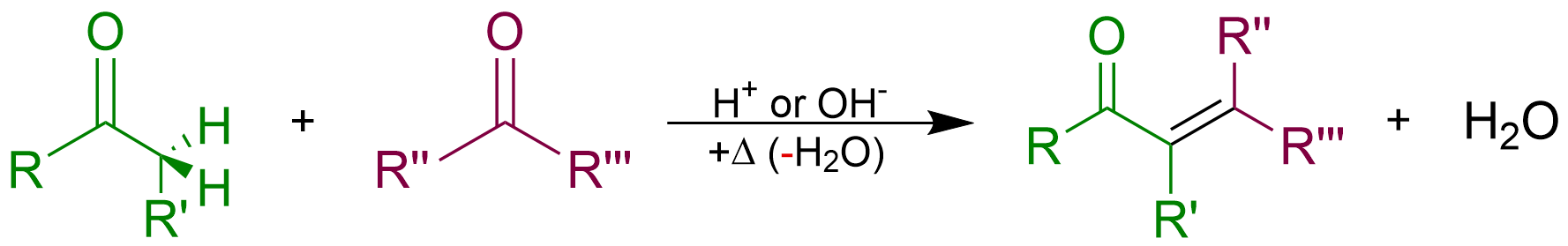|
Yamaguchi Esterification
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride (TCBC, Yamaguchi reagent) to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester. It was first reported by Masaru Yamaguchi ''et al.'' in 1979.Kawanami, Y.; Dainobu, Y.; Inanaga, J.; Katsuki, T.; Yamaguchi, M. "Synthesis of Thiol Esters by Carboxylic Trichlorobenzoic Anhydrides". ''Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn.'' 1981, ''54'', 943–944. It is especially useful in the synthesis of macro-lactones and highly functionalised esters. Reaction mechanism The aliphatic carboxylate adds to the carbonyl carbon of Yamaguchi reagent, forming a mixed anhydride, which is then attacked by DMAP regioselectively at the less hindered carbon, producing acyl-substituted DMAP. This highly electrophilic agent is then attacked by the alcohol to form the product ester. The ''in situ'' formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regioselectivity
In organic chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of chemical bonding or breaking in one direction over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a strong base will abstract from an organic molecule, or where on a substituted benzene ring a further substituent will be added. A specific example is a halohydrin formation reaction with 2-propenylbenzene: : Because of the preference for the formation of one product over another, the reaction is selective. This reaction is regioselective because it selectively generates one constitutional isomer rather than the other. Various examples of regioselectivity have been formulated as rules for certain classes of compounds under certain conditions, many of which are named. Among the first introduced to chemistry students are Markovnikov's rule for the addition of protic acids to alkenes, and the Fürst-Plattner rule for the addition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reactions
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolide
Macrolides are a class of mostly natural products with a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but has since been used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are a diverse group with many members of very different properties: * Macrolides with 14-, 15-, or 16-membered rings and two attached sugar molecules are antibiotics that bind to bacterial ribosomes, the key representative being erythromycin. The term "macrolide antibiotics" tend to refer to just this class. * Some macrolides with very large (20+ membered) rings are immunosuppresants, the prototypical one being rapamycin. * Some 23-membered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsunobu Reaction
The Mitsunobu reaction is an organic reaction that converts an alcohol into a variety of functional groups, such as an ester, using triphenylphosphine and an azodicarboxylate such as diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD) or diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (DIAD). Although DEAD and DIAD are most commonly used, there are a variety of other azodicarboxylates available which facilitate an easier workup and/or purification and in some cases, facilitate the use of more basic nucleophiles. It was discovered by Oyo Mitsunobu (1934–2003). In a typical protocol, one dissolves the alcohol, the carboxylic acid, and triphenylphosphine in tetrahydrofuran or other suitable solvent (e.g. diethyl ether), cool to 0 °C using an ice-bath, slowly add the DEAD dissolved in THF, then stir at room temperature for several hours. The alcohol reacts with the phosphine to create a good leaving group then undergoes an inversion of stereochemistry in classic SN2 fashion as the nucleophile displaces it. A c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation Macrolactone V1-Seite001
Formation may refer to: Linguistics * Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes * Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes Mathematics and science * Cave formation or speleothem, a secondary mineral deposit formed in a cave * Class formation, a topological group acting on a module satisfying certain conditions * Formation (group theory), a class of groups that is closed under some operations * Formation constant, an equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex in solution * Formation enthalpy, standard heat of formation of a compound * Formation (group theory), a class of groups * Formation (geology), a formally named rock stratum or geological unit * Formation of rocks, how rocks are formed * Formation and evolution of the Solar System, history of the Solar System * Rock formation, an isolated, scenic, or spectacular surface rock outcrop * Vegetation formation, a concept used to classify vegetation communities Milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaguchi Formation Mixed Anhydrid V1-Seite001
Yamaguchi may refer to: People *Yamaguchi (surname), the 14th most popular Japanese surname, including a list of people. Places *Yamaguchi Prefecture, the westernmost prefecture of Honshū island of Japan **Yamaguchi (city), capital of Yamaguchi Prefecture *** Yamaguchi Station (Yamaguchi), a JR West railway station, located in the center of Yamaguchi-shi ***Shin-Yamaguchi Station, a railway station in Yamaguchi-shi (Sanyō Shinkansen line) *Yamaguchi, Nagano, a village in Nagano Prefecture Fiction *Kumiko "Yankumi" Yamaguchi, the character played by Yukie Nakama in ''Gokusen'', a Japanese TV show *Yamaguchi-sensei, a doctor in the manga/anime series '' Fighting Spirit'' *U.S.S. ''Yamaguchi'', an ''Ambassador Class'' Federation starship in the ''Star Trek'' franchise *Yamaguchi Digital Pets, a fictional digital pets company mentioned in ''Fanboy & Chum Chum'' *Yamaguchi Tadashi, a member of the Karasuno volleyball club in the manga/anime series ''Haikyu!!'' Other uses * Yamaguch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophilic
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons. Electrophiles mainly interact with nucleophiles through addition and substitution reactions. Frequently seen electrophiles in organic syntheses include cations such as H+ and NO+, polarized neutral molecules such as HCl, alkyl halides, acyl halides, and carbonyl compounds, polarizable neutral molecules such as Cl2 and Br2, oxidizing agents such as organic peracids, chemical species that do not satisfy the octet rule such as carbenes and radicals, and some Lewis acids such as BH3 and DIBAL. Organic chemistry Addition of halogens These occur between alkenes and electrophiles, often halogens as in halogen addition reactions. Common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters. They are derived from the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids by esterification. They can be saturated or unsaturated. Lactones are formed by lactonization, the intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids. Nomenclature Greek alphabet#Letters, Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size. Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH and the -COOH groups along said backbone. The first carbon atom after the carbon in the -COOH group on the parent compound is labelled α, the second will be labeled β, and so forth. Therefore, the prefixes also indicate the size of the lactone ring: α-lactone = 3-membered ring, β-lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated (in which all the C-C bonds are single, requiring the structure to be completed, or 'saturated', by hydrogen) like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds, whether straight or branched, and which contain no rings of any type, are always aliphatic. Cyclic compounds can be aliphatic if they are not aromatic. Structure Aliphatics compounds can be saturated, joined by single bonds (alkanes), or unsaturated, with double bonds ( alkenes) or triple bonds ( alkynes). If other elements ( heteroatoms) are bound to the carbon chain, the most common being oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and chlorine, it is no longer a hydrocarbon, and therefore no longer an aliphatic compound. However, such compounds may still be referred to as aliph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaguchi Lactonization
Yamaguchi may refer to: People *Yamaguchi (surname), the 14th most popular Japanese surname, including a list of people. Places *Yamaguchi Prefecture, the westernmost prefecture of Honshū island of Japan **Yamaguchi (city), capital of Yamaguchi Prefecture *** Yamaguchi Station (Yamaguchi), a JR West railway station, located in the center of Yamaguchi-shi ***Shin-Yamaguchi Station, a railway station in Yamaguchi-shi (Sanyō Shinkansen line) *Yamaguchi, Nagano, a village in Nagano Prefecture Fiction *Kumiko "Yankumi" Yamaguchi, the character played by Yukie Nakama in ''Gokusen'', a Japanese TV show *Yamaguchi-sensei, a doctor in the manga/anime series '' Fighting Spirit'' *U.S.S. ''Yamaguchi'', an ''Ambassador Class'' Federation starship in the ''Star Trek'' franchise *Yamaguchi Digital Pets, a fictional digital pets company mentioned in ''Fanboy & Chum Chum'' *Yamaguchi Tadashi, a member of the Karasuno volleyball club in the manga/anime series ''Haikyu!!'' Other uses * Yamaguch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |