|
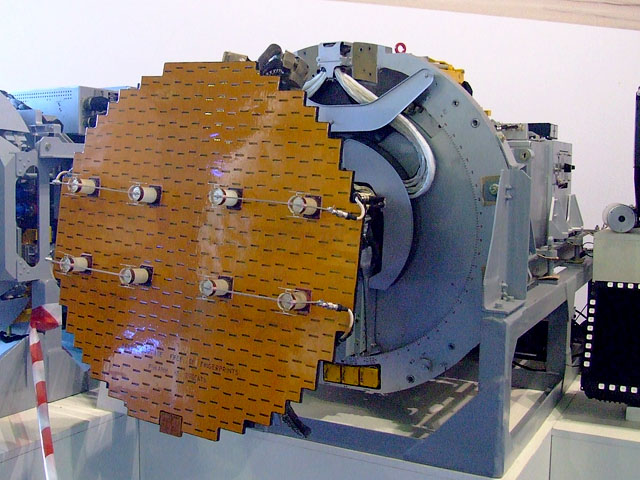
YLC-15 Radar
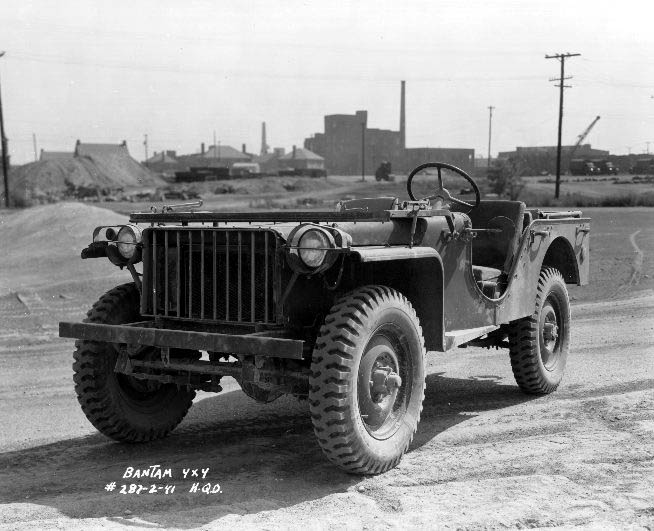
YLC-15 is a fully coherent, Pulse Doppler air defence radar of Chinese origin. It is designed primarily to detect targets at ranges of up to 16 km. It also provides the capability to identify hovering helicopters or low altitude cruise missiles. The YLC-15 radar features compact size, and light weight. Except for the antenna and pedestal, the radar can be broken down into three sections each no more than 30 kg, can be mounted on any vehicles, which enable it especially suitable for small arm missions in the battlefield. The YLC-15 also exhibits outstanding performance in power consumption and reliability. Its target detection and ECCM capabilities considerably extend its operation in a severe battlefield environment. The radar has been shown mounted on the BJ212/BJ2020 jeep and its equivalent. The manufacturer of the system is Nanjing Research Institute of Electronics Technology (NRIET) / Nanjing Institute No. 1 / 南京电子技术研究所. Specifications *Frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Doppler
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics. The first operational Pulse Doppler radar was in the CIM-10 Bomarc, an American long range supersonic missile powered by ramjet engines, and which was armed with a W40 nuclear weapon to destroy entire formations of attacking enemy aircraft. Pulse-Doppler systems were first widely used on fighter aircraft starting in the 1960s. Earlier radars had used pulse-timing in order to determine range and the angle of the antenna (or similar means) to determine the bearing. However, this only worked when the radar antenna was not pointed down; in that case the reflection off the ground overwhelmed any returns from other objects. As the ground moves at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Defence
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, subsurface ( submarine launched), and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures (e.g. barrage balloons). It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries, the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight. In some countries, such as Britain and Germany during the Second World War, the Soviet Union, and modern NATO and the United States, ground-based air defence and air defence airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of STOL (Short TakeOff and Landing) or STOVL (Short TakeOff and Vertical Landing) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. In 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale production.Munson 1968.Hirschberg, Michael J. and David K. Dailey"Sikorsky". ''US and Russian Helicopter Development in the 20th Century'', American Helicopter Society, International. 7 July 2000. Although most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, the configuration of a single main rotor accompanied by a vertical anti-torque tail rotor (i.e. unicopter, not to be confused with the single-blade monocopter) has become the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile
In military terminology, a missile is a missile guidance, guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocket is made guided). Missiles have five system components: targeting (warfare), targeting, guidance system, flight system, engine and warhead. Missiles come in types adapted for different purposes: surface-to-surface missile, surface-to-surface and air-to-surface missiles (ballistic missile, ballistic, cruise missile, cruise, anti-ship missile, anti-ship, anti-submarine missile, anti-submarine, anti-tank missile, anti-tank, etc.), surface-to-air missiles (and anti-ballistic missile, anti-ballistic), air-to-air missiles, and anti-satellite weapons. Airborne explosive devices without propulsion are referred to as shell (projectile), shells if fired by an artillery piece and bombs if dropped by an aircraft. Unguided jet- or rocke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductors ( elements), electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter. Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally ( omnidirectional antennas), or preferentially in a particular direction ( directional, or high-gain, or “beam” antennas). An antenna may include components not conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Counter-countermeasures
Electronic counter-countermeasures (ECCM) is a part of electronic warfare which includes a variety of practices which attempt to reduce or eliminate the effect of electronic countermeasures (ECM) on electronic sensors aboard vehicles, ships and aircraft and weapons such as missiles. ECCM is also known as electronic protective measures (EPM), chiefly in Europe. In practice, EPM often means resistance to jamming. A more detailed description defines it as the electronic warfare operations taken by a radar to offset the enemy's countermeasure. History Ever since electronics have been used in battle in an attempt to gain superiority over the enemy, effort has been spent on techniques to reduce the effectiveness of those electronics. More recently, sensors and weapons are being modified to deal with this threat. One of the most common types of ECM is radar jamming or spoofing. This originated with the Royal Air Force's use of what they codenamed ''Window'' during World War II, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeep
Jeep is an American automobile marque, now owned by multi-national corporation Stellantis. Jeep has been part of Chrysler since 1987, when Chrysler acquired the Jeep brand, along with remaining assets, from its previous owner American Motors Corporation (AMC). Jeep's current product range consists solely of sport utility vehicles – both crossovers and fully off-road worthy SUVs and models, including one pickup truck. Previously, Jeep's range included other pick-ups, as well as small vans, and a few roadsters. Some of Jeep's vehicles—such as the Grand Cherokee—reach into the luxury SUV segment, a market segment the 1963 Wagoneer is considered to have started. Jeep sold 1.4 million SUVs globally in 2016, up from 500,000 in 2008, two-thirds of which in North America, and was Fiat-Chrysler's best selling brand in the U.S. during the first half of 2017. In the U.S. alone, over 2400 dealerships hold franchise rights to sell Jeep-branded vehicles, and if Jeep were spun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanjing Research Institute Of Electronics Technology
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu province of the People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and the second largest city in the East China region. The city has 11 districts, an administrative area of , and a total recorded population of 9,314,685 . Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region, Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties, kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949, and has thus long been a major center of culture, education, research, politics, economy, transport networks and tourism, being the home to one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's administrative structure, enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly less than that of a province. Nanjing has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Band
The S band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a part of the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). Thus it crosses the conventional boundary between the UHF and SHF bands at 3.0 GHz. The S band is used by airport surveillance radar for air traffic control, weather radar, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites, especially those used by NASA to communicate with the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station. The 10 cm radar short-band ranges roughly from 1.55 to 5.2 GHz. The S band also contains the 2.4–2.483 GHz ISM band, widely used for low power unlicensed microwave devices such as cordless phones, wireless headphones (Bluetooth), wireless networking (WiFi), garage door openers, keyless vehicle locks, baby monitors as well as for medical diathermy machines and microwave ovens (typically at 2.495 GHz). India's reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Radars
Ground may refer to: Geology * Land, the surface of the Earth not covered by water * Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth Electricity * Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured * Earthing system, part of an electrical installation that connects with the Earth's conductive surface * Ground and neutral, closely related terms Law * Ground (often grounds), in law, a rational motive or basis for a belief, conviction, or action taken, such as a legal action or argument: * Grounds for divorce, regulations specifying the circumstances under which a person will be granted a divorce Music * ''Ground'' (album), the second album by the Nels Cline Trio * "Ground" (song), one of the songs in the debut album of the Filipino rock band Rivermaya * Ground bass, in music, a bass part that continually repeats, while the melody and harmony over it change * '' The Ground'', a 2005 album by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |