|
Yangan Masonic Hall
Yangan Masonic Hall is a heritage-listed masonic hall at 36 King Street, Yangan, Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. It was built from 1898 to 1957. It is also known as Yangan Masonic Temple and was formerly the Yangan School of Arts (not to be confused with present Yangan School of Arts). It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992. History The Yangan Masonic Hall was acquired by the Yangan Lodge as their meeting place in 1912. Erected c.1898 it was built as Yangan's first School of Arts when the town was developing as one of the Darling Downs' small but prosperous towns. The Yangan and Swanfels area (then named Loganvale) was explored by Allan Cunningham in 1827. In 1840 the Leslie brothers established Canning Downs, one of the station outposts being Heifer Creek whose first hut and stockyard were established at what became Yangan. The town developed to serve the industries of the Swanfels Valley: timber getting, sandstone quarrying, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangan, Queensland
Yangan is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Yangan had a population of 386 people. Geography The locality is traversed by Swan Creek, a tributary of the Condamine River. Sandstone is extracted from a quarry directly south of the town's centre from a property which fronts Swan Creek. History The district was known as Upper Swan Creek, but in 1887 took the name ''Yangan'' from its railway station. The name ''Yangan'' is reported to be an Aboriginal word meaning ''proceed'' or ''go away''. Swan Creek (No. 2) School opened on 27 May 1874. In 1878 it was renamed Swan Creek Upper State School. In 1887 it became Yangan State School. On Monday 15 May 1905 the Bishop of Brisbane St Clair Donaldson consecrated the new Anglican church, St Peter's. The architect was Conrad Dornbusch and the contractor was Mr J. Purcell. The final service was held on Palm Sunday 25 March 2018 and a deconsecration service was held on Saturday 21 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masonic Buildings Completed In 1898
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedestal
A pedestal (from French ''piédestal'', Italian ''piedistallo'' 'foot of a stall') or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In civil engineering, it is also called ''basement''. The minimum height of the plinth is usually kept as 45 cm (for buildings). It transmits loads from superstructure to the substructure and acts as the retaining wall for the filling inside the plinth or raised floor. In sculpting, the terms base, plinth, and pedestal are defined according to their subtle differences. A base is defined as a large mass that supports the sculpture from below. A plinth is defined as a flat and planar support which separates the sculpture from the environment. A pedestal, on the other hand, is defined as a shaft-like form that raises the sculpture and separates it from the base. An elevated pedestal or plinth that bears a statue, and which is raised from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornices
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon the architrave ("main beam") and is capped by the moldings of the cornice. A frieze can be found on many Greek and Roman buildings, the Parthenon Frieze being the most famous, and perhaps the most elaborate. This style is typical for the Persians. In interiors, the frieze of a room is the section of wall above the picture rail and under the crown moldings or cornice. By extension, a frieze is a long stretch of painted, sculpted or even calligraphic decoration in such a position, normally above eye-level. Frieze decorations may depict scenes in a sequence of discrete panels. The material of which the frieze is made of may be plasterwork, carved wood or other decorative me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handrail
A handrail is a rail that is designed to be grasped by the hand so as to provide safety or support. In Britain, handrails are referred to as banisters. Handrails are usually used to provide support for body or to hold clothings in a bathroom or similar areas. Handrails are commonly used while ascending or descending stairways and escalators in order to prevent injurious falls or to hold necessities. Handrails are typically supported by balusters or attached to walls. Similar items not covered in this article include bathroom handrails—which help to prevent falls on slippery, wet floors—other grab bars, used, for instance, in ships' galleys, and barres, which serve as training aids for ballet dancers. Guard rails and balustrades line drop-offs and other dangerous areas, keeping people and vehicles out. British specifications British Standard and British Standard Code of Practice are harmonized to European Normal (EN) series. Handrail height is set between . US s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracket (architecture)
A bracket is an architectural element: a structural or decorative member. It can be made of wood, stone, plaster, metal, or other media. It projects from a wall, usually to carry weight and sometimes to "...strengthen an angle". A corbel or console are types of brackets. In mechanical engineering a bracket is any intermediate component for fixing one part to another, usually larger, part. What makes a bracket a bracket is that it is intermediate between the two and fixes the one to the other. Brackets vary widely in shape, but a prototypical bracket is the L-shaped metal piece that attaches a shelf (the smaller component) to a wall (the larger component): its vertical arm is fixed to one (usually large) element, and its horizontal arm protrudes outwards and holds another (usually small) element. This shelf bracket is effectively the same as the architectural bracket: a vertical arm mounted on the wall, and a horizontal arm projecting outwards for another element to be attached o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
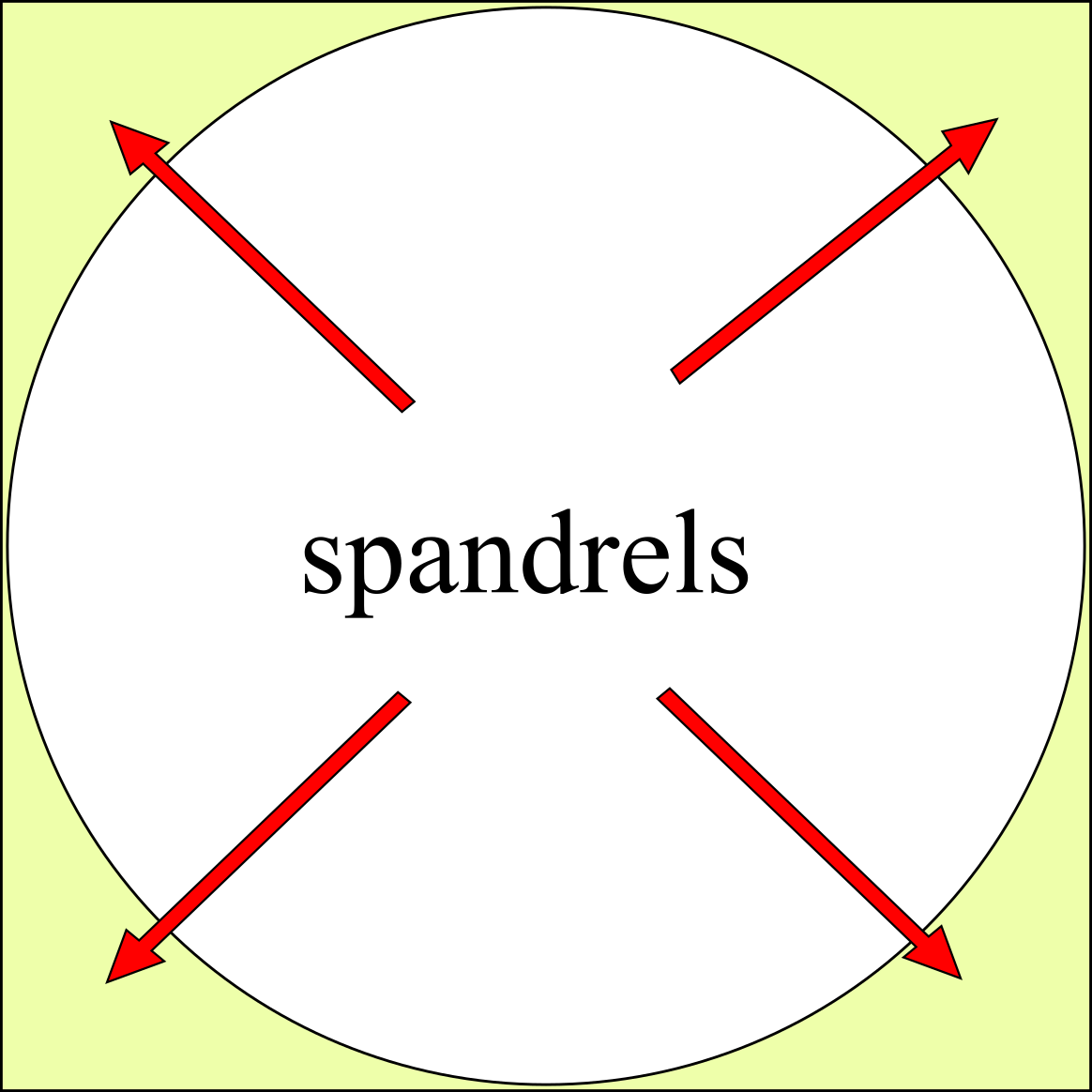
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation (engineering)
In engineering, a foundation is the element of a structure which connects it to the ground, transferring loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep. Foundation engineering is the application of soil mechanics and rock mechanics (geotechnical engineering Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. It uses the principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics for the solution of its respective engineering problems. It a ...) in the design of foundation elements of structures. Purpose Foundations provide the structure's stability from the ground: * To distribute the weight of the structure over a large area in order to avoid overloading the underlying soil (possibly causing unequal settlement). * To anchor the structure against natural forces including earthquakes, floods, droughts, frost heaves, tornadoes and wind. * To provide a level su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesthetic concerns. The term gable wall or gable end more commonly refers to the entire wall, including the gable and the wall below it. Some types of roof do not have a gable (for example hip roofs do not). One common type of roof with gables, the gable roof, is named after its prominent gables. A parapet made of a series of curves ( Dutch gable) or horizontal steps ( crow-stepped gable) may hide the diagonal lines of the roof. Gable ends of more recent buildings are often treated in the same way as the Classic pediment form. But unlike Classical structures, which operate through trabeation, the gable ends of many buildings are actually bearing-wall structures. Gable style is also used in the design of fabric structures, with varying d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porch
A porch (from Old French ''porche'', from Latin ''porticus'' "colonnade", from ''porta'' "passage") is a room or gallery located in front of an entrance of a building. A porch is placed in front of the facade of a building it commands, and forms a low front. Alternatively, it may be a vestibule, or a projecting building that houses the entrance door of a building. Porches exist in both religious and secular architecture. There are various styles of porches, many of which depend on the architectural tradition of its location. Porches allow for sufficient space for a person to comfortably pause before entering or after exiting a building, or to relax on. Many porches are open on the outward side with balustrade supported by balusters that usually encircles the entire porch except where stairs are found. The word "porch" is almost exclusively used for a structure that is outside the main walls of a building or house. Porches can exist under the same roof line as the rest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)