|
Xun You
Xun You (157–September 214), courtesy name Gongda, was a statesman who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China and served as an adviser to the warlord Cao Cao. Born in the influential Xun family of Yingchuan Commandery (around present-day Xuchang, Henan), Xun You was recruited into the civil service by the general He Jin. When the warlord Dong Zhuo hijacked and controlled the Han central government between 189 and 192, Xun You plotted with four others to assassinate him but was discovered and imprisoned. Following his release after Dong Zhuo's death, he wanted to serve as the Administrator of Shu Commandery (around present-day Chengdu, Sichuan) but eventually settled as an official in Jing Province. In 196, after Cao Cao received the figurehead Han sovereign, Emperor Xian, and reestablished the new imperial capital in Xu (許; present-day Xuchang, Henan), he summoned Xun You to the capital to serve as a Master of Writing and Military Adviser. From then on, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xun (surname)
Xun () is the Standard Chinese, Mandarin pinyin romanization of the Chinese surname written as a Chinese character. It is romanized Hsün in Wade–Giles. Xun is the 201st surname in the Song dynasty Chinese classics, classic text ''Hundred Family Surnames''. It is not among the top 300 most common Chinese surnames. Notable people * Xun Xi (:zh:荀息, 荀息; died 651 BC), minister of Duke Wu of Jin, enfeoffed at Xun * Xun Kuang or Master Xun (ca. 312–230 BC), ancient Confucian philosopher * Xun Shuang (128–190), Eastern Han dynasty politician and historian * Xun Chen ( 2nd century), Eastern Han dynasty advisor to warlord Han Fu (warlord), Han Fu * Xun You (157–214), Eastern Han dynasty statesman and adviser to warlord Cao Cao * Xun Yu (163–212), Eastern Han dynasty statesman and adviser to warlord Cao Cao * Xun Yi (died 274), Jin dynasty politician * Xun Can ( 209–237), Three Kingdoms-era scholar and philosopher * Xun Xu (died 289), Western Jin dynasty politician, arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
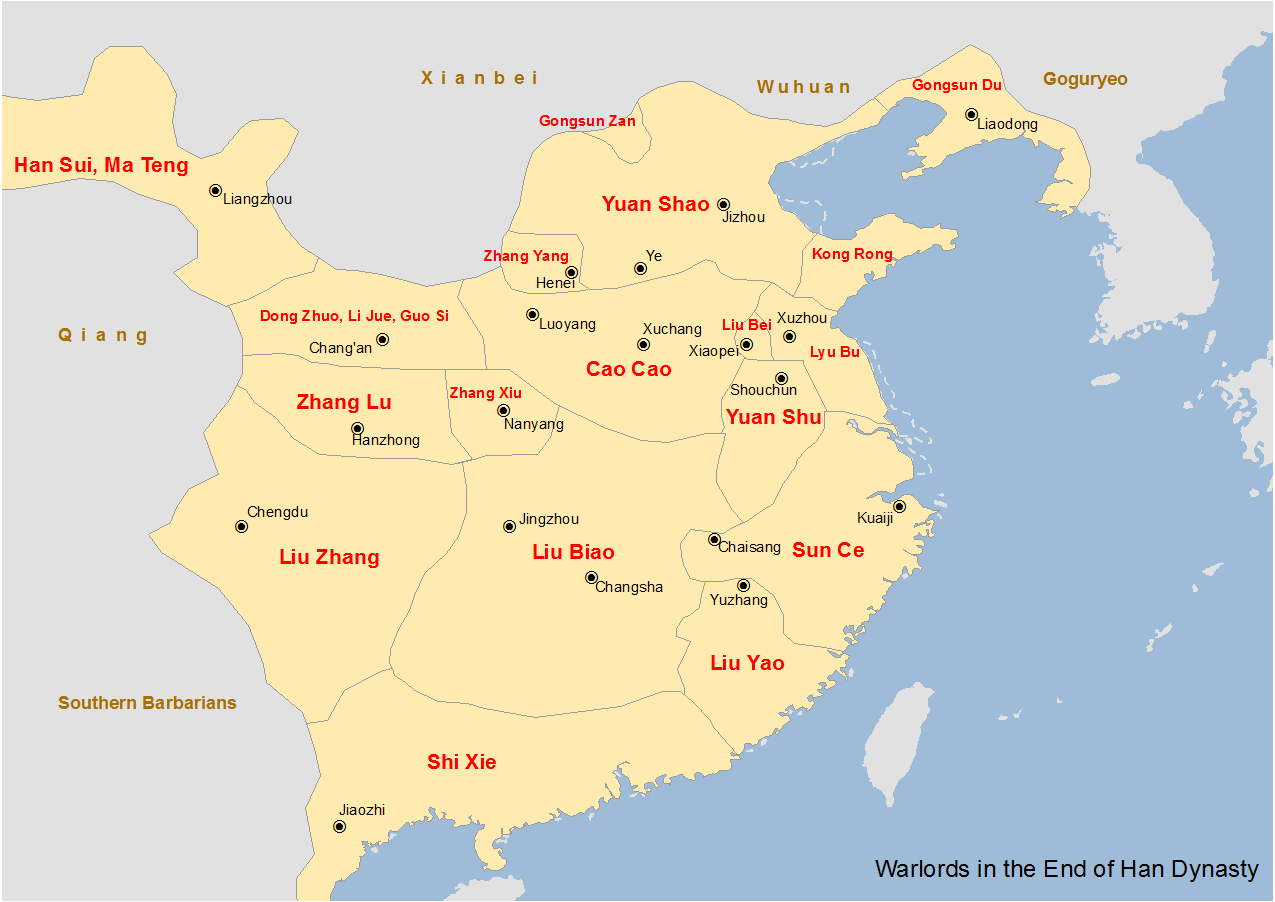
Zhang Xiu (warlord)
Zhang Xiu (died 207) was a military general and minor warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. In 197, he clashed with the warlord Cao Cao, who was then the ''de facto'' head of the Han central government, at the Battle of Wancheng and subsequent skirmishes. However, in 200, he heeded the suggestion from his adviser Jia Xu and surrendered to Cao Cao, who accepted his surrender and appointed him as a general. Having fought on Cao Cao's side at the decisive Battle of Guandu against a rival warlord Yuan Shao and in the subsequent campaigns against Yuan Shao's heirs, Zhang Xiu made great contributions during his service under Cao Cao. In 207, he died en route to joining Cao Cao on a campaign against the Wuhuan tribes. The Han imperial court honoured with the posthumous title "Marquis Ding". Life Zhang Xiu was from Zuli County (), Wuwei Commandery (), which is in present-day Jingyuan County, Gansu. He was a distant nephew of Zhang Ji, who served under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangsu
Jiangsu is a coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province in East China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, third smallest, but the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, fifth most populous, with a population of 84.75 million, and the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population density, most densely populated of the 22 provinces of the People's Republic of China. Jiangsu has the highest GDP per capita and second-highest GDP of Chinese provinces, after Guangdong. Jiangsu borders Shandong in the north, Anhui to the west, and Zhejiang and Shanghai to the south. Jiangsu has a coastline of over along the Yellow Sea, and the Yangtze flows through the southern part of the province. Since the Sui dynasty, Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang dynasties, Jiangsu has been a national economic and commercial center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huai'an
) , leader_title1 = , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = , leader_title3 = , leader_name3 = , leader_title4 = , leader_name4 = , established_title = , established_date = , established_title1 = , established_date1 = , established_title2 = , established_date2 = , established_title3 = , established_date3 = , founder = , named_for = , area_magnitude = , unit_pref = , area_footnotes = , area_total_km2 =9950 , area_land_km2 = , area_water_km2 = , area_water_percent = , area_urban_km2 =4494.3 , area_metro_km2 =3202.6 , area_blank1_title = , area_blank1_km2 = , elevation_footnotes = , elevation_m = , elevation_ft = , elevation_max_m = , elevation_max_ft = , elevati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangling Commandery
Guangling Commandery was a historical commandery of China from Han dynasty to Tang dynasty, located in present-day central Jiangsu province in central coastal China. It was named after Guangling, a historical name of Yangzhou. In early Han dynasty, the commandery was known as Dongyang (東陽), and successively constituted part of the Wu Kingdom (195–154 BC) and the Jiangdu Kingdom (154–121 BC). In 121 BC, Jiangdu was abolished, and Guangling became a commandery. In 117 BC, Guangling was granted to Liu Xu (劉胥), a son of the reigning Emperor Wu, as a kingdom. Xu and his descendants ruled Guangling until the usurpation of Wang Mang. The commandery was restored when Eastern Han was founded. In 37 AD, it absorbed the Sishui Kingdom. In 58, it was granted to Liu Jing (劉荊), a son of the Emperor Guangwu, but was revoked when Jing was involved in a conspiracy in 67. In 140, the commandery administered 11 counties: Guangling, Jiangdu (江都), Gaoyou (高郵), Ping'an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Home (Chinese)
In Chinese culture, an ancestral home is the place of origin of one's extended family. It may or may not be the place where one is born. For instance, Lien Chan was born in Xi'an, but his ancestral home is Zhangzhou. Definition A subjective concept, a person's ancestral home could be the birthplace of ''any'' of their patriline ancestors. Su Shi limited it to five generations, i.e. it refers to the home of one's great-great-grandfather. Even more broadly, an ancestral home can refer to the first locality where a surname came to be established or prominent. Commonly, a person usually defines their hometown as what their father considers to be his ancestral home. In practice, most people would define their ancestral homes as the birthplace of their patriline ancestors from the early 20th century, around the time when government authorities began to collect such information from individuals. Moreover, a person's ancestral home can be defined in any level of locality, from prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fu Xuan
Fu Xuan (217–278Fu Xuan's biography in ''Book of Jin'' indicate that he died at the age of 62 (by East Asian reckoning) after Yang Huiyu's death (in July 278). (献皇后崩于弘训宫,设丧位。...于是贵游慑伏,台阁生风。寻卒于家,时年六十二,谥曰刚。) ''Jin Shu'', vol.47), courtesy name Xiuyi, posthumous name Gang (刚), was a Chinese historian, poet, and politician who lived in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period and later under the Jin dynasty. He was one of the most prolific authors of ''fu'' poetry of his time. He was a grandson of Fu Xie (), a son of Fu Gan (), and the father of Fu Xian ().''Britannica Kokusai Dai-Hyakkajiten'' article "Fu Xuan" (''Fu Gen'' in Japanese). Shogakukan.''Kanjigen'' entry "Fu Xuan" (''Fu Gen'' in Japanese). Gakken 2006. Life Although he lost his father early and grew up poor, Fu Xuan eventually became famous in literature and music. Nominated as a civil service candidate by the local prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruan Ji
Ruan Ji (210–263), courtesy name Sizong, was a Chinese musician, poet, and military officer who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period. He was one of the Seven Sages of the Bamboo Grove. The guqin melody ''Jiukuang'' ( 'Drunken ecstasy', or 'Wine-mad') is believed to have been composed by him. At one time an infantry colonel, he was also known as Ruan Bubing (; 'Ruan of the infantry'). Life Ruan Ji was born in Chenliu (in the southern part of modern-day Kaifeng, Henan). His father was Ruan Yu, one of the famed Seven Scholars of Jian'an who were promoted by the Cao clan in the Jian'an poetry era. The Ruan family were loyal to the Cao Wei, as opposed to the Sima family; however their moral convictions and willingness to speak out generally outmatched their actual military or political power. It is fair to say that Ruan Ji was born into peril, his time period being the Period of Disunity. Ruan Ji was poetically part of both the poetry of the Jian'an pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annotations To Records Of The Three Kingdoms
''Annotated Records of the Three Kingdoms'' () by Pei Songzhi (372–451) is an annotation completed in the 5th century of the 3rd century historical text ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', compiled by Chen Shou. After the fall of the Eastern Jin, Pei Songzhi became the Gentleman of Texts under the Liu Song dynasty, and was given the assignment of editing the book, which was completed in 429. This became the official history of the Three Kingdoms period, under the title ''Sanguozhi zhu'' (''zhu'' meaning "notes"). Pei went about providing detailed explanations to some of the geography and other elements mentioned in the original. More importantly, he made corrections to the work, in consultation with records he collected of the period. In regard to historical events and figures, as well as Chen Shou's opinions, he added his own commentary. From his broad research, he was able to create a history which was relatively complete, without many of the loose ends of the original. Some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pei Songzhi
Pei Songzhi (372–451), courtesy name Shiqi, was a Chinese historian and politician who lived in the late Eastern Jin dynasty and the Liu Song dynasty. His ancestral home was in Wenxi County, Shanxi Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ..., but he moved to the Jiangnan region later. He is best known for making annotations to the historical text '' Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi'') written by Chen Shou in the third century, providing additional details omitted from the original work. His commentary, completed in 429, became integral to later editions of the ''Sanguozhi'', making the joint work three times as long as the original.Yuet Keung Lo, "Pei Songzhi", in ''A Global Encyclopedia of Historical Writing'', edited by D. R. Woolf (Garland Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Shou
Chen Shou ( zh , t = 陳壽 ; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is best known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''), which records the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period. Chen Shou wrote the ''Sanguozhi'' primarily in the form of biographies of notable persons of those eras. Today, Chen's ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is part of the '' Twenty-Four Histories'' canon of Chinese history. Historical sources on Chen Shou's life There are two biographies of Chen Shou. The first one is in the '' Chronicles of Huayang'', which was written by Chang Qu in the fourth century during the Eastern Jin dynasty. The second one is in the ''Book of Jin'', which was written by Fang Xuanling and others in the seventh century during the Tang dynasty. Life He started his career as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is a Chinese official history written by Chen Shou in the late 3rd century CE, covering the end of the Han dynasty (220 CE) and the subsequent Three Kingdoms period (220–280 CE). It is regarded as to be the authoritative source text for these periods. Compiled following the reunification of China under the Jin dynasty (266–420), the work chronicles the political, social, and military events within rival states Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu into a single text organized by individual biography. The ''Records'' are the primary source of information for the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', considered to be one of the four classic novels emblematic of written vernacular Chinese. While large subsections of the work have been selected and translated into English, the entire corpus has yet to receive an unabridged English translation. Origin and structure The '' Book of Han'' and ''Records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |