|
Wundt Illusion
The Wundt illusion is an optical illusion that was first described by the German psychologist Wilhelm Wundt Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt (; ; 16 August 1832 – 31 August 1920) was a German physiologist, philosopher, and professor, known today as one of the fathers of modern psychology. Wundt, who distinguished psychology as a science from philosophy and ... in the 19th century. The two red vertical lines are both straight, but they may look as if they are bowed inwards to some observers. The distortion is induced by the crooked lines on the background, as in the Orbison illusion. The Hering illusion produces a similar, but inverted effect. Vertical-horizontal illusion Another variant of the Wundt illusion is the '' Horizontal–Vertical Illusion'', introduced by Wundt in 1858. The two intersecting lines are equal in length although the vertical line appears to be much longer. The horizontal line needs to be extended up to 30% to match the perceptual length of the vertical lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Illusion
Within visual perception, an optical illusion (also called a visual illusion) is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual perception, percept that arguably appears to differ from reality. Illusions come in a wide variety; their categorization is difficult because the underlying cause is often not clear but a classification proposed by Richard Gregory is useful as an orientation. According to that, there are three main classes: physical, physiological, and cognitive illusions, and in each class there are four kinds: Ambiguities, distortions, paradoxes, and fictions. A classical example for a physical distortion would be the apparent bending of a stick half immerged in water; an example for a physiological paradox is the motion aftereffect (where, despite movement, position remains unchanged). An example for a physiological fiction is an afterimage. Three typical cognitive distortions are the Ponzo illusion, Ponzo, Poggendorff illusion, Poggendorff, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Wundt
Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt (; ; 16 August 1832 – 31 August 1920) was a German physiologist, philosopher, and professor, known today as one of the fathers of modern psychology. Wundt, who distinguished psychology as a science from philosophy and biology, was the first person ever to call himself a psychologist. He is widely regarded as the "father of experimental psychology"."Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt" in ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy''. In 1879, at the , Wundt founded the first formal laboratory for psychological research. This marked psychology as an independent field of study. By creating this laboratory he was able to establish psychology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbison Illusion
The Orbison illusion (or Orbison's illusion) is an optical illusion first described by American psychologist William Orbison (1912–1952) in 1939. The illusion consists of a two dimensional figure, such as a circle or square, superimposed over a background of radial line A cylindrical coordinate system is a three-dimensional coordinate system that specifies point positions by the distance from a chosen reference axis ''(axis L in the image opposite)'', the direction from the axis relative to a chosen reference d ...s or concentric circles. The result is an optical illusion in which both the figure and the rectangle which contains it appear distorted; in particular, squares appear slightly bulged, circles appear elliptical, and the containing rectangle appears tilted. References * * Optical illusions {{psych-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hering Illusion
The Hering illusion is one of the geometrical-optical illusions Geometrical-optical illusions are visual illusions, also optical illusions, in which the geometrical properties of what is seen differ from those of the corresponding objects in the visual field. Geometrical properties In studying geometry one co ... and was discovered by the German physiologist Ewald Hering in 1861. When two straight and parallel lines are presented in front of radial background (like the spokes of a bicycle), the lines appear as if they were bowed outwards. The Orbison illusion is one of its variants, while the Wundt illusion produces a similar, but inverted effect. There are several possible explanations for why perceptual distortion produced by the radiating pattern. The illusion was ascribed by Hering to an overestimation of the angle made at the points of intersection. If true, then the straightness of the parallel lines yields to that of the radiating lines, implying that there is a hie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
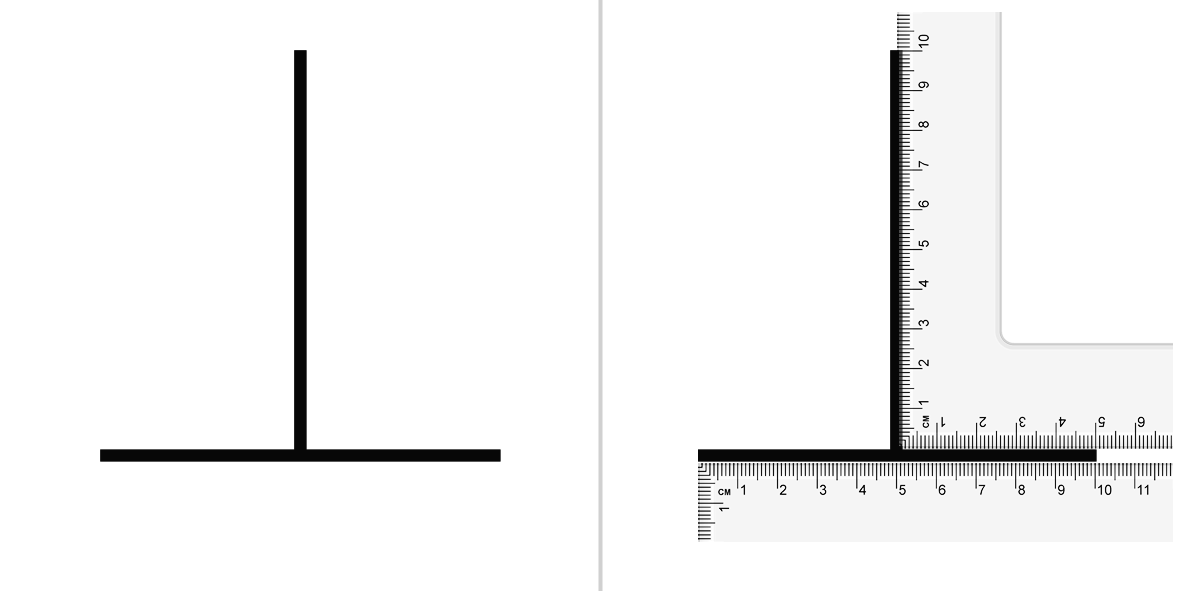
Vertical–horizontal Illusion
The vertical–horizontal illusion is the tendency for observers to overestimate the length of a vertical line relative to a horizontal line of the same length. This involves a bisecting component that causes the bisecting line to appear longer than the line that is bisected. People often overestimate or underestimate the length of the bisecting line relative to the bisected line of the same length. This even happens if people are aware that the lines are of the same length. Cross-cultural differences in susceptibility to the vertical–horizontal illusion have been noted. People from Western cultures and people living in urban landscapes show more susceptibility than those living in eastern or open landscapes. Types of vertical–horizontal illusions There are several different configurations of the vertical–horizontal illusion. The three configurations which seem to produce the highest illusion magnitude are the L configuration, the plus (+) configuration, and the inverted-T c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |