|
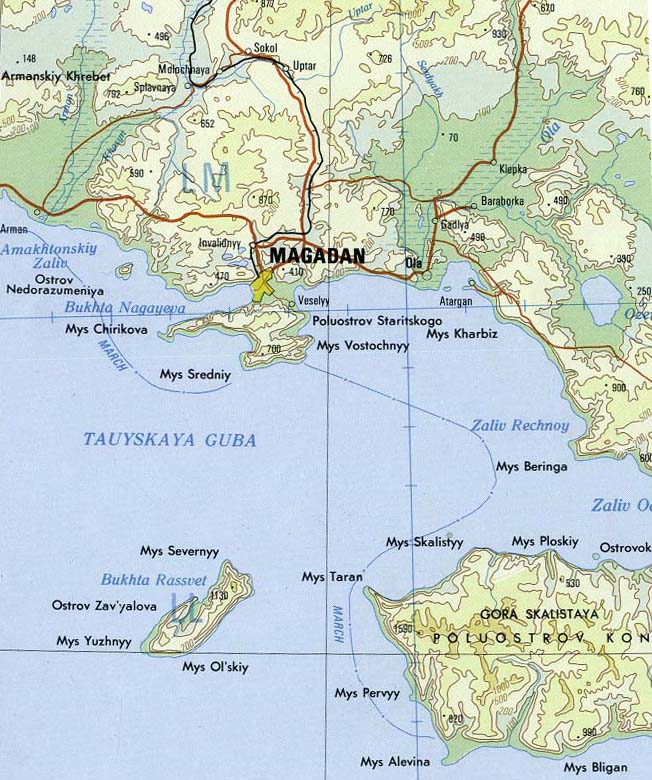
Yana (Sea Of Okhotsk)
The Yana () is a river in Magadan Oblast, Russian Far East. It has a drainage basin of . Tauisk village is located at the mouth of the river. The basin of the river includes tundra zones which provide a habitat for the brown bear, bird species such as the long-toed stint and the common snipe, as well as amphibians such as the Siberian salamander. Course The Yana river is formed at the confluence of the Right Yana (Правая Яна) and the Left Yana (Левая Яна) at an elevation of , from which point the river is long. Including the long Right Yana, which has its source in the eastern end of the Suntar-Khayata Range, the total length is . The shorter Left Yana has its source in the Kolyma Highlands. The Yana flows roughly southeastwards across mountainous terrain. In its last stretch it enters a floodplain among wetlands just east of the Taui River (Kava) and west of the Arman. Finally it flows into the Amakhton Bay, part of the Taui Bay of the Sea of Okhotsk.Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magadan Oblast
Magadan Oblast is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Russian Far East, Far East region of the country, and is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Magadan Oblast has a population of 136,085 (Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census), making it the least populated oblast and the third-least populated federal subject in Russia. Magadan is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center, capital of Magadan Oblast with the majority of the oblast's inhabitants living in the city itself. The coastline has a less severe climate than the interiors, although both are very cold for its latitude. It borders Chukotka Autonomous Okrug in the north, Kamchatka Krai in the east, Khabarovsk Krai in the south and the Sakha Republic in the west. The economy is primarily based on mining, particularly gold, silver and other non-ferrous metals. History Magadan Oblast was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberian Salamander
''Salamandrella keyserlingii'', the Siberian salamander, is a species of salamander found in Northeast Asia. It lives in wet woods and riparian groves. Distribution It is found primarily in Siberia east of the Sosva River and the Urals, in the East Siberian Mountains, including the Verkhoyansk Range, northeast to the Anadyr Highlands, east to the Kamchatka Peninsula and south into Manchuria, with outlying populations also in northern Kazakhstan and Mongolia, northeastern China, and on the Korean Peninsula. It is believed to be extirpated from South Korea. An isolated population exists on Hokkaidō, Japan, in the Kushiro Shitsugen National Park. A breeding ground of Siberian salamanders in Paegam, South Hamgyong, is designated North Korean natural monument #360. Description Adults are from 9.0 to 12.5 cm in length. Their bodies are bluish-brown in color, with a purple stripe along the back. Thin, dark brown stripes occur between and around the eyes, and also sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rivers Of Russia
Russia can be divided into a European and an Asian part. The dividing line is generally considered to be the Ural Mountains. The European part is drained into the Arctic Ocean, Baltic Sea, Black Sea, and Caspian Sea. The Asian part is drained into the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Notable rivers of Russia in Europe are the Volga (which is the longest river in Europe), Pechora, Don, Kama, Oka and the Northern Dvina, while several other rivers originate in Russia but flow into other countries, such as the Dnieper (flowing through Russia, then Belarus and Ukraine and into the Black Sea) and the Western Dvina (flowing through Russia, then Belarus and Latvia into the Baltic Sea). In Asia, important rivers are the Ob, the Irtysh, the Yenisei, the Angara, the Lena, the Amur, the Yana, the Indigirka, and the Kolyma. In the list below, the rivers are grouped by the seas or oceans into which they flow. Rivers that flow into other rivers are ordered by the proximit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sette-Daban & Suntar-Khayata ONC D-8
The Sette-Daban (, ) is a range of mountains in far North-eastern Russia. Administratively the range belongs partly to the Sakha Republic and partly to the Khabarovsk Krai of the Russian Federation. The area of the Sette-Daban is largely uninhabited. The R504 Kolyma Highway passes through the northern part of the range. The climate prevailing in the Sette-Daban is continental and severe. The average air temperature in January is a chilly . The average temperature in the river valleys may reach a maximum of in July. History In 1829, German physicist Georg Adolf Erman during a round-the-world (1828-1830) journey reported the existence of "Seven Ranges" (Sette Daban) between 135° and 140° E in the area of one of the upper tributaries of the Yudoma. The range was surveyed in 1934 by geologist Yuri Bilibin (1901—1952) together with mining engineer Evgeny Bobin (1897—1941) in the course of an expedition sent by the government of the Soviet Union. After conducting the first t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Earth
Google Earth is a web mapping, web and computer program created by Google that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satellite images, aerial photography, and geographic information system, GIS data onto a 3D globe, allowing users to see cities and landscapes from various angles. Users can explore the globe by entering addresses and coordinates, or by using a Computer keyboard, keyboard or computer mouse, mouse. The program can also be downloaded on a smartphone or Tablet computer, tablet, using a touch screen or stylus to navigate. Users may use the program to add their own data using Keyhole Markup Language and upload them through various sources, such as forums or blogs. Google Earth is able to show various kinds of images overlaid on the surface of the Earth and is also a Web Map Service client. In 2019, Google revealed that Google Earth covers more than 97 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arman (river)
The Arman (; ) is a river in Magadan Oblast, Russian Far East. It is long, with a drainage basin of . The name of the Arman originated in the Even language, Even language, meaning "spring" or "mashed ice". In the upper course there are stretches where the river is known as Artelnyi (Agchakh) and Akhchan.Армань - Water of Russia (in Russian) Course The river has its source in the Olsky Plateau of the Upper Kolyma Highlands, to the west of Atka, Russia, Atka at an elevation of about . It flows roughly southwards across a mountainous area. In its last stretch is descends to a floodplain with wetlands to the west of Magadan, where it flows across the Arman Range. Further downstream it is joined by the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taui River
The Taui (), also known as Kava () for part of its course, is a river in Khabarovsk Krai and Magadan Oblast, Russian Far East. It has a drainage basin of . The river is a spawning ground for salmon and is part of the Magadan Nature Reserve. Its last stretch is navigable. Course The Taui river, as the Kava, is formed at an elevation of at the confluence of rivers Rasava and Lozovaya flowing from the Kheidzhan Range, Upper Kolyma Highlands. The Taui flows first southeastwards and then roughly eastwards along the Kava-Taui Plain (Кава-Тауйская равнина), a wide floodplain. In its last stretch it enters an area of wetlands. Finally it flows into the Amakhton Bay, part of the Taui Bay of the Sea of Okhotsk. Its mouth lies west of the Arman lagoon and just southwest of the mouth of the Yana.Google Earth The river freezes before mid October and stays frozen until mid May. The Kheidzhan Range separates the Taui basin from the Inya basin to the west. The main tribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrology), discharge.Goudie, A. S., 2004, ''Encyclopedia of Geomorphology'', vol. 1. Routledge, New York. The soils usually consist of clays, silts, sands, and gravels deposited during floods. Because of regular flooding, floodplains frequently have high soil fertility since nutrients are deposited with the flood waters. This can encourage farming; some important agricultural regions, such as the Nile and Mississippi Basin, Mississippi Drainage basin, river basins, heavily exploit floodplains. Agricultural and urban regions have developed near or on floodplains to take advantage of the rich soil and freshwater. However, the Flood risk, risk of inundation has led to increasing efforts to Flood control, control flooding. Formation Most floodplai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolyma Highlands
Kolyma (, ) or Kolyma Krai () is a historical region in the Russian Far East that includes the basin of Kolyma River and the northern shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, as well as the Kolyma Mountains (the watershed of the two). It is bounded to the north by the East Siberian Sea and the Arctic Ocean, and by the Sea of Okhotsk to the south. Kolyma Krai was never formally defined and over time it was split among various administrative units. , it consists roughly of the Magadan Oblast, north-eastern areas of Yakutia, and the Bilibinsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The area, part of which is within the Arctic Circle, has a subarctic climate with very cold winters lasting up to six months of the year. Permafrost and tundra cover a large part of the region. Average winter temperatures range from (even lower in the interior), and average summer temperatures, from . There are rich reserves of gold, silver, tin, tungsten, mercury, copper, antimony, coal, oil, and peat. Twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suntar-Khayata Range
Suntar-Khayata Range (, ) is a granite mountain range rising along the border of the Sakha Republic in the north with Amur Oblast and Khabarovsk Krai in the south. The R504 Kolyma Highway passes through the northern part of the range by Kyubeme. Geography The Suntar-Khayata is approximately 450–550 km long and 60 km wide. high Mus-Khaya Mountain, located in the Sakha Republic, is the highest point of the range. Berill Mountain, at is the highest summit in Khabarovsk Krai. Mount Khakandya (Гора Хакандя) is an ultra-prominent peak that is high. The Suntar-Khayata Range is geographically a southeastern prolongation of the Verkhoyansk Range. Until mid 20th century it was treated as a separate range, together with the Skalisty Range, highest point , and the Sette Daban, highest point , to the southwest. The Yudoma-Maya Highlands are located to the south of the range [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |