|
Yantar-4K1
Yantar-4K1 ( meaning amber) was a type of Soviet reconnaissance satellite which supplemented and eventually replaced the Zenit spacecraft. It was the second satellite of the Yantar series and was managed by the Soviet military intelligence agency, the GRU. These satellites were in orbit for 45 days and photographed sites of interest using a film camera. It had its first test launch in May 1979. It was only in military service from 1982 to 1983, had the GRAU index 11F693 and was given the name Oktan (), meaning octane. Yantar-4K1 was a modification of Yantar-2K. It had a better camera, a Zhemchug-18, and was in orbit for 45 days rather than the 30 days of Yantar-2K. Other systems were the same as the Yantar-2K and both types of satellites were launched in the same period. Launches from Plesetsk had an inclination of 67.1-67.2 degrees, one from Baikonur had 64.9 degree orbits and one launch in April 1983 (Kosmos 1457) had an orbit of 70.4 degrees. Yantar-2K was replaced by the Ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yantar-4K2
Yantar ( meaning amber) were a series of Russian (previously Soviet Union, Soviet) reconnaissance satellites, which supplemented and eventually replaced the Zenit (satellite), Zenit spacecraft. Kosmos 2175, a Yantar-4K2 or ''Kobalt'' spacecraft, was the first satellite to be launched by the Russian Federation following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Yantar-Terilen was the first real-time digital system. Yantar satellites also formed the basis for the later Orlets, Resurs and Persona (satellite), Persona satellites. 179 have been launched, nine of which were lost in launch failures. All Yantar satellites were launched using the Soyuz-U carrier rocket until Kosmos 2480 in 2012 which was announced as the last launch of that rocket from Plesetsk Cosmodrome, Plesetsk. Subsequent launches used the modernized Soyuz-2.1a rocket. The last Yantar mission was Kosmos 2505, a Yantar-4K2M or ''Kobalt-M'', launched on 5 June 2015. Reconnaissance missions have been taken over by the Persona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yantar-2K
Yantar-2K ( meaning amber) was a type of Soviet reconnaissance satellite which supplemented and eventually replaced the Zenit spacecraft. It was the first satellite of the Yantar series and was managed by the Soviet military intelligence agency, the GRU. These satellites were in orbit for 30 days and photographed sites of interest using a film camera. Yantar-2K was proposed in 1967 and had its first test launch in May 1974. It was in military service from 1978 to 1983 and was given the name Feniks (), meaning phoenix. Equipment Yantar differed from Zenit in that it had to stay in orbit for a month unlike Zenit's 8–14 days. It also had 2 film return capsules, something it had in common with the US KH-7 GAMBIT reconnaissance satellite. Yantar had three parts: the aggregate/equipment module (AO - Agregatnyy Otsek), the instrument module (PO - Pribornnyy Otsek) and the special equipment module/special apparatus module (OSA - otsek spetsialnoy apparatury). The special equipment mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TsSKB
Rocket and Space Centre "Progress" (), commonly known as RKTs Progress (), is a Russian joint-stock company under Roscosmos. It is responsible for building and operating the Soyuz family of rockets, which serve as the primary launch vehicles for the Russian space program. The company traces its origins to the Soviet-era State Aviation Factory No. 1, established in Samara in 1941, which came to be known as "Progress." In 1974, the Central Specialized Design Bureau (TsSKB) was established to refine the R-7 rocket’s design. In 1996, these two entities merged to form the company TsSKB-Progress. History The company traces its origins to the Dux Factory, established in Moscow in 1894 as a small bicycle manufacturer. At the start of the 20th century, the Dux Factory transitioned from bicycles to producing cars and airships. By 1910, its focus shifted to aircraft manufacturing. During World War I, Dux supplied the Russian Army with various aircraft, including the Morane-Saulnier G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
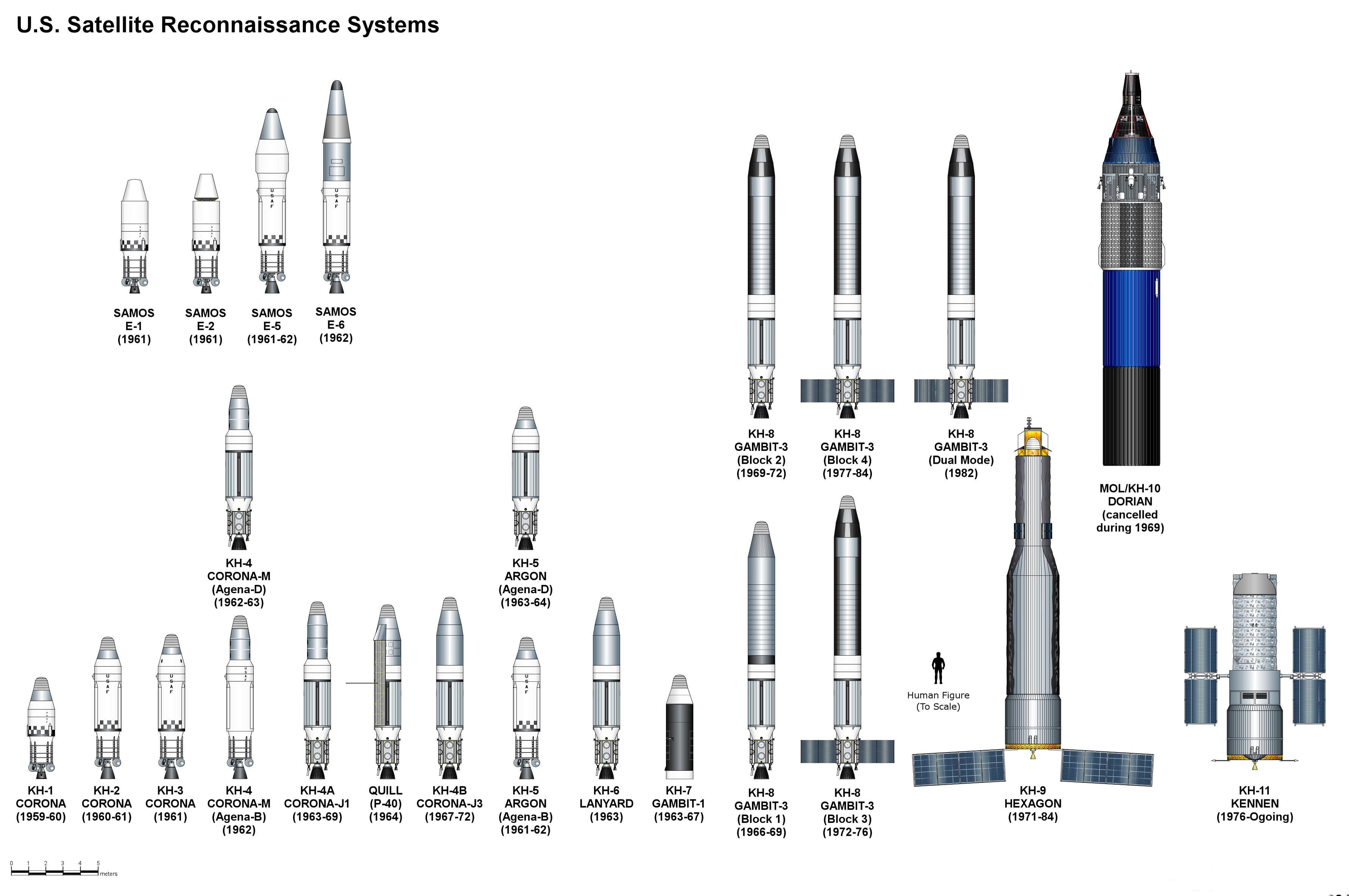
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, peaking in number at an altitude around , while the farthest in LEO, before medium Earth orbit (MEO), have an altitude of 2,000 km, about one-third of the Earth radius, radius of Earth and near the beginning of the Van Allen radiation belt#Inner belt, inner Van Allen radiation belt. The term ''LEO region'' is used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. No human spaceflights other than the lunar missions of the Apollo program (1968-1972) have gone beyond L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GRU (Soviet Union)
Main Intelligence Directorate ( rus, Главное разведывательное управление, Glavnoye razvedyvatel'noye upravleniye, ˈglavnəjə rɐzˈvʲɛdɨvətʲɪlʲnəjə ʊprɐˈvlʲenʲɪjə), abbreviated GRU ( rus, ГРУ, p=ɡɨ̞‿rɨ̞‿ˈu, ), was the foreign military intelligence agency of the General Staff of the Soviet Armed Forces until 1991. For a few months it was also the foreign military intelligence agency of the newly established Russian Federation until 7 May 1992 when it was dissolved and the GRU (Russian Federation), Russian GRU took over its activities. History The GRU's first predecessor in Russia formed on October 21, 1918 by secret order under the sponsorship of Leon Trotsky (then the civilian leader of the Red Army), signed by Jukums Vācietis, the first commander-in-chief of the Red Army (RKKA), and by Ephraim Sklyansky, deputy to Trotsky; it was originally known as the Registration Directorate (''Registrupravlenie'', or RU). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 1097
Cosmos generally refers to an orderly or harmonious system. Cosmos or Kosmos may also refer to: Space * ''Cosmos 1'', a privately funded solar sail spacecraft project * Cosmic Evolution Survey (COSMOS), a Hubble Space Telescope Treasury Project * Kosmos (rocket family), a series of Soviet/Russian rockets * Kosmos (satellite), a series of Soviet/Russian satellites * Universe, synonymous with cosmos * COSMOS field, an image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope Places * Cosmos, Minnesota, United States * Cosmos, Rio de Janeiro, a neighborhood of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil * Kosmos, South Africa, a village in North West Province * Kosmos, Washington, an unincorporated community in Washington, United States Books * ''Cosmos'' (serial novel), a 17-chapter serial novel published in ''Science Fiction Digest'' (later ''Fantasy Magazine'') in 1933 - 1934 * ''Cosmos'' (Humboldt book), a scientific treatise by Alexander von Humboldt * ''Cosmos'' (Gombrowicz novel), a 1965 novel by Witold Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenit (satellite)
Zenit (, , Zenith) was a series of military photoreconnaissance satellites launched by the Soviet Union The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ... between 1961 and 1994. To conceal their nature, all flights were given the public Kosmos designation. Description The basic design of the Zenit satellites was similar to the Vostok crewed spacecraft, sharing the return and service modules. It consisted of a spherical re-entry capsule in diameter with a mass of around . This capsule contained the camera system, its film, recovery beacons, parachutes and a destruct charge. In orbit, this was attached to a service module that contained batteries, electronic equipment, an orientation system and a liquid-fuelled rocket engine that would slow the Zenit for re-entry, before th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |