|
Write XOR Execute
W^X (write xor execute, pronounced ''W xor X'') is a security policy in operating systems and software frameworks. It implements executable space protection by ensuring every memory page (a fixed-size block in a program’s virtual address space, the memory layout it uses) is either writable or executable, but not both. Without such protection, a program can write (as data "W") CPU instructions in an area of memory intended for data and then run (as executable "X"; or read-execute "RX") those instructions. This can be dangerous if the writer of the memory is malicious. The terminology was first introduced in 2003 for Unix-like systems, but is today also used by some multi-platform systems (such as .NET). Other operating systems have adopted similar policies under different names (e.g., DEP in Windows). In Unix, W^X is typically controlled via the mprotect system call. It is relatively simple on processor architectures supporting fine-grained page permissions, such as SPARC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Exclusive Or
Exclusive or, exclusive disjunction, exclusive alternation, logical non-equivalence, or logical inequality is a logical operator whose negation is the logical biconditional. With two inputs, XOR is true if and only if the inputs differ (one is true, one is false). With multiple inputs, XOR is true if and only if the number of true inputs is odd. It gains the name "exclusive or" because the meaning of "or" is ambiguous when both operands are true. XOR ''excludes'' that case. Some informal ways of describing XOR are "one or the other but not both", "either one or the other", and "A or B, but not A and B". It is symbolized by the prefix operator J Translated as and by the infix operators XOR (, , or ), EOR, EXOR, \dot, \overline, \underline, , \oplus, \nleftrightarrow, and \not\equiv. Definition The truth table of A\nleftrightarrow B shows that it outputs true whenever the inputs differ: Equivalences, elimination, and introduction Exclusive disjunction essentially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
NX Bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certain areas of the virtual address space as non-executable, preventing the processor from running any code stored there. This technique, known as executable space protection or Write XOR Execute, protects computers from malicious software that attempts to insert harmful code into another program’s data storage area and execute it, such as in a buffer overflow attack. The term "NX bit" was introduced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) as a marketing term. Intel markets this feature as the XD bit (execute disable), while the MIPS architecture refers to it as the XI bit (execute inhibit). In the ARM architecture, introduced in ARMv6, it is known as XN (execute never). The term NX bit is often used broadly to describe similar executable space p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Address Space Layout Randomization
Address space layout randomization (ASLR) is a computer security technique involved in preventing exploitation of memory corruption vulnerabilities. In order to prevent an attacker from reliably redirecting code execution to, for example, a particular exploited function in memory, ASLR randomly arranges the address space positions of key data areas of a process, including the base of the executable and the positions of the stack, heap and libraries. When applied to the kernel, this technique is called ''kernel address space layout randomization'' (''KASLR''). History The Linux PaX project first coined the term "ASLR", and published the first design and implementation of ASLR in July 2001 as a patch for the Linux kernel. It is seen as a complete implementation, providing a patch for kernel stack randomization since October 2002. The first mainstream operating system to support ASLR by default was OpenBSD version 3.4 in 2003, followed by Linux in 2005. Benefits Addres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
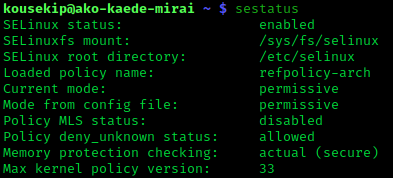 |
SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a Linux kernel security module that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls (MAC). SELinux is a set of kernel modifications and user-space tools that have been added to various Linux distributions. Its architecture strives to separate enforcement of security decisions from the security policy, and streamlines the amount of software involved with security policy enforcement. The key concepts underlying SELinux can be traced to several earlier projects by the United States National Security Agency (NSA). Overview The NSA Security-enhanced Linux Team describes NSA SELinux as a set of patches to the Linux kernel and utilities to provide a strong, flexible, mandatory access control (MAC) architecture into the major subsystems of the kernel. It provides an enhanced mechanism to enforce the separation of information based on confidentiality and integrity requirements, which allows th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. Firefox is available for Windows 10 or later versions of Windows, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and other operating systems, such as ReactOS. Firefox is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser. Firefox is the spiritual successor of Netscape Navigator, as the Mozilla community was created by Netscape in 1998, before its acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Just-in-time Compilation
In computing, just-in-time (JIT) compilation (also dynamic translation or run-time compilations) is compilation (of computer code) during execution of a program (at run time) rather than before execution. This may consist of source code translation but is more commonly bytecode translation to machine code, which is then executed directly. A system implementing a JIT compiler typically continuously analyses the code being executed and identifies parts of the code where the speedup gained from compilation or recompilation would outweigh the overhead of compiling that code. JIT compilation is a combination of the two traditional approaches to translation to machine code— ahead-of-time compilation (AOT), and interpretation—and combines some advantages and drawbacks of both. Roughly, JIT compilation combines the speed of compiled code with the flexibility of interpretation, with the overhead of an interpreter and the additional overhead of compiling and linking (not j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Run-time System
In computer programming, a runtime system or runtime environment is a sub-system that exists in the computer where a program is created, as well as in the computers where the program is intended to be run. The name comes from the compile time and runtime division from compiled languages, which similarly distinguishes the computer processes involved in the creation of a program (compilation) and its execution in the target machine (the runtime). Most programming languages have some form of runtime system that provides an environment in which programs run. This environment may address a number of issues including the management of application memory, how the program accesses variables, mechanisms for passing parameters between procedures, interfacing with the operating system (OS), among others. The compiler makes assumptions depending on the specific runtime system to generate correct code. Typically the runtime system will have some responsibility for setting up and managing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Library (computer Science)
In computing, a library is a collection of resources that can be leveraged during software development to implement a computer program. Commonly, a library consists of executable code such as compiled functions and classes, or a library can be a collection of source code. A resource library may contain data such as images and text. A library can be used by multiple, independent consumers (programs and other libraries). This differs from resources defined in a program which can usually only be used by that program. When a consumer uses a library resource, it gains the value of the library without having to implement it itself. Libraries encourage software reuse in a modular fashion. Libraries can use other libraries resulting in a hierarchy of libraries in a program. When writing code that uses a library, a programmer only needs to know how to use it not its internal details. For example, a program could use a library that abstracts a complicated system call so that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Trampoline (computers)
In computer programming, the word trampoline has a number of meanings, and is generally associated with jump instructions (i.e. moving to different code paths). Low-level programming Trampolines (sometimes referred to as indirect jump vectors) are memory locations holding addresses pointing to interrupt service routines, I/O routines, etc. Execution jumps into the trampoline and then immediately jumps out, or bounces, hence the term ''trampoline''. They have many uses: * Trampoline can be used to overcome the limitations imposed by a central processing unit (CPU) architecture that expects to always find vectors in fixed locations. * When an operating system is booted on a symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) machine, only one processor, the bootstrap processor, will be active. After the operating system has configured itself, it will instruct the other processors to jump to a piece of trampoline code that will initialize the processors and wait for the operating system to start sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Linker (computing)
A linker or link editor is a computer program that combines intermediate software build files such as object file, object and library (computing), library files into a single executable file such as a program or library. A linker is often part of a toolchain that includes a compiler and/or assembler (computing), assembler that generates intermediate files that the linker processes. The linker may be integrated with other toolchain development tool, tools such that the user does not interact with the linker directly. A simpler version that writes its Input/output, output directly to Computer memory, memory is called the ''loader'', though loader (computing), loading is typically considered a separate process. Overview Computer programs typically are composed of several parts or modules; these parts/modules do not need to be contained within a single object file, and in such cases refer to each other using symbol (computing), symbols as addresses into other modules, which are ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Exec Shield
Exec Shield is a project started at Red Hat, Inc in late 2002 with the aim of reducing the risk of worm or other automated remote attacks on Linux systems. The first result of the project was a security patch for the Linux kernel that emulates an NX bit on x86 CPUs that lack a native NX implementation in hardware. While the Exec Shield project has had many other components, some people refer to this first patch as Exec Shield. The first Exec Shield patch attempts to flag data memory as non-executable and program memory as non-writeable. This suppresses many security exploits, such as those stemming from buffer overflows and other techniques relying on overwriting data and inserting code into those structures. Exec Shield also supplies some address space layout randomization for the mmap() and heap base. The patch additionally increases the difficulty of inserting and executing shellcode, rendering most exploits ineffective. No application recompilation is necessary to fully uti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Line In The Sand
Line in the sand is an idiom, a metaphorical (sometimes literal) point beyond which no further advance will be accepted or made. Related terms include unilateral boundary setting, red lines and ultimatums to define clear consequences if a line is crossed. Origin Biblical link to John 8John 8:6. Some have (perhaps erroneously) interpreted Jesus' writing in the sand, as drawing a line in the sand in order to address those who are about to stone a woman caught in adultery. However, the literal translation is not that he drew a line in the sand, but that he "wrote" (or "drew lines" in some translations) in the sand, an important distinction. The exact origin of the phrase is unknown: the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' suggests a transitional use from 1950, but a definitely figurative use only as late as 1978: There is reference to an actual line being drawn in several historical, or legendary, military events: *One of the earliest recorded instance is in Indian epic ''Ramaya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |