|
XP-56 Black Bullet
The Northrop XP-56 Black Bullet is a unique prototype fighter interceptor built by the Northrop Corporation. It was one of the most radical of the experimental aircraft built during World War II. Ultimately, it was unsuccessful and did not enter production. Design and development The initial idea for the XP-56 was quite radical for 1939. It was to have no horizontal tail, only a small vertical tail, used an experimental engine, and be produced using a novel metal, magnesium. The aircraft was to be a wing with a small central fuselage added to house the engine and pilot. It was hoped that this configuration would have less aerodynamic drag than a conventional airplane. The idea for this single-seat aircraft originated in 1939 as the Northrop N2B model. It was designed around the Pratt & Whitney liquid-cooled X-1800 engine in a pusher configuration driving contra-rotating propellers. The U.S. Army ordered Northrop to begin design work on 22 June 1940, and after reviewing the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop N-1M
The Northrop N-1M (''Northrop Model 1 Mockup''), also known by the nickname "Jeep", is a retired American experimental aircraft used in the development of the flying wing concept by Northrop Aircraft during the 1940s. Design and development Jack Northrop became involved with all-wing aircraft designs in the late 1920s, with his first flying wing research prototype being built in the 1928–1930 time period. That first prototype, registered X-216H, had evolved from earlier design studies but was not yet a true flying wing as it retained a tail unit comprising twin rudders with a single horizontal stabilizer running between them; both rudders were connected by twin booms to the thick, all-wing blended fuselage. The aircraft had an open cockpit in the center wing section and single, rear-facing, pusher propeller connected to a Menasco Cirrus inverted-four piston engine blended into the all-wing shape. X-216H was first flown in 1929 with Edward Bellande at the controls; the airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop XP-56 Black Bullet 061024-F-1234P-009
Northrop may refer to: Businesses * Northrop Corporation, an American aircraft manufacturer formed in 1939 * Northrop Grumman, an American aircraft manufacturer formed in 1994 as a merger of the above company with Grumman * Northrop Loom, an American designed weaving loom Places United States * Northrop, Minnesota, a town * Northrop, Minneapolis, Minnesota, a neighborhood * Northrop Auditorium, on the Minneapolis campus of the University of Minnesota * Northrop Field, a former stadium for the University of Minnesota * Northrop High School, Fort Wayne, Indiana * Northrop University, a former aviation institute * Mount Northrop, Minnesota People * Northrop (surname), including a list of people with the name * Northrop Frye Herman Northrop Frye (July 14, 1912 – January 23, 1991) was a Canadian literary critic and literary theorist, considered one of the most influential of the 20th century. Frye gained international fame with his first book, ''Fearful Symmetr ... (1912–199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul E
Paul may refer to: People * Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people * Paul (surname), a list of people * Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament * Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo Paul & Paula * Paul Stookey, one-third of the folk music trio Peter, Paul and Mary * Billy Paul, stage name of American soul singer Paul Williams (1934–2016) * Vinnie Paul, drummer for American Metal band Pantera * Paul Avril, pseudonym of Édouard-Henri Avril (1849–1928), French painter and commercial artist * Paul, pen name under which Walter Scott wrote ''Paul's letters to his Kinsfolk'' in 1816 * Jean Paul, pen name of Johann Paul Friedrich Richter (1763–1825), German Romantic writer Places * Paul, Cornwall, a village in the civil parish of Penzance, United Kingdom *Paul (civil parish), Cornwall, United Kingdom * Paul, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community *Paul, Idaho, United States, a city *Paul, Nebraska, Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suitland, Maryland
Suitland is a suburb of Washington, D.C., approximately one mile (1.6 km) southeast of Washington, D.C. Suitland is a census designated place (CDP), as of the 2020 census, its population was 25,839. Prior to 2010, it was part of the Suitland-Silver Hill, Maryland, Suitland-Silver Hill census-designated place. History Suitland is named after 19th century landowner and businessman Senator Samuel Taylor Suit, whose estate, "Suitland,” was located near the present-day intersection of Suitland and Silver Hill Roads. 17th and 18th centuries In the 1600s, the Piscataway tribe inhabited the lands in southern Maryland. European settlers first visited Saint Clement's Island on the Potomac River and then established their first Maryland colony downriver at Saint Mary's City in 1634, and by the 1660s through the 1680s, settlers had moved into what is now known as Prince George's County. Faced with this encroachment, the Piscataways left the area in 1697, and moved north to what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeman Field
: ''For the civil use of this facility after 1946, see Freeman Municipal Airport '' Freeman Army Airfield is an inactive United States Army Air Forces base located in south-southwest of Seymour, Indiana. Established in 1942, the base became the first military helicopter pilot training airfield. In 1944, black bomber pilots were trained at Freeman. It was the scene of a racial incident that outraged many Americans which led to the military re-evaluating its racial policies. After the war, captured German, Italian and Japanese aircraft were brought to the base for evaluation and testing. It was closed in 1946. History Freeman Army Airfield was named in honor of Captain Richard S. Freeman. A native of Indiana and 1930 graduate of West Point. He was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross,the Mackay Trophy, and was also one of the pioneers of the Army Air Mail Service. Captain Freeman was killed on 6 February 1941 in the crash of a B-17 Flying Fortress (B-17B 38-216) near Lovelo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington D
Washington most commonly refers to: * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States * Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Fort Washington (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
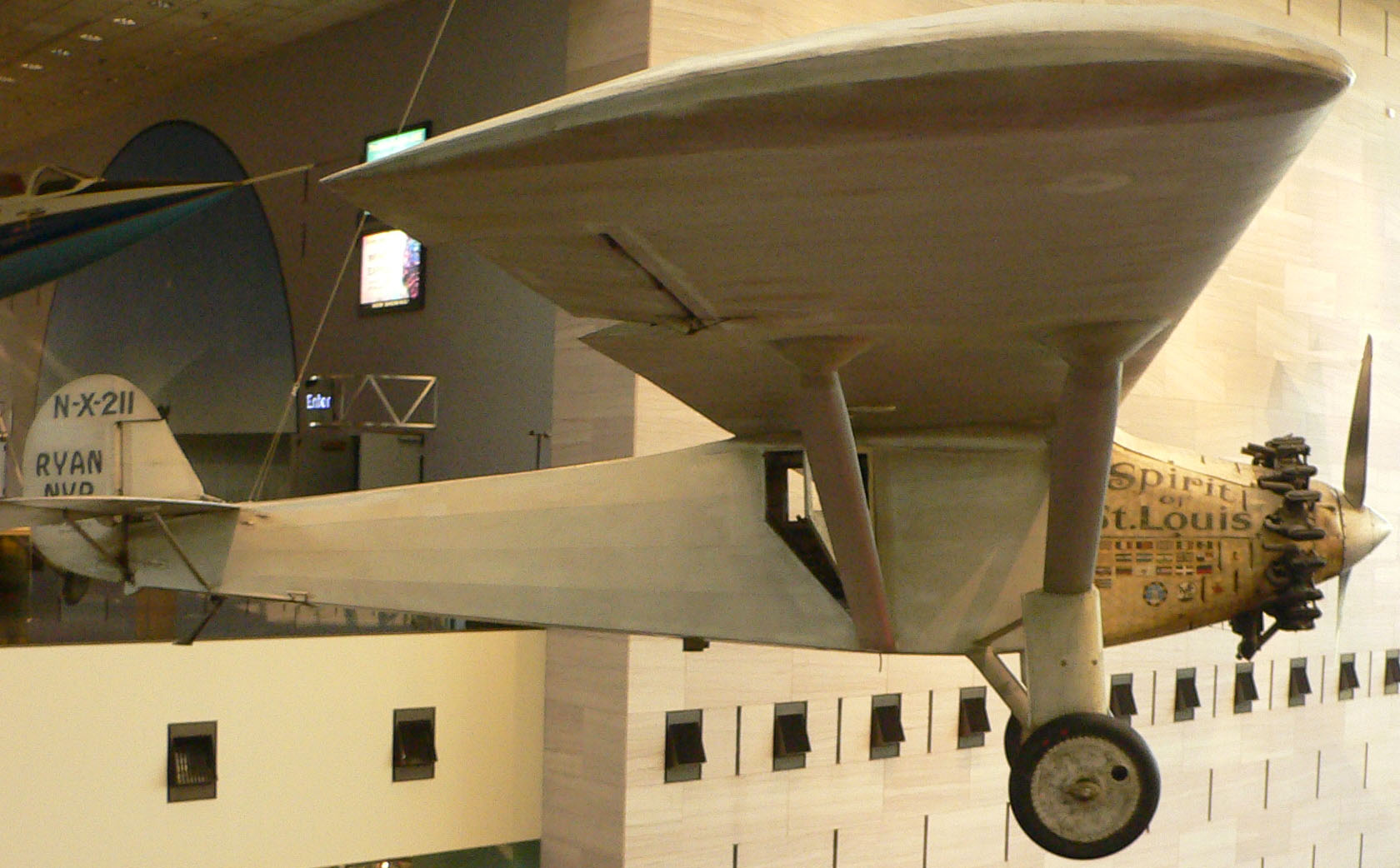
National Air And Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum (NASM) of the Smithsonian Institution is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States, dedicated to history of aviation, human flight and space exploration. Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, its main building opened on the National Mall near L'Enfant Plaza in 1976. In 2023, the museum welcomed 3.1 million visitors, making it the list of most-visited museums in the United States, fourth-most visited museum in the United States and List of most-visited museums, eleventh-most in the world. The museum is a center for research into the history and science of aviation and spaceflight, as well as planetary science and terrestrial geology and geophysics. Almost all of its spacecraft and aircraft on display are original primary or backup craft (rather than facsimiles). Its collection includes the Apollo 11 Command module Columbia, Command Module ''Columbia'', the Mercury-Atlas 6, ''Friendship 7'' capsule which was flown by John Glenn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the Federal government of the United States#branches, three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. The Smithsonian Institution has historical holdings of over 157 million items, 21 museums, 21 libraries, 14 education and research centers, a zoo, and historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in Washington, D.C. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York (state), New York, and Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wescott Myers
John Wescott Myers (born Los Angeles, California, June 13, 1911 – died Beverly Hills, California, January 31, 2008) was a World War II test pilot who helped develop the P-61 fighter plane. The son of Louis Wescott Myers, a prominent California judge and lawyer, Myers was educated at The Thacher School, Stanford University and Harvard Law School. He returned to California to practice law, but was an avid pilot. When the US entered World War II, Myers took a job in the legal department of Lockheed, hoping to get piloting work. He was soon ferrying aircraft for them as a sideline, and did some test-piloting on the YP-38. He joined Northrop Aircraft in 1941 as chief engineering test pilot, flying many of Northrop's experimental planes. He was heavily involved with the P-61 program; he test-piloted the plane, and then taught American pilots on the Pacific Front to fly it. He was called "Maestro" for his flying skills. While in New Guinea, Myers gave a ride to fellow trainer Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muroc Air Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is Edwards, California. Established in the 1930s as Muroc Field, the facility was renamed Muroc Army Airfield and then Muroc Air Force Base before its final renaming in 1950 for World War II USAAF veteran and test pilot Capt. Glen Edwards. Edwards is the home of the Air Force Test Center, Air Force Test Pilot School, and NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center. It is the Air Force Materiel Command center for conducting and supporting research and development of flight, as well as testing and evaluating aerospace systems from concept to combat. It also hosts many test activities conducted by America's commercial aerospace industry. Notable occurrences at Edwards include Chuck Yeager's flight that broke the sound barrier in the Bell X-1, test fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |