|
Yaakov Nahmias
Yaakov "Koby" Nahmias is an Israeli biomedical engineer and entrepreneur. Nahmias is a professor at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and an affiliated member of the NIH-funded BioMEMS Resource Center at Massachusetts General Hospital. Nahmias is the founding director of the Alexander Grass Center for Bioengineering. He is a co-founder of Israel’s BioDesign Medical Innovation program, recently listed as a major reason for Boston Scientific's continued investment in Israel. In 2014, he won the Rappaport Prize for Biomedical Sciences for his “groundbreaking work on liver tissue engineering” and the “development of nanotechnology therapies for the treatment of diabetes”. Nahmias edited a book titled ''Microdevices in Biology and Medicine'', and is currently serving as a technology consultant for L’Oreal, and a member of the European Research Council panel for applied life sciences and biotechnology. In 2018, Nahmias became the co-founder and chief scientific office ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( or , ; ), sometimes rendered as Tel Aviv-Jaffa, and usually referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the Gush Dan metropolitan area of Israel. Located on the Israeli Mediterranean coastline and with a population of 495,600, it is the economic and technological center of the country and a global high tech hub. If East Jerusalem is considered part of Israel, Tel Aviv is the country's second-most-populous city, after Jerusalem; if not, Tel Aviv is the most populous city, ahead of West Jerusalem. Tel Aviv is governed by the Tel Aviv-Yafo Municipality, headed by Mayor Ron Huldai, and is home to most of Israel's foreign embassies. It is a beta+ world city and is ranked 53rd in the 2022 Global Financial Centres Index. Tel Aviv has the third- or fourth-largest economy and the largest economy per capita in the Middle East. Tel Aviv is ranked the 4th top global startup ecosystem hub. The city currently has the highest cost of living in the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Future Meat Technologies
Believer Meats, from 2018 to 2022 known as Future Meat Technologies, or Future Meat for short, is a biotechnology firm, which produces cultured meat from chicken cells and is working on cultured lamb and beef. Based in USA, its main office is located in Chicago, while its primary production facility is operating in Wilson, NC. Future Meat Technologies mainly seeks to supply hardware and cell lines to manufacturers of cultured meat rather than directly selling food products to consumers. In November 2022, Future Meat Technologies rebranded to Believer Meats. History Future Meat Technologies was founded in 2018 by Yaakov Nahmias, a biomedical engineering professor of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He became Future Meat's chief scientific officer. The company was founded in Israel and built a 10,700 square-foot facility in Rehovot, just south of Tel Aviv. The company presented its cultured meat prototype to the public in 2019. In October 2019, it raised $14 million to bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Medical School Faculty
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. Its influence, wealth, and rankings have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Harvard was founded and authorized by the Massachusetts General Court, the governing legislature of colonial-era Massachusetts Bay Colony. While never formally affiliated with any denomination, Harvard trained Congregational clergy until its curriculum and student body were gradually secularized in the 18th century. By the 19th century, Harvard emerged as the most prominent academic and cultural institution among the Boston elite. Following the American Civil War, under Harvard president Charles William Eliot's long tenure from 1869 to 1909, Harvard developed multiple professional schools, which transforme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Minnesota Alumni
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eden Prairie
Eden Prairie is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States. It had a population of 64,198 at the 2020 census, making it the 16th-largest city in Minnesota. The city is adjacent to the north bank of the Minnesota River, upstream from its confluence with the Mississippi River, about southwest of downtown Minneapolis. Set in the Twin Cities' outer suburbs, the community was designed as a mixed-income city model and is home to numerous commercial firms, including the headquarters of SuperValu, C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Winnebago Industries, Starkey Hearing Technologies, Lifetouch Inc., SABIS, and MTS Systems Corporation. It contains the Eden Prairie Center mall and is the hub of SouthWest Transit, providing public transportation to three adjacent suburbs. The television stations KMSP and WFTC are based in Eden Prairie. The nonprofit news organizatioEden Prairie Local News(EPLN) also serves the community. The area features numerous municipal and regional parks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringenin
Naringenin is a flavanone from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is commonly found in citrus fruits, especially as the predominant flavonone in grapefruit. The fate and biological functions of naringenin in vivo are unknown, remaining under preliminary research, as of 2024. High consumption of dietary naringenin is generally regarded as safe, mainly due to its low bioavailability. Taking dietary supplements or consuming grapefruit excessively may impair the action of anticoagulants and increase the toxicity of various prescription drugs. Similar to furanocoumarins present in citrus fruits, naringenin may evoke CYP3A4 suppression in the liver and intestines, possibly resulting in adverse interactions with common medications. Structure Naringenin has the skeleton structure of a flavanone with three hydroxy groups at the 4′, 5, and 7 carbons. It may be found both in the aglycol form, naringenin, or in its glycosidic form, naringin, which has the addition of the disac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VLDL
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein, LDL, low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. VLDL is assembled in the liver from triglycerides, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. VLDL is converted in the bloodstream to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). VLDL particles have a diameter of 30–80 nanometers (nm). VLDL transports endogeny, endogenous products, whereas chylomicrons transport exogenous (dietary) products. In the early 2010s both the lipid composition and protein composition of this lipoprotein were characterised in great detail. Physical properties Very-low-density lipoprotein size is variable, with diameters ranging from approximately 35 to 70&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
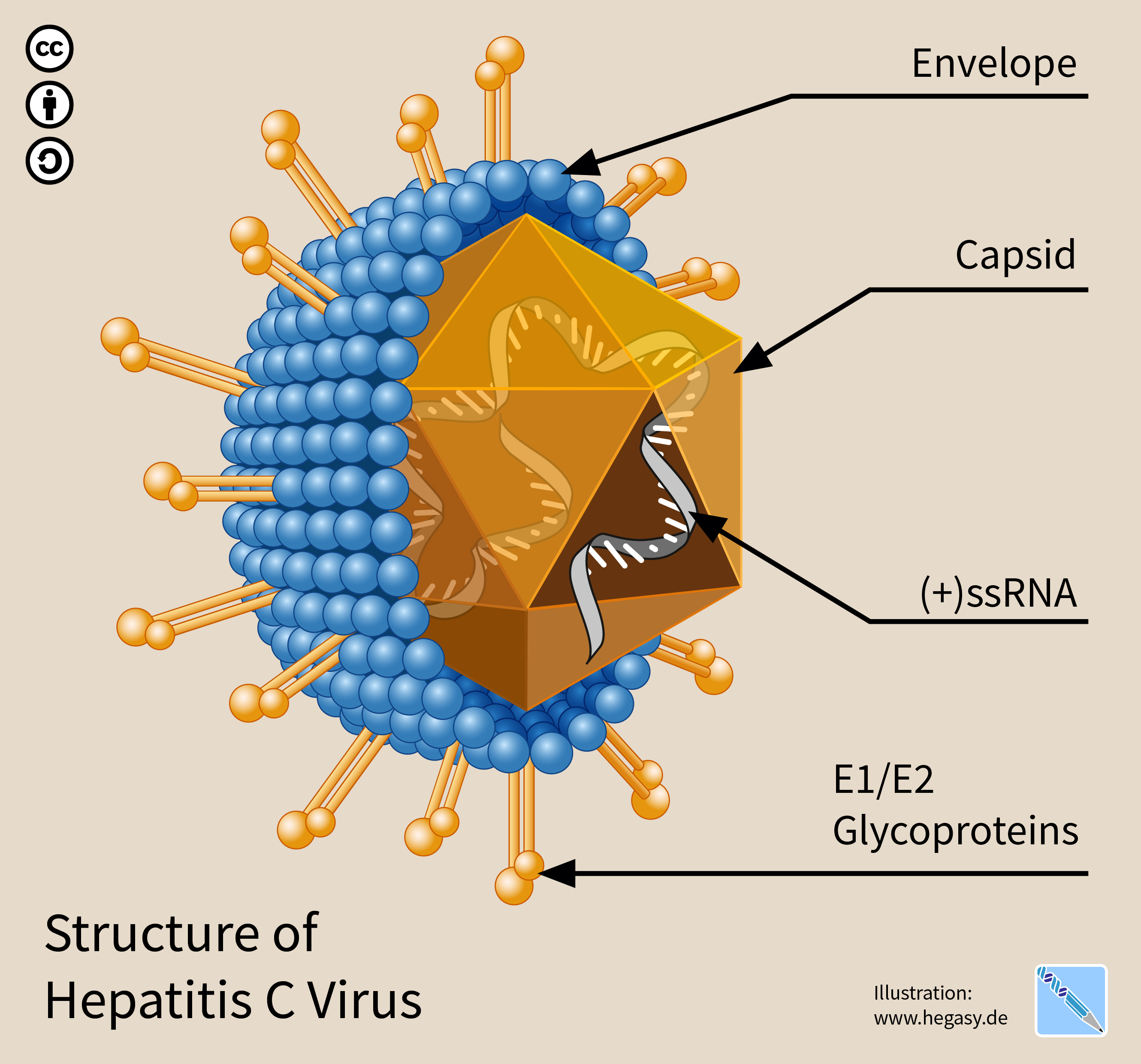
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus '' Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Yarmush
Martin (Maish) L. Yarmush (born October 8, 1952 in Brooklyn, New York) is an academic, American scientist, physician, and engineer known for his work in biotechnology and bioengineering. His faculty career began in 1984 at MIT in the Department of Chemical Engineering as a Principal Research Associate (Associate Research Professor) and Lucille P. Markey Scholar in Biomedical Science. In 1988 he joined Rutgers University as Professor of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering and a member of the Center of Advanced Biotechnology and Medicine. In 1995, he returned to the Boston area to serve as the Helen Andrus Benedict Professor of Surgery and Bioengineering in the Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology, and to establish the Center for Engineering in Medicine (now the Center for Engineering in Medicine and Surgery) at the Harvard Affiliated Teaching Hospitals. In 2007 he returned to Rutgers to hold the Paul and Mary Monroe Endowed Chair in Science and Engineering and serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell (biology), cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple biological organisation, levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including scientific method, observation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |