|
Xitun Formation
The Xitun Formation is a palaeontological formation which is named after Xitun village in Qujing, a location in South China. This formation includes many remains of fossilized fish and plants of the Early Devonian period (Late Lochkovian). It was originally referred to as the Xitun Member of the Cuifengshan Formation (now the Cuifengshan Group). Fossil content Vertebrates Acanthodians Actinopterygians Chondrichthyes Jawless fish Placoderms Sarcopterygians Plants See also * List of fossil sites This list of fossil sites is a worldwide list of localities known well for the presence of fossils. Some entries in this list are notable for a single, unique find, while others are notable for the large number of fossils found there. Many of t ...— ''(with link directory)'' References Geologic formations of China Devonian System of Asia Devonian China Devonian northern paleotropical deposits Paleontology in China {{China-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelodonti
Thelodonti (from Greek: "feeble teeth")Maisey, John G., Craig Chesek, and David Miller. Discovering fossil fishes. New York: Holt, 1996. is a class of extinct jawless fishes with distinctive scales instead of large plates of armor. There is much debate over whether the group of Palaeozoic fish known as the Thelodonti (formerly coelolepids) represent a monophyletic grouping, or disparate stem groups to the major lines of jawless and jawed fish. Thelodonts are united in possession of " thelodont scales". This defining character is not necessarily a result of shared ancestry, as it may have been evolved independently by different groups. Thus the thelodonts are generally thought to represent a polyphyletic group, although there is no firm agreement on this point. On the basis that they are monophyletic, they are reconstructed as being ancestrally marine and invading freshwater on multiple occasions. "Thelodonts" were morphologically very similar, and probably closely relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
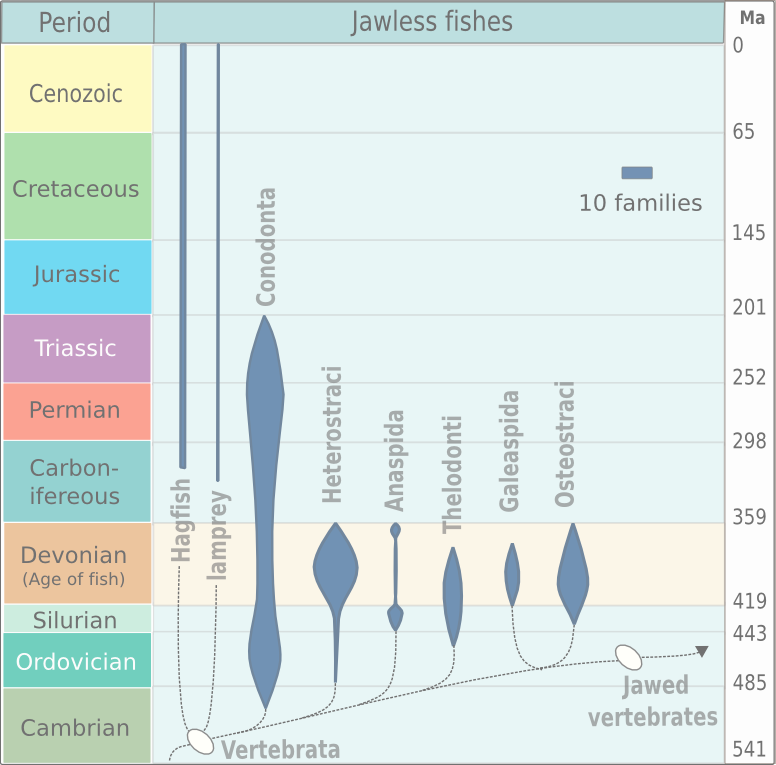
Jawless Fish
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (Cyclostomata, cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister taxon, sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are jawed vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, scales, and a heart with its chambers in series. Extant chondrichthyes range in size from the 10 cm (3.9 in) finless sleeper ray to the 10 m (32 ft) whale shark. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish) and Holocephali ( chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is gradually replaced by a vertebral column during development, except in Holocephali, where the notochord stays intact. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobe Finned Fish
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar bone surrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Finned Fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or horny spines (rays), as opposed to the fleshy, lobed fins that characterize the class Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). These actinopterygian fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the link or connection between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). By species count, actinopterygians dominate the vertebrates, and they constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 species of fish. They are ubiquitous throughout freshwater and marine environments from the deep sea to the highest mountain streams. Extant species can range in size from '' Paedocypris'', at , to the massive ocean sunfish, at , and the long-bodied oarfish, at . The vast majority of Actinopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |