|
XS (EVS)
XS is the studio production server of the Belgian company EVS Broadcast Equipment. It has been inspired from the XT3 server but can be controlled by dedicated controllers from EVS for the studio environment: Xsense, IPDirector, Xscreen, Insio or by non-EVS controllers such as automation systems, linear or hybrid editors, switchers and controllers through API or standard protocols. Designed to replace VTRs, the server allows incoming feeds to be recorded, quickly enriched by metadata and played out or instantly streamed or transferred to post-production. The server benefits from loop recording and allows to record, control and play media. It has from 2 to 6 channels SD/HD and 6-channel 3D/ 1080p ( 3G or dual link) and offers the same features in a 3D environment. It supports several formats and codec A codec is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a data stream or signal. ''Codec'' is a portmanteau of coder/decoder. In electronic communications, an en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XS Server From EVS
XS may refer to: Arts and entertainment * XS (comics), a DC Comics superheroine * ''XS'' (manhwa), a South Korean comic by Song Ji-Hyung () * XS (radio station), a defunct station in Neath Port Talbot, Wales * "XS" (song), a 2020 song by Rina Sawayama * ''XS'' (video game), a 1997 FPS game made by GT interactive * '' Xiaolin Showdown'', an American animated television series * '' XS: The Opera Opus'' (1984-6) no wave opera Science, technology, and mathematics * XS (Perl), an interface through which computer programs written in Perl can call C language subroutines * Yamaha Motif, a series of synthesizers * XS (EVS), a production server of EVS Broadcast Equipment * Para-Ski XS, a Canadian powered parachute design * Cross section (geometry) * iPhone XS, smartphone by Apple Inc. Other uses * XS Energy Drink, drinks produced by AMWAY * XS, a nightclub at the Encore Las Vegas * Xavier School, a secondary school in San Juan, Metro Manila, Philippines * Extra Small (XS), a size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-production
Post-production is part of the process of filmmaking, video production, audio production, and photography. Post-production includes all stages of production occurring after principal photography or recording individual program segments. The first part of the post-production process is the traditional non-linear (analog) film editing at the outset of post-production has mostly been replaced by digital or video editing software that operates as a non-linear editing (NLE) system. The advantage of being able to have this non-linear capacity is in the flexibility for editing scenes out of order, making creative changes at will, carefully shaping the film in a thoughtful, meaningful way for emotional effect. Once the production team is satisfied with the picture editing, the picture editing is said to be "locked." At this point begins the turnover process, where the picture is prepared for lab and color finishing and the sound is "spotted" and turnover to the composer and sound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News
News is information about current events. This may be provided through many different Media (communication), media: word of mouth, printing, Mail, postal systems, broadcasting, Telecommunications, electronic communication, or through the testimony of Witness, observers and witnesses to events. News is sometimes called "hard news" to differentiate it from soft media. Common topics for news reports include war, government, politics, education, health, the Climate change, environment, economy, business, fashion, entertainment, and sport, as well as Wikipedia:Unusual articles, quirky or unusual events. Government proclamations, concerning Monarchy, royal ceremonies, Law, laws, Tax, taxes, public health, and Crime, criminals, have been dubbed news since ancient times. Technology, Technological and Social change, social developments, often driven by government communication and espionage networks, have increased the speed with which news can spread, as well as influenced its conten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codec
A codec is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a data stream or signal. ''Codec'' is a portmanteau of coder/decoder. In electronic communications, an endec is a device that acts as both an encoder and a decoder on a signal or data stream, and hence is a type of codec. ''Endec'' is a portmanteau of encoder/decoder. A coder or encoder encodes a data stream or a signal for transmission or storage, possibly in encrypted form, and the decoder function reverses the encoding for playback or editing. Codecs are used in videoconferencing, streaming media, and video editing applications. History In the mid-20th century, a codec was a device that coded analog signals into digital form using pulse-code modulation (PCM). Later, the name was also applied to software for converting between digital signal formats, including companding functions. Examples An audio codec converts analog audio signals into digital signals for transmission or encodes them for storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Television
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, phase and frequency of an analog signal. Analog signals vary over a continuous range of possible values which means that electronic noise and interference may be introduced. Thus with analog, a moderately weak signal becomes snowy and subject to interference. In contrast, picture quality from a digital television (DTV) signal remains good until the signal level drops below a threshold where reception is no longer possible or becomes intermittent. Analog television may be wireless (terrestrial television and satellite television) or can be distributed over a cable network as cable television. All broadcast television systems used analog signals before the arrival of DTV. Motivated by the lower bandwidth requirements of compressed digital signals, beginning in the 2000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
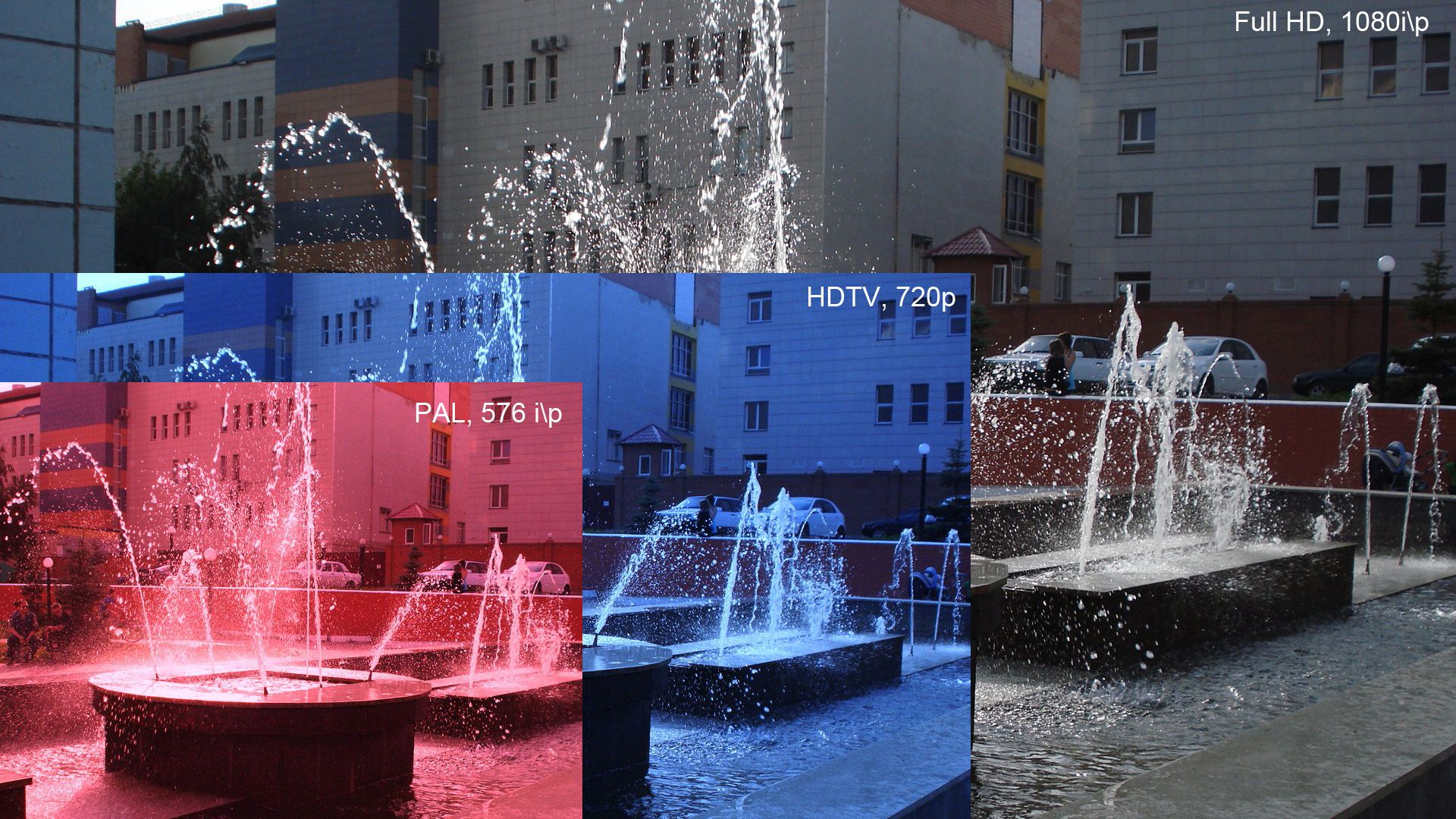
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoscopy
Stereoscopy (also called stereoscopics, or stereo imaging) is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3D displays that display an image in three full dimensions, allowing the observer to increase information about the 3-dimensional objects being displayed by head and eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Recording
Loop recording is the process of recording audio continuously to an endless tape (if magnetic tape is used) or to computer memory, or recording video feeds (such as from video surveillance or camera signals) on a video server. This process is a never-ending one: at the end of the internal disk drive, the recording process continues to record at the beginning, erasing the previously recorded material and replacing it with the new content. Generally, it is possible to write-protect some selected parts (as video clips) to prevent erasure. This process is used on video servers to allow continuous recording, and instant access to any material ingested in the previous hours. This guarantees that the recorder will never miss an action in some live events such as live sports. Video servers This process is used in: * the XT ">/nowiki> server from EVS Broadcast Equipment EVS Broadcast Equipment SA is a Belgian company that manufactures live outside broadcast digital video prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer (computing)
In computer technology, transfers per second and its more common secondary terms gigatransfers per second (abbreviated as GT/s) and megatransfers per second (MT/s) are informal language that refer to the number of operations transferring data that occur in each second in some given data-transfer channel. It is also known as sample rate, i.e. the number of data samples captured per second, each sample normally occurring at the clock edge. The terms are neutral with respect to the method of physically accomplishing each such data-transfer operation; nevertheless, they are most commonly used in the context of transmission of digital data. 1 MT/s is 106 or one million transfers per second; similarly, 1 GT/s means 109, or equivalently in the US/ short scale, one billion transfers per second. Units The choice of the symbol ''T'' for ''transfer'' conflicts with the International System of Units, in which ''T'' stands for the tesla unit of magnetic flux density (so "Megatesla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Server
{{refimprove, date=September 2014 A video server is a computer-based device that is dedicated to delivering video. Video servers are used in a number of applications, and often have additional functions and capabilities that address the needs of particular applications. For example, video servers used in security, surveillance and inspection applications typically are designed to capture video from one or more cameras and deliver the video via a computer network. In video production and broadcast applications, a video server may have the ability to record and play recorded video, and to deliver many video streams simultaneously. Video broadcast and production In TV broadcast industries, a server is a device used to store broadcast quality images and allows several users to edit stories using the images they contain simultaneously. The video server can be used in a number of contexts, some of which include: * News: providing short news video clips as part of a news broadcast as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streaming Media
Streaming media is multimedia that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content itself. Distinguishing delivery method from the media applies specifically to telecommunications networks, as most of the traditional media delivery systems are either inherently ''streaming'' (e.g. radio, television) or inherently ''non-streaming'' (e.g. books, videotape, audio CDs). There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or poor buffering of the content, and users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content. With the use of buffering of the content for just a few seconds in advance of playback, the quality can be much improved. Livestreaming is the real-time delivery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |