|
Yan (Three Kingdoms)
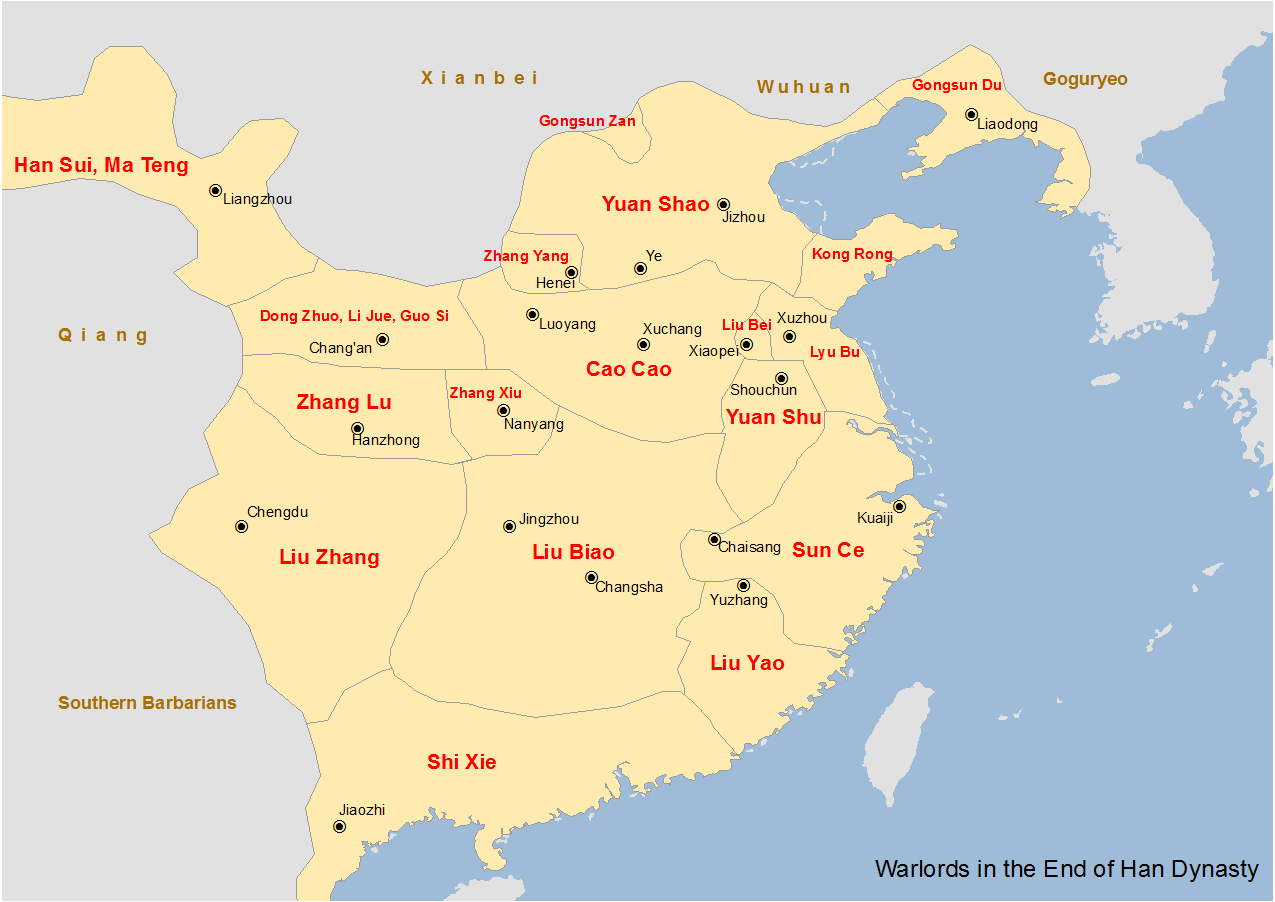
Yan () was a Chinese kingdom that existed from July 237 to September 238 CE in the Liaodong Peninsula during the Three Kingdoms period. Its predecessor was an independent regime ruled by Gongsun Du and his son Gongsun Kang from 190 to 237. Though it only claimed independence in 237, historians such as Wang Zhongshu and Hou Tao consider it to be a de facto independent regime from when Gongsun Du established his rule in Liaodong in 190. Although it existed during the Three Kingdoms period, it is not counted as one of the eponymous three kingdoms: Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. Nevertheless, writers such as Kang Youwei consider it to be a "fourth country". Predecessors Gongsun Du Gongsun Du's father Gongsun Yan (公孫延) lived in Xuantu Commandery where Gongsun Du became minister in 170. Although he was dismissed from his post, he became administrator of Liaodong Commandery in 190 or 189 on the recommendation of Dong Zhuo. Gongsun Du established a monarchial rule and complet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Wu
Wu (Chinese language, Chinese: 吳; pinyin: ''Wú''; Middle Chinese *''ŋuo'' < Eastern Han Chinese: ''*ŋuɑ''), known in historiography as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu, was a Dynasties of China, dynastic state of China and one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the Three Kingdoms period. It previously existed from 220 to 222 as a vassal kingdom nominally under Cao Wei, its rival state, but declared complete independence in November 222. It was elevated to an empire in May 229 after its founding ruler, Sun Quan (Emperor Da), declared himself Emperor of China, emperor. The name "Wu" was derived from the place it was based in—the Jiangnan (Yangtze River Delta) region, which was also historically known as "Wu (region), Wu". It was called "Dong Wu" ("Eastern Wu") or "Sun Wu" by historians to distinguish it from other Chinese historical states with similar names in that region, such as the Wu (state), Wu state in the Spring and Autumn period and the Wuyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongliao Commandery
Zhongliao Township Glossary of Names for Administrative Divisions. Ministry of the Interior. 26 March 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2017. is a rural township in , . Geography |
Yuan Shang
Yuan Shang (died December 207), courtesy name Xianfu, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was the third son and successor of the warlord Yuan Shao. In the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', Yuan Shang was described as "strong but arrogant", and he was his father's favourite son. Usurpation of Yuan Shao's legacy It is documented in the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' and ''Dianlüè'' that Yuan Shao favoured Yuan Shang due to his good looks, and he preferred Yuan Shang to be his choice for succession. However, Yuan Shao was never able to finalise on his decision regarding who should succeed him as the Governor of Ji Province. Following Yuan Shao's death in 202, many of his followers suggested that his eldest son, Yuan Tan, should assume control of the Yuan family's assets, as tradition dictated, but Yuan Shang and his supporters would not yield. Apprehensive that Yuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Shao
Yuan Shao (, ; died 28 June 202), courtesy name Benchu (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred towards the end of the Han dynasty. He was also an elder half-brother of Yuan Shu, a warlord who controlled the Huai River region, though the two were not on good terms with each other. One of the most powerful warlords of his time, Yuan Shao spearheaded a Campaign against Dong Zhuo, coalition of warlords against Dong Zhuo, who held Emperor Xian of Han, Emperor Xian hostage in the imperial capital, Luoyang, but failed due to internal disunity. In 200, he launched a campaign against his rival Cao Cao but was defeated at the Battle of Guandu. He died of illness two years later in Ye (ancient China), Ye. His eventual failure despite his illustrious family background and geographical advantages was commonly blamed on his indecisiveness and inabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daifang Commandery
The Daifang Commandery was an administrative division established by the Chinese Han dynasty on the Korean Peninsula between 204 and 220. It was conquered by Goguryeo in 314. History Gongsun Kang, a warlord in Liaodong, separated the southern half from the Lelang commandery and established the Daifang commandery sometime between 204 and 220 to make administration more efficient. He controlled southern natives with Daifang instead of Lelang. In 238 under the order of Emperor Ming of Cao Wei, Sima Yi defeated the Gongsun family and annexed Liaodong, Lelang and Daifang to Wei. A dispute over the control of southern natives caused their revolt. The armies of Lelang and Daifang eventually stifled it. Daifang Commandery was inherited by the Jin dynasty. Due to the bitter civil War of the Eight Princes, Jin became unable to control the Korean peninsula at the beginning of the 4th century. Zhang Tong (張統) broke away from Jin in Lelang and Daifang. After Luoyang, the capital of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lelang Commandery
The Lelang Commandery was a Commandery (China), commandery of the Han dynasty established after it had conquered Wiman Joseon in 108 BC and lasted until Goguryeo conquered it in 313. The Lelang Commandery extended the rule of the Four Commanderies of Han as far south as the Han River (Korea), Han River in present-day South Korea. South Korean scholars have described its administrative areas as being limited to the Pyongan and Hwanghae regions, whose southern bounds lie roughly 75 miles north of the Han River. History Han dynasty In 108 BC, Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty conquered the area under Ugeo of Gojoseon, King Ugeo, a grandson of Wiman of Gojoseon, King Wiman. The Emperor set up Lelang, Lintun Commandery, Lintun, Xuantu Commandery, Xuantu and Zhenfan Commandery, Zhenfan, known as the Four Commanderies of Han in the northern Korean peninsula and Liaodong peninsula. The ''Book of Han'' records Lelang belonged to Youzhou, located in northwestern Gojoseo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalu River
The Yalu River () or Amnok River () is a river on the border between China and North Korea. Together with the Tumen River to its east, and a small portion of Paektu Mountain, the Yalu forms the border between China and North Korea. Its valley has been the scene of several military conflicts in the past centuries. It borders North Korea to the south and China to the north. Name The Chinese name ''Yalu'' ("duck-green") was first attested during the Tang dynasty. According to the '' Tongdian'' (8th century), the river was named after its color, which resembled that of a mallard's head. The Korean name "Amnok" follows the Sino-Korean reading of the same name. In ancient times, the river was known as ''Peishui'' (''Paesu'', 浿水) or ''Mazishui'' (''Majasu'', 馬訾水). Historically, it was also known by the Korean name of ''Arinarye'' (아리나례강, 阿利那禮江). ''Ari'', a word from Old Korean used to refer to the 'spirituality (신령성; 神靈性) of the sun'. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jilin
) , image_skyline = Changbaishan Tianchi from western rim.jpg , image_alt = , image_caption = View of Heaven Lake , image_map = Jilin in China (+all claims hatched).svg , mapsize = 275px , map_alt = Map showing the location of Jilin Province , map_caption = Map showing the location of Jilin Province , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = China , named_for = from ''girin ula'', a Manchu language, Manchu phrase meaning "along the river" , seat_type = Capital , seat = , seat1_type = , seat1 = , parts_type = Divisions , parts_style = para , p1 = 9 Prefectures of China, prefectures , p2 = 60 Counties of China, counties , p3 = 1006 Townships of China, townships , government_type = Provinces of China, Province , governing_body = Jilin Provinci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji'an, Jilin
Ji'an (; formerly ) is a county-level city in the southwestern part of Jilin province, People's Republic of China. It is administered by the prefecture-level city of Tonghua and is the southernmost county-level division in the province. Ji'an has an area of and a population of approximately 230,000. The city was given its current status in 1988. Ji'an is separated from Manpo, Chagang Province, North Korea by the Yalu River; it has an international border running . History Archaeological excavations in the Ji'an area have unearthed several Yemaek sites along the Amnok River and its tributary the Hunjiang, which belong to the regional Neolithic and Bronze ages. After the fall of Wiman Joseon to the Han dynasty in 108 BCE, Ji'an was part of Goguryeo County under the administration of Xuantu Commandery. In 3 CE, the second ruler of Goguryeo, King Yuri, moved the state's capital to Gungnae (modern Ji'an) and established the mountain fortress Hwando nearby to defend it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hwando Mountain Fortress
Hwando () is a mountain fortress of the ancient Korean kingdom of Goguryeo, built to protect Goguryeo's second capital, Gungnae. It is located in present-day Ji'an city of the province of Jilin, China. The fortress is located 2.5 km west of Ji'an, Jilin province in Northeast China, near the North Korean border. It is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Capital Cities and Tombs of the Ancient Koguryo Kingdom, together with nearby Gungnae City and the Ohnyeosan City, because of its historical importance and exceptional architecture. History In 3 CE, King Yuri of Goguryeo moved the capital to Gungnae Fortress, and built the Wina Rock fortress. (page 18) of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sansang Of Goguryeo
King Sansang (died 227, r. 196–227 ) was the 10th ruler of Goguryeo, the northernmost of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. He was the third son of the eighth king Sindae and the younger brother of the ninth king Gogukcheon, who died without an heir. Family *Father: King Sindae () *Consort and their respective issue(s): #''Queen'', of the U clan (); daughter of U So () – No issue. #A woman from Jutong village () ## Prince Uwigeo () Background and rise to the throne Upon Gogukcheon's death, his queen Lady U supported Sansang's claim and had him placed on the throne. She then became Sansang's queen.Pae-yong Yi, 《Women in Korean History 한국 역사 속의 여성들》, Ewha Womans University Press, 2008. , pp.122-123 This indicates that the custom of Levirate marriage was still practiced in Goguryeo, but also demonstrated Lady U's power in court. Balgi, older brother to Sansang, led a rebel force attacking the capital, gaining military support of Chinese faction. Sansang h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gongsun Gong
Gongsun Gong ( zh, t=公孫恭, p=Gōngsūn Gōng, ; ) was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and early Three Kingdoms. He was a son of Gongsun Du and a younger brother of Gongsun Kang, who both consecutively served as the Administrators of Liaodong Commandery in northeastern China. In 207, he advised his brother Gongsun Kang to execute the warlords Yuan Xi and Yuan Shang , who had fled to Liaodong Commandery for shelter after their defeat by the warlord Cao Cao. Gongsun Kang did so and sent the Yuans' heads to Cao Cao. After Gongsun Kang died, Gongsun Gong succeeded his brother as the new Administrator of Liaodong Commandery because Gongsun Kang's sons were too young at the time to assume the office. Gongsun Gong remained as a vassal of the Eastern Han dynasty and later pledged allegiance to the Cao Wei state, which replaced the Eastern Han dynasty in 220. In the same year, the Wei emperor Cao Pi granted Gongsun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |