|
Wybren Jan Buma
Wybren Jan Buma (1910–1999) was a scholar of Frisian languages and history, known for editing and translating Germanic law codes including the Asega-bôk The Asega-bôk, English: "Book of the Judges", was part of the legal code for the Rustringian Frisians. The oldest known manuscript version, the ''First Riustring Manuscript'' (now in Oldenburg) is, besides the oldest extant text in Frisian, one of ... (his was the first modern scholarly edition thereof), the legal code for the Rustringian Frisians and one of the oldest surviving continental Germanic law codes. References Reference bibliography * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Buma, Wybren Jan Germanic studies scholars 1910 births 1999 deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
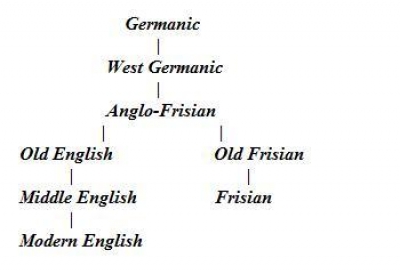
Frisian Languages
The Frisian (, ) languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 500,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and foreign influences. There are three different Frisian branches, which are usually called the Frisian languages, despite the fact that their so-called dialects are often not mutually intelligible even within these branches. These branches are: West Frisian, which is by far the most spoken of the three and is an official language in the Dutch province of Friesland, where it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frisian History
Frisia has changed dramatically over time, both through floods and through a change in identity. It is part of the Nordwestblock which is a hypothetical historic region linked by language and culture. Roman times The Frisii began settling in Frisia around 500 BC. According to Pliny the Younger, in Roman times, the Frisians (or, as it may be, their close neighbours, the Chauci) lived on terps, man-made hills. According to other sources, the Frisians lived along a broader expanse of the North Sea (or "Frisian Sea") coast. Frisia at this time comprised the present-day provinces of Friesland and North Holland. Frisians appear to have been among the Germanic groups who invaded Britain during the so-called Migration period (''Völkerwanderung''), as Angles and Saxons travelled from their home base through Frisian territory in what is now northern Germany and central Netherlands.Mostert, "Frisians", pp. 194-5. Kingdom of Frisia The 8th-century historian Bede also used the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asega-bôk
The Asega-bôk, English: "Book of the Judges", was part of the legal code for the Rustringian Frisians. The oldest known manuscript version, the ''First Riustring Manuscript'' (now in Oldenburg) is, besides the oldest extant text in Frisian, one of the oldest remaining continental codes of Germanic law. History and background A codex containing a copy of the code, the First Riustring Manuscript, survives in the archives at Oldenburg (24, 1, Ab. 1). While Joseph Bosworth believed it to have been written somewhere between 1212 and 1250 A.D., twentieth-century scholars date it ca. 1300, although some of the materials that it incorporates date to 1050. That version is the oldest surviving work written in Old Frisian, and one of the oldest surviving continental Germanic law codes (the Gulating law, possibly ca. 1150, may be older). The first modern scholarly edition was published in 1961 by Wybren Jan Buma in Dutch; a year later Buma, in cooperation with Germanic law scholar Wilhelm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rüstringen
Rüstringen or Rustringen was an old Frisian gau, which lies between the modern district Friesland and the Weser river in modern Lower Saxony. Nowadays, only a small part of the original territory remains, namely the Butjadingen peninsula. The largest part of historical Rüstringen has been lost to the sea in the Middle Ages due to various storm surges and now forms the Jadebusen The Jade Bight (or ''Jade Bay''; german: Jadebusen) is a bight or bay on the North Sea coast of Germany. It was formerly known simply as ''Jade'' or ''Jahde''. Because of the very low input of freshwater, it is classified as a bay rather than an ... bay. External linksButjadingen and Rüstringen Geography of Lower Saxony {{LowerSaxony-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculum (journal)
''Speculum: A Journal of Medieval Studies'' is a quarterly academic journal An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and ... published by University of Chicago Press on behalf of the Medieval Academy of America. Established in 1926 by Edward Kennard Rand, it is widely regarded as the most prestigious journal in medieval studies. The journal's primary focus is on the time period from 500 to 1500 in Western Europe, but also on related subjects such as Byzantine, Hebrew, Arabic, Armenian studies, Armenian and Slavic peoples, Slavic studies. , the Editor-in-chief, editor is Katherine Jansen, Katherine L. Jansen. The organization and its journal were first proposed in 1921 at a meeting of the Modern Language Association, and the journal's focus was interdisciplinary from its beginning, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Studies Scholars
Germanic may refer to: * Germanic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group identified by their use of the Germanic languages ** List of ancient Germanic peoples and tribes * Germanic languages :* Proto-Germanic language, a reconstructed proto-language of all the Germanic languages * Germanic name * Germanic mythology, myths associated with Germanic paganism * Germanic religion (other) * SS ''Germanic'' (1874), a White Star Line steamship See also * Germania (other) * Germanus (other) * German (other) * Germanicia Caesarea Marash (Armenian: Մարաշ), officially Kahramanmaraş () and historically Germanicea (Greek: Γερμανίκεια), is a city in the Mediterranean Region of Turkey and the administrative center of Kahramanmaraş Province. Before 1973, Kahra ... * * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1910 Births
Year 191 ( CXCI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Bradua (or, less frequently, year 944 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 191 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Parthia * King Vologases IV of Parthia dies after a 44-year reign, and is succeeded by his son Vologases V. China * A coalition of Chinese warlords from the east of Hangu Pass launches a punitive campaign against the warlord Dong Zhuo, who seized control of the central government in 189, and held the figurehead Emperor Xian hostage. After suffering some defeats against the coalition forces, Dong Zhuo forcefully relocates the imperial capital from Luoyang to Chang'an. Before leaving, Dong Zhuo orders his troops to loot the tombs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |