toparchy of Iamnia, Azotus, Phasaelis from 4 BCE. Life She first married Joseph ( :fr:Joseph (iduméen)), whom she accused of familiarities with Mariamne, wife of Herod, and thus procured his death.Salome entry in The Cyclopedia of Biblical, Theological and Ecclesiastical Literature by James Strong and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herod The Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, Roman Jewish client state, client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian Kingdom of Judea, Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renovation of the Second Temple#Herod's Temple, Second Temple in Jerusalem and the expansion of the Temple Mount towards its north, the enclosure around the Cave of the Patriarchs in Hebron, the construction of the port at Caesarea Maritima, the fortress at Masada, and Herodium. Vital details of his life are recorded in the works of the 1st century CE Roman–Jewish historian Josephus. Herod also appears in the Christian Gospel of Matthew as the ruler of Judea who orders the Massacre of the Innocents at the time of the Nativity of Jesus, birth of Jesus, although most Herod biographers do not believe that this event occurred. Despite his successes, including singleh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan Bahat
Dan Bahat ( he, דן בהט, born 1938) is an Israeli archaeologist especially known for his excavations in Jerusalem , particularly at the Western Wall tunnels. Biography Dan Bahat was born in Poland to parents who were citizens of Mandatory Palestine.Dan Bahat: Curriculum vitae Bar-Ilan University The family moved to in 1939 and became Israeli citizens in 1952. He served in the from 1956 to 1958. In 1964 he gained a |
Philistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek ( LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their polity, after having already been subjugated for centuries by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. After becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and archaeological record by the late 5th century BC.. The Philistines are known for their biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramses III at Medinet Habu, in which they are called (accepted as cognate with Hebrew ); the parallel Assyrian term is , , or . Etymology The English te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Antiquities Authority
The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA, he, רשות העתיקות ; ar, داﺌرة الآثار, before 1990, the Israel Department of Antiquities) is an independent Israeli governmental authority responsible for enforcing the 1978 Law of Antiquities. The IAA regulates excavation and conservation, and promotes research. The Director-General is Mr. Eli Escusido, and its offices are housed in the Rockefeller Museum. The Israel Antiquities Authority plans to move into a new building for the National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel in Jerusalem, next to the Israel Museum. History The Israel Department of Antiquities and Museums (IDAM) of the Ministry of Education was founded on July 26, 1948, after the establishment of the State of Israel. It took over the functions of the Department of Antiquities of the British Mandate in Israel and Palestine. Originally, its activities were based on the British Mandate Department of Antiquities ordinances. IDAM was the statutory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Romans during the First Jewish–Roman War as head of Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in 67 AD to Roman forces led by Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish Messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Emperor of Rome. In response, Vespasian decided to keep Josephus as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became Emperor in 69 AD, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the emperor's family name of Flavius. Simon Claude Mimouni, ''Le Judaïsme ancien du VIe siècle avant notre ère au IIIe siècle de notre ère : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tānāḵh''), also known in Hebrew as Miqra (; Hebrew: ''Mīqrā''), is the Biblical canon, canonical collection of Hebrew language, Hebrew scriptures, including the Torah, the Nevi'im, and the Ketuvim. Different branches of Judaism and Samaritanism have maintained different versions of the canon, including the 3rd-century Septuagint text used by Second-Temple Judaism, the Syriac language Peshitta, the Samaritan Torah, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and most recently the 10th century medieval Masoretic Text, Masoretic text created by the Masoretes currently used in modern Rabbinic Judaism. The terms "Hebrew Bible" or "Hebrew Canon" are frequently confused with the Masoretic text, however, this is a medieval version and one of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia ( Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |