|
XXVII Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
The XXVII Corps (, or ''XXVII.AK'') was an infantry corps in the German army. It fought in several notable actions during World War II. The corps was originally raised in August 1939 in Wehrkreis VII. Wartime service 1939 Organisation (September 1939): 16th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 16th, 69th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 69th, 211th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 211th and 216th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 216th Infantry Divisions During September 1939 the XXVII Corps was used to screen the Dutch-German border. 1940 Organisation (June 1940): 211th, 213th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 213th, 218th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 218th and 239th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 239th Infantry Divisions The Corps participated in Nazi Germany's Battle of France, Invasion of France as part of Army Group C. In May, it crossed the southern Netherlands and Belgium towards Roubaix, where it helped in surrounding the French First Army (France), 1st Army. Later in the campaig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 63,047 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command was created in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Realm) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
216th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 216th Infantry Division () was a German Army division that was created during the Second World War; it was active from 1939–1943. It served on the Western Front in 1940 and later took part in the Eastern Front campaign, being involved in the disastrous Battle of Kursk. Operational history The division was created on 26 August 1939 by reorganizing several Border Defense and Army Reserve units from Lower Saxony, primarily in the area surrounding the city of Hannover. It was organized under the pre-war infantry division "alter Art," structure; consisting of three 3-battalion infantry regiments (brigades), an artillery regiment of four battalions, a combat engineer battalion, a signal battalion, and an antitank battalion, as well as divisional services. Its total strength was approximately 17,200 men. The division was based at Hameln and was part of Wehrkreis XI. The 216th Infantry Division did not participate in the Invasion of Poland, since it was occupying defensive positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
162nd Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 162nd Infantry Division ''(162. Infanterie-Division)'' was an infantry division of the '' Heer'' of Nazi Germany's ''Wehrmacht'' during World War II. It is not to be confused with its vastly different successor formation, the 162nd Turkestani Division. History The 162nd Infantry Division was formed on 1 December 1939 at Groß Born army training area. It was initially assembled as part of the seventh ''Aufstellungswelle'' using replacement units of Wehrkreis II (Stettin) and contained the Infantry Regiment 303 and 314 with three battalions each, as well as the Light Artillery Detachment 236 with three batteries. It initially absorbed the Infantry Replacement Regiments 32 ( Kolberg), 207 ( Schneidemühl) and 2 (Greifswald). The initial commander of the division was Hermann Franke, who would hold this post until 13 May 1942.This initial divisional order of battle was later upgraded on 10 January 1940 through the addition of the Field Replacement Battalions 12 (Schwerin), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
129th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 129th Infantry Division (''German language, German: Hessen-Thuerinische 129. Infanterie-Division'') was an Infantry Division (military), Division of the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army during World War II. History The 129th Infantry Division was formed in Hanau, in Wehrkreis XI on 20 October 1940 as Division 11 and incorporated personnel from Hessen and Thuringia.Mitcham, p. 181 Elements of 9th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 9th, 33rd Infantry Division (Germany), 33rd and 251st Infantry Division (Germany), 251st Infantry Divisions formed approximately 30% of the division. After the training of the division ended in April 1941, it was sent to East Prussia and took part in Operation Barbarossa. As part of Army Group Center, the division fought in several battles of the central sector of the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front, such as those in Battle of Białystok–Minsk, Białystok, Battle of Smolensk (1941), Smolensk and Vyazma. In October–November 1941 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
86th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The German 86th Infantry Division () was created on 26 August 1939. The division was disbanded on 3 November 1943. Commanding officers *General der Infanterie Joachim Witthöft, 26 August 1939 *General der Artillerie Helmuth Weidling, 1 January 1942 Order of battle *Infanterie-Regiment 167 *Infanterie-Regiment 184 *Infanterie-Regiment 216 *Artillerie-Regiment 186 *Divisionseinheiten 186 References ;Bibliography * Tessin, Georg (1972). ''Verbände und Truppen der deutschen Wehrmacht und Waffen-SS im Zweiten Weltkrieg 1939–1945. Sechster Band. Die Landstreitkräfte 71–130''. Osnabrück, Germany: Biblio-Verlag. . 0*086 Military units and formations established in 1939 1939 establishments in Germany Military units and formations disestablished in 1943 {{Germany-WWII-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
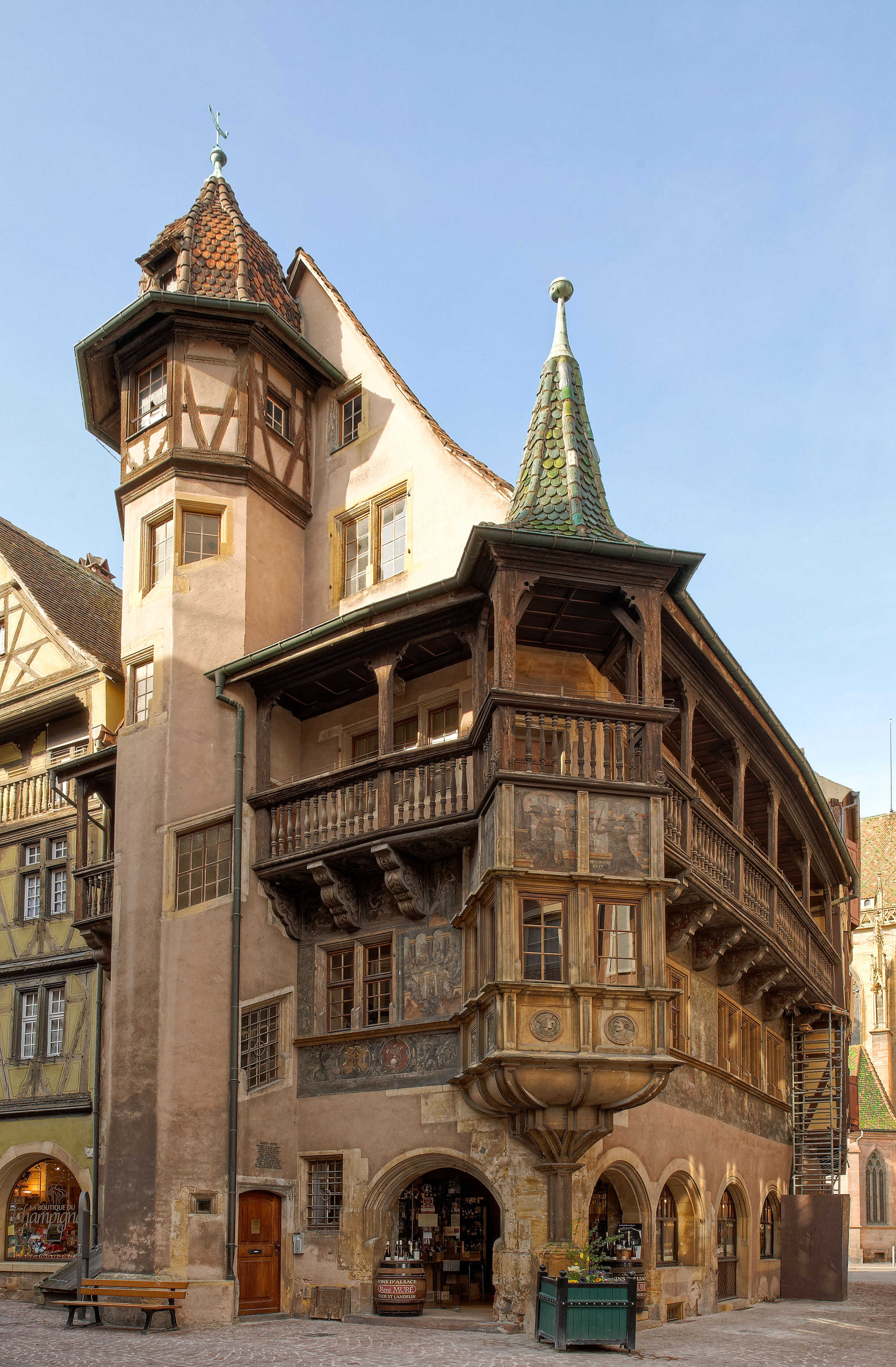
Colmar
Colmar (; ; or ) is a city and commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Alsace region of north-eastern France. The third-largest commune in Alsace (after Strasbourg and Mulhouse), it is the seat of the prefecture of the Haut-Rhin department and of the subprefecture of the Colmar-Ribeauvillé arrondissement. The city is renowned for its well-preserved old town, its numerous architectural landmarks and its museums, among which is the Unterlinden Museum, which houses the '' Isenheim Altarpiece''. Colmar is located on the Alsatian Wine Route and considers itself to be the capital of Alsatian wine ('). History Colmar was first mentioned by Charlemagne in his chronicle about Saxon wars. This was the location where the Carolingian Emperor Charles the Fat held a diet in 884. Colmar was granted the status of a free imperial city by Emperor Frederick II in 1226. In 1354 it joined the Décapole city league.G. Köbler, ''Historisches Lexikon der deutschen Länder'', 7th editi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Switzerland border, Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Constance downstream, it forms part of the Germany-Switzerland border, Swiss-German border. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border. It then flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally, the Rhine turns to flow predominantly west to enter the Netherlands, eventually emptying into the North Sea. It drains an area of 185,000 km2. Its name derives from the Gaulish language, Gaulish ''Rēnos''. There are two States of Germany, German states named after the river, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, in addition to several districts of Germany, districts (e.g. Rhein-Sieg-Kreis, Rhein-Sieg). The departments of France, department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Army (France)
The First Army () was a field army of France that fought during World War I and World War II. It was also active during the Cold War. World War I On mobilization in August 1914, General Auguste Dubail was put in the charge of the First Army, which comprised the 7th, 8th, 13th, 14th, and 21st Army Corps, two divisions of cavalry and one reserve infantry division. It was massed between Belfort and the general line Mirecourt-Lunéville with headquarters at Epinal. First Army then took part, along with the French Second Army, in the Invasion of Lorraine. The First Army intended to take the strongly defended town of Sarrebourg. Bavarian Crown Prince Rupprecht, commander of the German Sixth Army, was tasked with stopping the French invasion. The French attack was repulsed by Rupprecht and his stratagem of pretending to retreat and then strongly attacking back. On 20 August Rupprecht launched a major counter-offensive, driving the French armies out. Dubail was replaced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roubaix
Roubaix ( , ; ; ; ) is a city in northern France, located in the Lille metropolitan area on the Belgian border. It is a historically mono-industrial Communes of France, commune in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department, which grew rapidly in the 19th century from its textile industries, with most of the same characteristic features as those of English and American Boomtown, boom towns. This former new town has faced many challenges linked to deindustrialisation such as urban decay, with their related economic and social implications, since its major industries fell into decline by the middle of the 1970s. Located to the northeast of Lille, adjacent to Tourcoing, Roubaix is the of two Cantons of France, cantons and the third largest city in the French Regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France ranked by population with nearly 99,000 inhabitants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the south, and the North Sea to the west. Belgium covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.8 million; its population density of ranks List of countries and dependencies by population density, 22nd in the world and Area and population of European countries, sixth in Europe. The capital and Metropolitan areas in Belgium, largest metropolitan region is City of Brussels, Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a complex Federation, federal system structured on regional and linguistic grounds. The country is divided into three highly autonomous Communities, regions and language areas o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands consists of Provinces of the Netherlands, twelve provinces; it borders Germany to the east and Belgium to the south, with a North Sea coastline to the north and west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with the United Kingdom, Germany, and Belgium. The official language is Dutch language, Dutch, with West Frisian language, West Frisian as a secondary official language in the province of Friesland. Dutch, English_language, English, and Papiamento are official in the Caribbean Netherlands, Caribbean territories. The people who are from the Netherlands is often referred to as Dutch people, Dutch Ethnicity, Ethnicity group, not to be confused by the language. ''Netherlands'' literally means "lower countries" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group C
Army Group C () was an army group of the German Wehrmacht during World War II. In its first deployment between 1939 and 1941, its main assignment was the defense of the Franco-German border during the Phony War and the Western Campaign, after which it was moved to East Prussia to become Army Group North. When Army Group C was recreated from 1943 to 1945, it was used to coordinate German forces on the Italian front. History 1939–1941 Army Group C was first formed in Frankfurt on 26 August 1939, from Army Group Command 2 (itself formed on 1 October 1919 as ''Reichswehrgruppenkommando'') in Frankfurt/Main. The only commander of the army group throughout its first tenure of service was Wilhelm Ritter von Leeb, who had been reactivated from retirement upon the outbreak of the war.Meyer, Georg (1985). Leeb, Wilhelm Ritter von'' In: ''Neue Deutsche Biographie'' (in German). Vol. 14, Duncker & Humblot, Berlin, ISBN 3428001958, pp. 51–53.Between September 1939 and June 1940, Army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |