|
YbBiPt
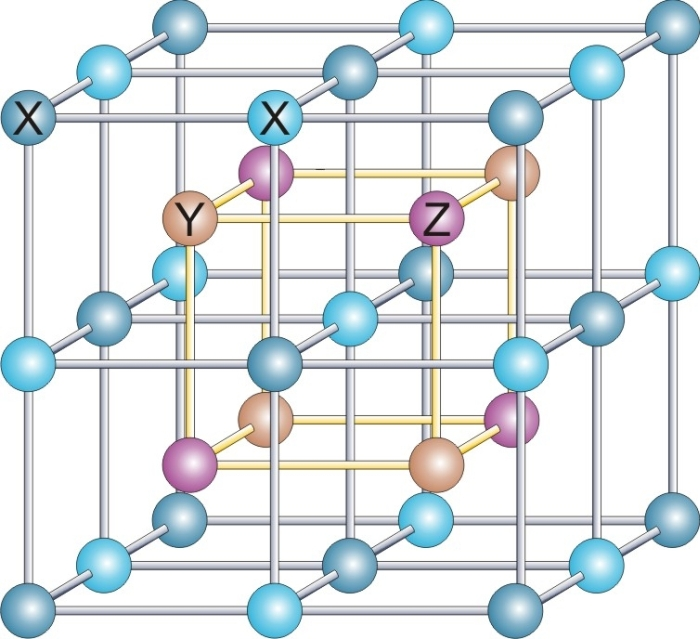
YbBiPt (ytterbium-bismuth-platinum; also named YbPtBi) is an intermetallic material which at low temperatures exhibits an extremely high value of specific heat, which is a characteristic of heavy-fermion behavior. YbBiPt has a noncentrosymmetric cubic crystal structure; in particular it belongs to the ternary half-Heusler compounds. Discovery YbBiPt was discovered by Zachary Fisk ( Los Alamos National Laboratory) and coworkers in 1991 in the context of material research devoted to correlated electron systems such as heavy-fermion metals and Kondo insulators. Then the material was studied in detail due to its unconventional properties at very low temperatures (below 1 K). Material properties YbBiPt crystallizes in the MgAgAs structure, which is also known as the half-Heusler structure. YbBiPt exhibits metallic behavior, e.g. continuously decreasing electrical resistivity upon cooling. The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows an anomaly at 0.4K and linear behavior a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heusler Compound
Heusler compounds are magnetic intermetallics with face-centered cubic crystal structure and a composition of XYZ (half-Heuslers) or X2YZ (full-Heuslers), where X and Y are transition metals and Z is in the p-block. The term derives from the name of German mining engineer and chemist Friedrich Heusler, who studied such a compound (Cu2MnAl) in 1903. Many of these compounds exhibit properties relevant to spintronics, such as magnetoresistance, variations of the Hall effect, ferro-, antiferro-, and ferrimagnetism, half- and semimetallicity, semiconductivity with spin filter ability, superconductivity, topological band structure and are actively studied as Thermoelectric materials. Their magnetism results from a double-exchange mechanism between neighboring magnetic ions. Manganese, which sits at the body centers of the cubic structure, was the magnetic ion in the first Heusler compound discovered. (See the Bethe–Slater curve for details of why this happens.) Styles of writing c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heusler Alloy
Heusler compounds are magnetic intermetallics with face-centered cubic crystal structure and a composition of XYZ (half-Heuslers) or X2YZ (full-Heuslers), where X and Y are transition metals and Z is in the p-block. The term derives from the name of German mining engineer and chemist Friedrich Heusler, who studied such a compound (Cu2MnAl) in 1903. Many of these compounds exhibit properties relevant to spintronics, such as magnetoresistance, variations of the Hall effect, ferro-, antiferro-, and ferrimagnetism, half- and semimetallicity, semiconductivity with spin filter ability, superconductivity, topological band structure and are actively studied as Thermoelectric materials. Their magnetism results from a double-exchange mechanism between neighboring magnetic ions. Manganese, which sits at the body centers of the cubic structure, was the magnetic ion in the first Heusler compound discovered. (See the Bethe–Slater curve for details of why this happens.) Styles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Fermion Material
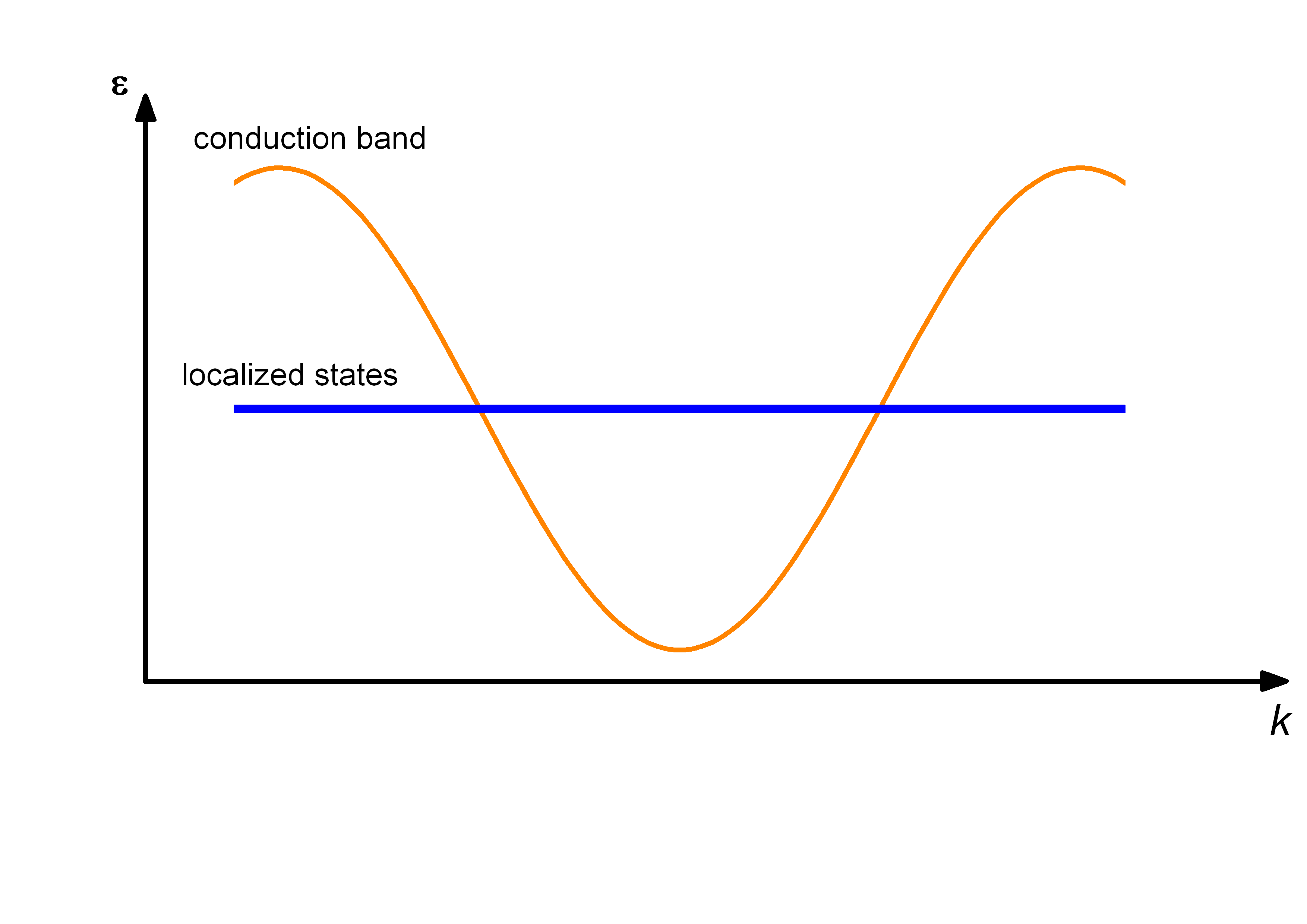
In solid-state physics, heavy fermion materials are a specific type of intermetallic compound, containing elements with 4f or 5f electrons in unfilled electron bands. Electrons are one type of fermion, and when they are found in such materials, they are sometimes referred to as heavy electrons. Heavy fermion materials have a low-temperature specific heat whose linear term is up to 1000 times larger than the value expected from the free electron model. The properties of the heavy fermion compounds often derive from the partly filled f-orbitals of rare-earth or actinide ions, which behave like localized magnetic moments. The name "heavy fermion" comes from the fact that the fermion behaves as if it has an effective mass greater than its rest mass. In the case of electrons, below a characteristic temperature (typically 10 K), the conduction electrons in these metallic compounds behave as if they had an effective mass up to 1000 times the free particle mass. This large effective m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ytterbium Compounds
Ytterbium compounds are chemical compounds that contain the element ytterbium (Yb). The chemical behavior of ytterbium is similar to that of the rest of the lanthanides. Most ytterbium compounds are found in the +3 oxidation state, and its salts in this oxidation state are nearly colorless. Like europium, samarium, and thulium, the trihalides of ytterbium can be reduced to the dihalides by hydrogen, zinc dust, or by the addition of metallic ytterbium. The +2 oxidation state occurs only in solid compounds and reacts in some ways similarly to the alkaline earth metal compounds; for example, ytterbium(II) oxide (YbO) shows the same structure as calcium oxide (CaO). Halides Ytterbium forms both dihalides and trihalides with the halogens fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. The dihalides are susceptible to oxidation to the trihalides at room temperature and disproportionate to the trihalides and metallic ytterbium at high temperature: :3 YbX2 → 2 YbX3 + Yb (X = F, Cl, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, in the American southwest. Best known for its central role in helping develop the first atomic bomb, LANL is one of the world's largest and most advanced scientific institutions. Los Alamos was established in 1943 as Project Y, a top-secret site for designing nuclear weapons under the Manhattan Project during World War II.The site was variously called Los Alamos Laboratory and Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. Chosen for its remote yet relatively accessible location, it served as the main hub for conducting and coordinating nuclear research, bringing together some of the world's most famous scientists, among them numerous Nobel Prize winners. The town of Los Alamos, directly north of the lab, grew extensively through this period. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kondo Insulator
In solid-state physics, Kondo insulators (also referred as Kondo semiconductors and heavy fermion semiconductors) are understood as materials with strongly correlated electrons, that open up a narrow band gap (in the order of 10 meV) at low temperatures with the chemical potential lying in the gap, whereas in heavy fermion materials the chemical potential is located in the conduction band. The band gap opens up at low temperatures due to hybridization of localized electrons (mostly f-electrons) with conduction electrons, a correlation effect known as the Kondo effect In physics, the Kondo effect describes the scattering of conduction electrons in a metal due to magnetic impurities, resulting in a characteristic change i.e. a minimum in electrical resistivity with temperature. The cause of the effect was fir .... As a consequence, a transition from metallic behavior to insulating behavior is seen in resistivity measurements. The band gap could be either direct or indirect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlated Electrons
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it usually refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are '' linearly'' related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the so-called demand curve. Correlations are useful because they can indicate a predictive relationship that can be exploited in practice. For example, an electrical utility may produce less power on a mild day based on the correlation between electricity demand and weather. In this example, there is a causal relationship, because extreme weather causes people to use more electricity for heating or cooling. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Compounds
Bismuth compounds are compounds containing the element bismuth (Bi). Bismuth forms trivalent and pentavalent compounds, the trivalent ones being more common. Many of its chemical properties are similar to those of arsenic and antimony, although they are less toxic than derivatives of those lighter elements. Oxides and sulfides At elevated temperatures, the vapors of the metal combine rapidly with oxygen, forming the yellow trioxide, . Wiberg, p. 768.Greenwood, p. 553. When molten, at temperatures above 710 °C, this oxide corrodes any metal oxide and even platinum. Krüger, p. 185 On reaction with a base, it forms two series of oxyanions: , which is polymeric and forms linear chains, and . The anion in is a cubic octameric anion, , whereas the anion in is tetrameric. The dark red bismuth(V) oxide, , is unstable, liberating gas upon heating. The compound NaBiO3 is a strong oxidising agent.Greenwood, p. 578. Bismuth sulfide, , occurs naturally in bismuth ores. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_chloride.jpg)


_oxide_2.jpg)