|
Yao Yue
Yao Yue () is one of the 20 books of the Analects of Confucius. Notably, it is the last book of the Analects. As the concluding book, Yaoyue is one of the hotly debated book of the Analects due to its distinct writing style and inconsistency with previous books. Name The name "Yao Yue" refers to the mythological Chinese king Yao. "Yue", in Classical Chinese, means "to say". Therefore, the phrase "Yao Yue" can be expounded as "Yao said". Content The book Yao Yue starts with a conversation initiated by Yao with his successor Shun. The conversation's subject was Yao's willing abdication and the appointment of Shun as his successor. The conversation constitutes half of the book Yao Yue while in the second half of the book, Confucius explained to his disciple Zizhang the ideal way of ruling a country. The Analects come to a conclusion with Confucius' teaching on destiny (), rites (), and the insight into words (). Interpretation The singularity of the book Yaoyue did not go un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analects
The ''Analects'', also known as the ''Sayings of Confucius'', is an ancient Chinese philosophical text composed of sayings and ideas attributed to Confucius and his contemporaries, traditionally believed to have been compiled by his followers. The consensus among scholars is that large portions of the text were composed during the Warring States period (475–221 BC), and that the work achieved its final form during the mid-Han dynasty (206 BC220 AD). During the early Han, the ''Analects'' was merely considered to be a commentary on the Five Classics. However, by the dynasty's end the status of the ''Analects'' had grown to being among the central texts of Confucianism. During the late Song dynasty (960–1279 AD) the importance of the ''Analects'' as a Chinese philosophy work was raised above that of the older Five Classics, and it was recognized as one of the "Four Books". The ''Analects'' has been one of the most widely read and studied books in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghua University
Tsinghua University (THU) is a public university in Haidian, Beijing, China. It is affiliated with and funded by the Ministry of Education of China. The university is part of Project 211, Project 985, and the Double First-Class Construction. It is also a member in the C9 League. Tsinghua University's campus is in northwest Beijing, on the site of the former imperial gardens of the Qing dynasty. The university has 21 schools and 59 departments, with faculties in science, engineering, humanities, law, medicine, history, philosophy, economics, management, education, and art. History Early 20th century (1911–1949) Tsinghua University was established in Beijing during a tumultuous period of national upheaval and conflicts with foreign powers which culminated in the Boxer Rebellion, an uprising against foreign influence in China. After the suppression of the revolt by a foreign alliance including the United States, the ruling Qing dynasty was required to pay indemnit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
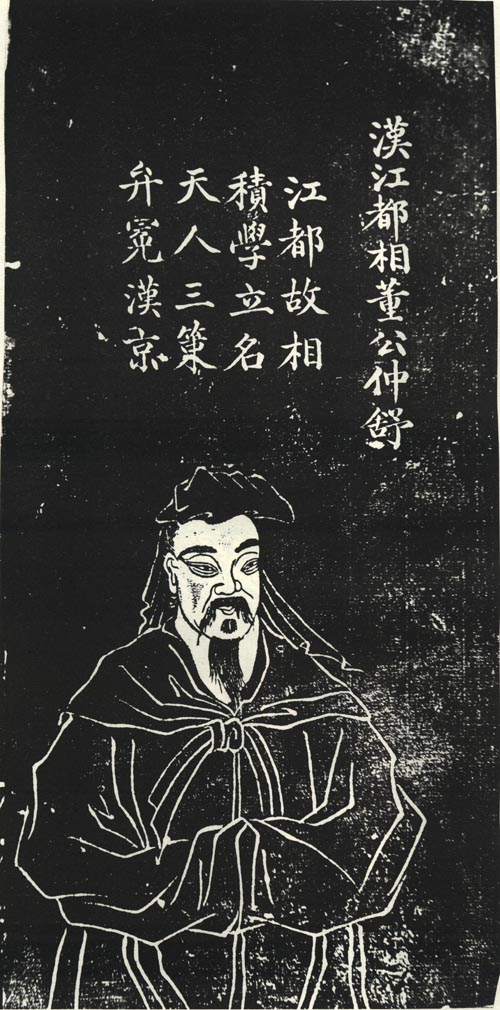
Dong Zhongshu
Dong Zhongshu (; 179–104 BC) was a Chinese philosopher, politician, and writer of the Han dynasty. He is traditionally associated with the promotion of Confucianism as the official ideology of the Chinese imperial state, favoring heaven worship over the tradition of cults celebrating the five elements. Enjoying great influence in the court in the last decades of his life, his adversary Gongsun Hong ultimately promoted his partial retirement from political life by banishing him to the Chancellery of Weifang, but his teachings were transmitted from there. Biography Dong was born in modern Hengshui, Hebei, in 179 BC. His birthplace is associated with Wencheng Township (, now located in Jing Country), so in the '' Luxuriant Dew of the Spring and Autumn Annals'' he is once mentioned as Lord Dong of Wencheng (). He entered the imperial service during the reign of Emperor Jing of Han and rose to high office under Emperor Wu of Han. His relationship with the emperor was unea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Shi (scholar)
Zhang Shi (1133–1181), also known by numerous Chinese courtesy name, courtesy names and various romanization of Chinese, romanizations, was a scholar during the Song Dynasty in China and key figure in Neo-Confucianism. Biography He was a native of Mianzhu (), Sichuan, and the son of a distinguished general and statesman named Zhang Jun (Song chancellor), Zhang Jun (1097–1164), who held the title of Duke of Yi (). After studying under Hu Hong, son of Hu Anguo, Zhang Shi commenced an official career and became aide-de-camp and secretary to his father. He held various posts, including prefect of Yanzhou Prefecture, Yanzhou, Yanzhou Prefecture, Yuanzhou, Jingjiang, and Jiangling County, Jiangling, eventually becoming senior compiler in the Youwen Hall (右文殿). In 1164 his father died, and Zhang Shi buried him according to his wish at the foot of Mount Heng (Hunan), Mount Heng in Hunan, remaining in seclusion near the grave for several years. While there he was visited in 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kong Anguo
Kong Anguo (; ca. 156 – ca. 74 BC), courtesy name Ziguo (), Kong Anguo was a Chinese classicist, philosopher, and politician of the Western Han dynasty of ancient China. A descendant of Confucius, he wrote the ''Shangshu Kongshi Zhuan'', a compilation and commentary of the "Old Text" '' Shangshu''. His work was lost, but a debated fourth-century forgery was officially recognized as a Confucian classic for over a millennium. Background Kong Anguo was a native of Qufu in Lu state, one of the many semi-autonomous kingdoms of the Western Han dynasty. He was the second son of Kong Zhong () and an eleventh-generation descendant of Confucius. He studied the ''Classic of Poetry'' and '' Shangshu'' (''Book of Documents'') from the famous Confucian scholars Shen Pei and Fu Sheng. Kong also served in the court of Emperor Wu of Han as the Grand Master of Remonstrance (). Old Text ''Shangshu'' According to tradition, the local ruler Prince Gong of Lu demolished a building of the Kong fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wishful Thinking
Wishful thinking is the formation of beliefs based on what might be pleasing to imagine, rather than on evidence, rationality, or reality. It is a product of resolving conflicts between belief and desire. Methodologies to examine wishful thinking are diverse. Various disciplines and schools of thought examine related mechanisms such as neural circuitry, human cognition and emotion, types of bias, procrastination, motivation, optimism, attention and environment. This concept has been examined as a fallacy. It is related to the concept of wishful seeing. Some psychologists believe that positive thinking is able to positively influence behavior and so bring about better results. This is called the " Pygmalion effect". Christopher Booker discussed wishful thinking in terms of "the fantasy cycle", which he described as "a pattern that recurs in personal lives, in politics, in history – and in storytelling." He added: "When we embark on a course of action which is unconscious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annping Chin
Annping Chin (; born 1950 in Taiwan) is an American historian and sinologist. She is a senior lecturer of history at Yale. Her fields of study include Confucianism, Taoism, and the Chinese intellectual tradition. Before Yale, she was on the faculty at Wesleyan University. Chin studied mathematics at Michigan State University and received her Ph.D. in Chinese thought from Columbia University. She lives in West Haven, Connecticut, with her husband Jonathan Spence until his death in 2021. She has two children, writer Mei Chin and video game designer Yar Woo. Chin was born in Taiwan in 1950 to a Manchu family from Liaoning. In 1962, she and her family moved to the U.S and have lived there ever since. Publications Chin has written or translated six books: *''The Analects'' (Penguin Classics, 2014), a new translation and commentary on the Analects of Confucius *''Confucius: A Life of Thought and Politics'' (Yale University Press, 2009) *''The Authentic Confucius: A Life of Though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li (Confucianism)
In traditional Confucian philosophy, is an ethical concept broadly translatable as 'rite'. According to Wing-tsit Chan, originally referred to religious sacrifices, but has come to mean 'ritual' in a broad sense, with possible translations including 'ceremony', 'ritual', 'decorum', 'propriety', and 'good form'. Hu Shih notes that has "even been equated with natural law" by some western scholars. In Chinese cosmology, refers to rites through which human agency participates in the larger order of the universe. One of the most common definitions of 'rite' is a performance transforming the invisible into the visible: through the performance of rites at appropriate occasions, humans make the underlying order visible. Correct ritual practice focuses and orders the social world in correspondence with the terrestrial and celestial worlds, keeping all three in harmony. Throughout the Sinosphere, was thought of as the abstract force that made government possible—along with the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Yun
''Ming yun'' () is a concept of the personal life and destiny in the Chinese folk religion. ''Ming'' means 'life', 'right', or 'destiny', and ''yun'' means 'circumstance' or 'individual choice'. ''Mìng'' is given and influenced by Tian 'heaven', akin to the Mandate of Heaven of monarchs as identified by Mencius. ''Ming yun'' is thus perceived as being both fixed, flexible, and open-ended.Lizhu, Na. 2013. p. 21 See also * ''Bao ying ''Bàoyìng'' ( zh, c=報應) is a concept of cosmic and moral reciprocity in the Chinese folk religion. It implies that people dwell in a moral universe, a universe that is kept ordained by mores, good actions, thus moral retribution is in fac ...'' * '' Yuanfen'' * '' Wu'' References Sources * Fan Lizhu, Chen Na. The Revival of Indigenous Religion in China'. Fudan University, 2013.{{China-reli-stub Concepts in Chinese folk religion Confucianism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |