|
YcaO
YcaO is a protein found in bacteria which is involved in the synthesis of thiazole/oxazole modified microcin antibiotics, such as bottromycin. YcaO performs ATP dependent cyclodehydration to form the oxazole and thiazole moieties of the microcin. The YcaO name origin is from a gene naming rubric that was established from the bacterium Escherichia coli. If a gene has an unknown function, it was given a four-letter name starting with the letter Y and the next three letters are given based on the genomic location. Methyl coenzyme M reductase (MCR) or Coenzyme-B sulfoethylthiotransferase is a protein known in thioamidation (a posttranslational modification). A Ycao enzyme dependent on ATP is needed for MCR thioamidation as well as a sulfide source. YcaO enzymes are needed to catalyze the ATP-dependent backbone cyclodehydration of polar amino acids such as Cysteine, Serine, and Threonine to the correct thiazoline and (methyl) oxazoline Heterocycle. The side chains of these amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottromycin
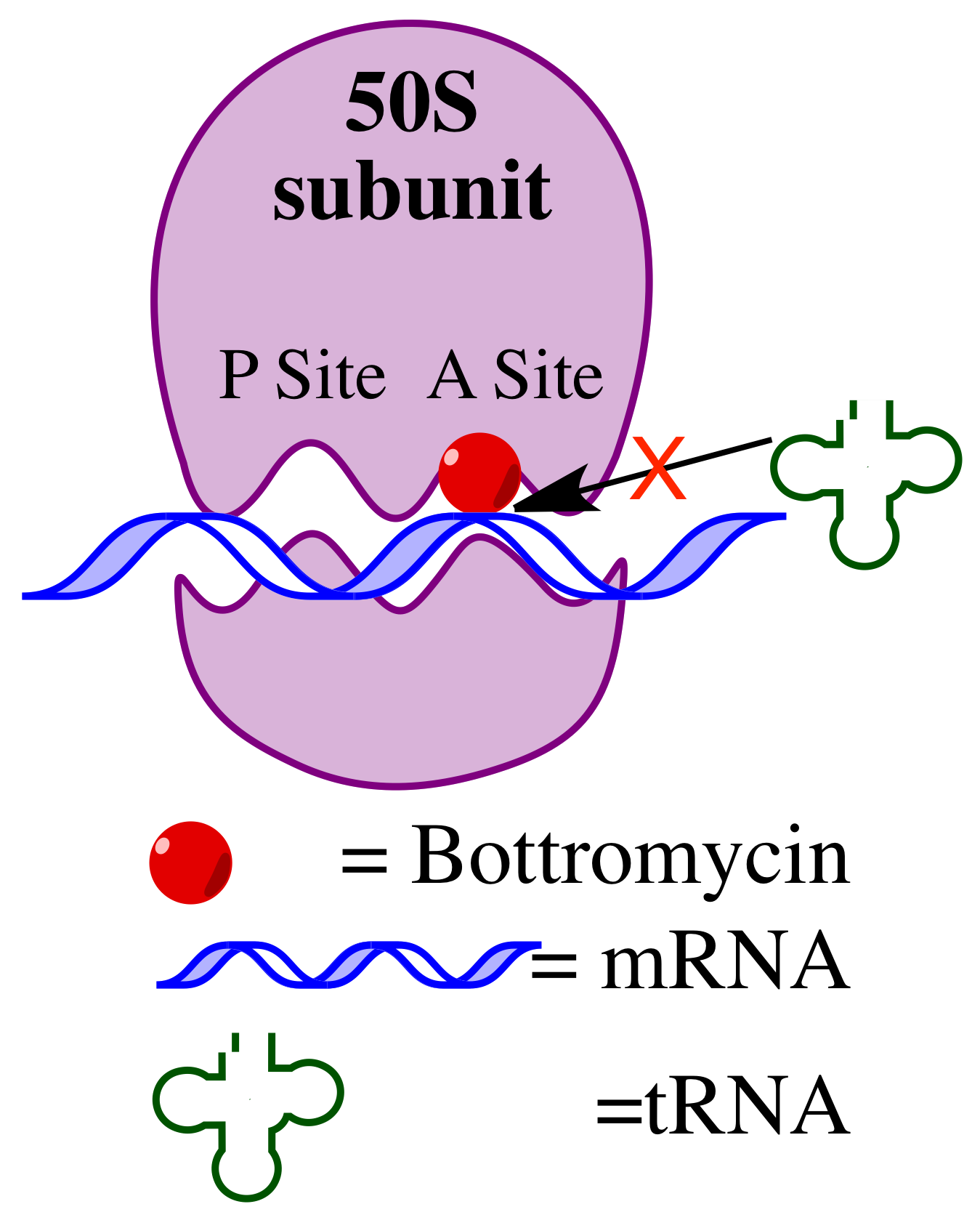
Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from ''Streptomyces bottropensis''. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic. Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, aminoacyl-''t''RNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity ''in vitro'', it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability ''in vivo'', some bottromycin derivatives have been explored. The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prochloron
''Prochloron'' (from the Greek ''pro'' (before) and the Greek ''chloros'' (green) ) is a genus of unicellular oxygenic photosynthetic prokaryotes commonly found as an extracellular symbiont on coral reefs, particularly in didemnid ascidians (sea squirts). Part of the phylum cyanobacteria, it was theorized ( endosymbiotic theory) that ''Prochloron'' is a predecessor of the photosynthetic components, chloroplasts, found in photosynthetic eukaryotic cells. However this theory is largely refuted by phylogenetic studies which indicate ''Prochloron'' is not on the same line of descent that lead to chloroplast-containing algae and land plants. ''Prochloron'' was discovered in 1975 by Ralph A. Lewin of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. ''Prochloron'' is one of three known prochlorophytes, cyanobacteria that contain both chlorophyll ''a'' and ''b'' bound to a special light-harvesting protein. Surprisingly, unlike most cyanobacteria ''Prochloron'' do not contain the red or blue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcin
Microcins are very small bacteriocins, composed of relatively few amino acids. For this reason, they are distinct from their larger protein cousins. The classic example is microcin V, of ''Escherichia coli''. Subtilosin A is another bacteriocin from ''Bacillus subtilis''. The peptide has a cyclized backbone and forms three cross-links between the sulphurs of Cys13, Cys7 and Cys4 and the alpha-positions of Phe22, Thr28 and Phe31. Microcins produced by commensal ''E. coli'' strains target and eliminate enteric pathogens such as ''Salmonella enterica ''Salmonella enterica'' (formerly ''Salmonella choleraesuis'') is a rod-shaped, flagellate, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus ''Salmonella''. It is divided into six subspecies, arizonae (IIIa), diarizonae ...'' by mimicking the siderophores the pathogens use for iron scavenging. Microcins also help commensal strains of ''E. coli'' outcompete pathogenic strains. BACTIBASE database is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazole
Oxazole is the parent compound for a vast class of heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds. These are azoles with an oxygen and a nitrogen separated by one carbon. Oxazoles are aromatic compounds but less so than the thiazoles. Oxazole is a weak base; its conjugate acid has a pKa, p''K''a of 0.8, compared to 7 for imidazole. Preparation The classic synthetic route the Robinson–Gabriel synthesis by dehydration of 2-acylaminoketones: The Fischer oxazole synthesis from cyanohydrins and aldehydes is also widely used: Other methods are known including the reaction of α-haloketones and formamide and the Van Leusen reaction with aldehydes and TosMIC. Biosynthesis In biomolecules, oxazoles result from the cyclization and oxidation of serine or threonine nonribosomal peptides: : Oxazoles are not as abundant in biomolecules as the related thiazoles with oxygen replaced by a sulfur atom. Reactions With a pKa of 0.8 for the conjugate acid (oxazolium salts), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiazole
Thiazole (), or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1). Molecular and electronic structure Thiazoles are members of the azoles, heterocycles that include imidazoles and oxazoles. Thiazole can also be considered a functional group when part of a larger molecule. Being planar thiazoles are characterized by significant pi-electron delocalization and have some degree of aromaticity, more so than the corresponding oxazoles. This aromaticity is evidenced by the 1H NMR chemical shift of the ring protons, which absorb between 7.27 and 8.77 ppm, indicating a strong diamagnetic ring current. The calculated pi-electron density marks C5 as the primary site for electrophilic substitution, and C2-H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Coenzyme M Reductase
In enzymology, coenzyme-B sulfoethylthiotransferase, also known as methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) or most systematically as 2-(methylthio)ethanesulfonate:N-(7-thioheptanoyl)-3-O-phosphothreonine S-(2-sulfoethyl)thiotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the formation of methane. It does so by combining the hydrogen donor coenzyme B and the methyl donor coenzyme M. Via this enzyme, most of the natural gas on earth was produced. Ruminants (e.g. cows) produce methane because their rumens contain methanogenic prokaryotes (Archaea) that encode and express the set of genes of this enzymatic complex. The enzyme has two active sites, each occupied by the nickel-containing F430 cofactor. : + CoM-S-S-CoB + methane The two substrates of this enzyme are 2-(methylthio)ethanesulfonate and N-(7-mercaptoheptanoyl)threonine 3-O-phosphate; its two products are CoM-S-S-CoB and methane. 3-Nitrooxypropanol inhibits the enzyme. In some species, the enzyme reacts in rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, but both D and L-cysteine are found in nature. LCysteine is a protein monomer in all biota, and D-cysteine acts as a signaling molecule in mammalian nervous systems. Cysteine is named after its discovery in urine, which comes from the urinary bladder or cyst, from Ancient Greek, Greek κύστις ''kýstis'', "bladder". The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide bond, disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. When used as a food additive, cysteine has the E number E920. Cysteine is Genetic code, encoded by the codo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, '' sericum''. Serine's structure was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form when dissolved in water), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as ''E. coli''. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG). Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices). Modifications The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications. The hydroxyl side-chain can und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |