|
Writings On Reckoning
The ''Book on Numbers and Computation'' (), or the ''Writings on Reckoning'', is one of the earliest known Chinese mathematical treatises. It was written during the early Western Han dynasty, sometime between 202 BC and 186 BC.Liu et al. (2003), 9. It was preserved among the Zhangjiashan Han bamboo texts and contains similar mathematical problems and principles found in the later Eastern Han period text of ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art''. Discovery The text was found in tomb M247 of the burial grounds near Zhangjiashan, Jiangling County, in Hubei province, excavated in December–January 1983–1984. This tomb belonged to an anonymous civil servant in early West Han dynasty. In the tomb were 1200 bamboo strips written in ink. Originally the strips were bound together with string, but the string had rotted away and it took Chinese scholars 17 years to piece together the strips. As well as the mathematical work the strips covered government statutes, law repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Mathematics
Mathematics emerged independently in China by the 11th century BCE. The Chinese independently developed a real number system that includes significantly large and negative numbers, more than one numeral system (base 2, binary and base 10, decimal), algebra, geometry, number theory and trigonometry. Since the Han dynasty, as diophantine approximation being a prominent numerical method, the Chinese made substantial progress on polynomial evaluation. Algorithms like regula falsi and expressions like simple continued fractions are widely used and have been well-documented ever since. They deliberately find the principal nth root, ''n''th root of positive numbers and the zero of a function, roots of equations. The major texts from the period, ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' and the ''Book on Numbers and Computation'' gave detailed processes for solving various mathematical problems in daily life. All procedures were computed using a counting board in both texts, and they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Xin (scholar)
Liu Xin (23 CE), courtesy name Zijun, was a Chinese astronomer, classicist, imperial librarian, mathematician, and politician during the Han dynasty#Western Han, Western Han and Xin dynasty, Xin dynasties. He later changed his name to Liu Xiu () due to the naming taboo of Emperor Ai of Han. He was the son of Imperial librarian Liu Xiang (scholar), Liu Xiang and an associate of other eminent thinkers such as the philosopher Huan Tan. Liu was a prominent supporter of the Old Text classics. Early life Liu Xin was the son of Confucian scholar Liu Xiang (scholar), Liu Xiang (77–6 BCE). Liu was a distant relative of Liu Bang, the founder of the Han dynasty, and was thus a member of the ruling dynastic clan (the Liu (surname), Liu family). Liu Xin's paternal grandfather ranked as a ''hou'' (, roughly 'Ranged Marquis#Han dynasty, marquess'). As a young man, Liu helped his father in cataloguing the contents of the imperial library, and his friendship with the well-connected mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty Texts
Han may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * "Han", a fifth season episode of ''The West Wing'' * Han (musician), born Han Ji-sung, a South Korean singer-songwriter, rapper, and record producer, member of Stray Kids * Han Lue, a character in the ''Fast & Furious'' franchise * Han Solo, a character in the ''Star Wars'' franchise Education * Han school, Japan, Edo period * HAN University of Applied Sciences, in the Netherlands People Ethnic groups * Han Chinese, or Han people (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group ** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese people who are fully or partially of Han Chinese descent * Han Minjok, or Han people (): the Korean native name referring to Koreans * Hän: one of the First Nations peoples of Canada Names * Han (name), a given name and surname ** Han (Chinese surname), also Haan, Hahn or Hann, the Romanized spelling of many Chinese family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Mathematics Texts
Chinese may refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China. **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese characters in traditional and simplified forms) *** Standard Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Manuscripts
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of abstract objects that consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Artifacts Of China
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, excavation, and eventually analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Wenjun
Wu Wenjun ( zh, s=吴文俊; 12 May 1919 – 7 May 2017), also commonly known as Wu Wen-tsün, was a Chinese mathematician, historian, and writer. He was an academician at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), best known for Wu class, Wu formula, and Wu's method of characteristic set. Biography Wu's ancestral hometown was Jiashan, Zhejiang. He was born in Shanghai in 1919. Wu graduated from Shanghai Jiao Tong University in 1940. In 1945, he taught several months at Hangchow University (later merged into Zhejiang University) in Hangzhou. In 1947, he went to France for further study at the University of Strasbourg. In 1949, he received his PhD from that university, for his thesis ''Sur les classes caractéristiques des structures fibrées sphériques'', written under the direction of Charles Ehresmann. Afterwards, he did some work in Paris with René Thom and discovered the Wu class and Wu formula in algebraic topology. In 1951 he was appointed to a post at Peking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a popular science magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publishes a monthly Dutch-language edition. First published on 22 November 1956, ''New Scientist'' has been available in online form since 1996. Sold in retail outlets (paper edition) and on subscription (paper and/or online), the magazine covers news, features, reviews and commentary on science, technology and their implications. ''New Scientist'' also publishes speculative articles, ranging from the technical to the philosophical. ''New Scientist'' was acquired by Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) in March 2021. History Ownership The magazine was founded in 1956 by Tom Margerison, Max Raison and Nicholas Harrison as ''The New Scientist'', with Issue 1 on 22 November 1956, priced at one shilling (). An article in the magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Dauben
Joseph Warren Dauben (born December 29, 1944, Santa Monica) is a Herbert H. Lehman Distinguished Professor of History at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York. He obtained his PhD from Harvard University in 1972. His PhD thesis ''The early development of Cantorian Set Theory'' was supervised by Dirk Struik. Dauben's fields of expertise are the history of science, the history of mathematics, the Scientific Revolution, the sociology of science, intellectual history, the 17th and 18th centuries, the history of Chinese science, and the history of botany. Positions Dauben is a 1980 Guggenheim fellow. He is a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and a fellow of the New York Academy of Sciences (since 1982).Faculty profile , Institute for the History of Natural Science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needham Research Institute
The Needham Research Institute (NRI; zh , t = 李約瑟研究所 ), located on the grounds of Robinson College, in Cambridge, England, is a centre for research into the history of science, technology and medicine in East Asia. The institute is named after the biochemist and historian Joseph Needham, who initiated the '' Science and Civilisation in China'' series. The current director is Mei Jianjun, a noted archaeo-metallurgist. The organization was founded as the East Asian History of Science Trust in August 1968. In June 1983 the trustees conferred the title Needham Research Institute. The Trustees of the NRI is a registered charity. The institute grew out of Needham's research collection, which was originally housed in Gonville and Caius College, where he was Master until his retirement in 1976. After several moves, it moved into its current purpose-built structure in Robinson College in 1991. The building was designed in the Chinese style, and has been described by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Cullen
Christopher Cullen is an English sinologist born in 1946. He has an MA from University of Oxford in engineering and a PhD from the School of Oriental and African Studies in classical Chinese. He is Director Emeritus of the Needham Research Institute and General Editor of the Science and Civilisation in China series, succeeding Joseph Needham. His own area of research is the Han Dynasty and he translated the Book on Numbers and Computation The ''Book on Numbers and Computation'' (), or the ''Writings on Reckoning'', is one of the earliest known Chinese mathematical treatises. It was written during the early Western Han dynasty, sometime between 202 BC and 186 BC.Liu et al. (2003), ... into English. Publications * * * --, and Vivienne Lo, eds., Medieval Chinese Medicine: The Dunhuang Medical Manuscripts'' Taylor & Francis, Needham Research Institute Series, 2004. . References External links * Christopher Cullen,Making sense of the cosmos in ancient China" Cambridge Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
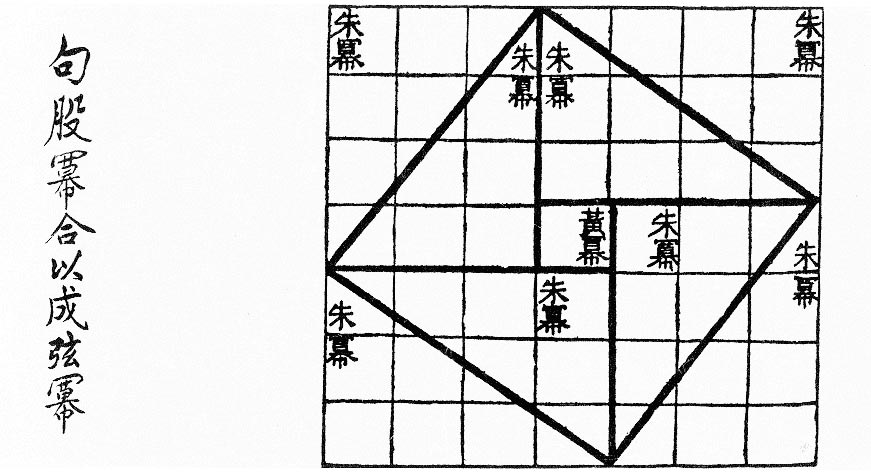
Zhoubi Suanjing
The ''Zhoubi Suanjing'', also known by many other names, is an ancient Chinese astronomical and mathematical work. The ''Zhoubi'' is most famous for its presentation of Chinese cosmology and a form of the Pythagorean theorem. It claims to present 246 problems worked out by the Duke of Zhou as well as members of his court, placing its composition during the 11th century BC. However, the present form of the book does not seem to be earlier than the Eastern Han (25–220 AD), with some additions and commentaries continuing to be added for several more centuries. The book was included as part of the '' Ten Computational Canons''. Names The work's original title was simply the ''Zhoubi'': the character is a literary term for the femur or thighbone but in context only refers to one or more gnomons, large sticks whose shadows were used for Chinese calendrical and astronomical calculations. Because of the ambiguous nature of the character , it has been alternatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |