|
Write-protect
Write protection is any physical mechanism that prevents writing, modifying, or erasing data on a device. Most commercial software, audio and video on writeable media is write-protected when distributed. Examples * IBM -inch magnetic tape reels, introduced in the 1950s, had a circular groove on one side of the reel, into which a soft plastic ring had to be placed in order to write on the tape. ("No ring, no write.") * Audio cassettes and VHS videocassettes have tabs on the top/rear edge that can be broken off (uncovered = protected). * 8 and -inch floppies can have, respectively, write-protect and write-enable notches on the right side (8-inch punched = protected; -inch covered/notch not present = protected). A common practice with single-sided floppies was to punch a second notch on the opposite side of the disk to enable use of both sides of the media, creating a flippy disk, so called because one originally had to flip the disk over to use the other side. * -inch floppy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USB Flash Drive
A USB flash drive (also called a thumb drive) is a data storage device that includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface. It is typically removable, rewritable and much smaller than an optical disc. Most weigh less than . Since first appearing on the market in late 2000, as with virtually all other computer memory devices, storage capacities have risen while prices have dropped. , flash drives with anywhere from 8 to 256 gigabytes (GB) were frequently sold, while 512 GB and 1 terabyte (TB) units were less frequent. As of 2018, 2 TB flash drives were the largest available in terms of storage capacity. Some allow up to 100,000 write/erase cycles, depending on the exact type of memory chip used, and are thought to physically last between 10 and 100 years under normal circumstances ( shelf storage timeUSB flash drives allow reading, writing, and erasing of data, with some allowing 1 million write/erase cycles in each cell of memory: if there were 100 use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Write Protect Ring
Write protection is any physical mechanism that prevents writing, modifying, or erasing data on a device. Most commercial software, audio and video on writeable media is write-protected when distributed. Examples * IBM -inch magnetic tape reels, introduced in the 1950s, had a circular groove on one side of the reel, into which a soft plastic ring had to be placed in order to write on the tape. ("No ring, no write.") * Audio cassettes and VHS videocassettes have tabs on the top/rear edge that can be broken off (uncovered = protected). * 8 and -inch floppies can have, respectively, write-protect and write-enable notches on the right side (8-inch punched = protected; -inch covered/notch not present = protected). A common practice with single-sided floppies was to punch a second notch on the opposite side of the disk to enable use of both sides of the media, creating a flippy disk, so called because one originally had to flip the disk over to use the other side. * -inch floppy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Cassette
The Compact Cassette or Musicassette (MC), also commonly called the tape cassette, cassette tape, audio cassette, or simply tape or cassette, is an analog magnetic tape recording format for audio recording and playback. Invented by Lou Ottens and his team at the Dutch company Philips in 1963, Compact Cassettes come in two forms, either already containing content as a prerecorded cassette (''Musicassette''), or as a fully recordable "blank" cassette. Both forms have two sides and are reversible by the user. Although other tape cassette formats have also existed - for example the Microcassette - the generic term ''cassette tape'' is normally always used to refer to the Compact Cassette because of its ubiquity. Its uses have ranged from portable audio to home recording to data storage for early microcomputers; the Compact Cassette technology was originally designed for dictation machines, but improvements in fidelity led to it supplanting the stereo 8-track cartridge and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Digital
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices. The standard was introduced in August 1999 by joint efforts between SanDisk, Panasonic (Matsushita) and Toshiba as an improvement over MultiMediaCards (MMCs), and has become the industry standard. The three companies formed SD-3C, LLC, a company that licenses and enforces intellectual property rights associated with SD memory cards and SD host and ancillary products. The companies also formed the SD Association (SDA), a non-profit organization, in January 2000 to promote and create SD Card standards. SDA today has about 1,000 member companies. The SDA uses several trademarked logos owned and licensed by SD-3C to enforce compliance with its specifications and assure users of compatibility. History 1999–2003: Creation In 1999, SanDisk, Panasonic (Matsushita), and Toshiba agreed to develop and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copyright Infringement
Copyright infringement (at times referred to as piracy) is the use of works protected by copyright without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, such as the right to reproduce, distribute, display or perform the protected work, or to make derivative works. The copyright holder is typically the work's creator, or a publisher or other business to whom copyright has been assigned. Copyright holders routinely invoke legal and technological measures to prevent and penalize copyright infringement. Copyright infringement disputes are usually resolved through direct negotiation, a notice and take down process, or litigation in civil court. Egregious or large-scale commercial infringement, especially when it involves counterfeiting, is sometimes prosecuted via the criminal justice system. Shifting public expectations, advances in digital technology and the increasing reach of the Internet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Read-only Access
Most file systems include attributes of files and directories that control the ability of users to read, change, navigate, and execute the contents of the file system. In some cases, menu options or functions may be made visible or hidden depending on a user's permission level; this kind of user interface is referred to as permission-driven. Two types of permissions are widely available: traditional Unix file system permissions and access-control lists (ACLs) which are capable of more specific control. File system variations The original File Allocation Table file system has a per-file all-user read-only attribute. NTFS implemented in Microsoft Windows NT and its derivatives, use ACLs to provide a complex set of permissions. OpenVMS uses a permission scheme similar to that of Unix. There are four categories (system, owner, group, and world) and four types of access permissions (Read, Write, Execute and Delete). The categories are not mutually disjoint: World includes Group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Forensics
Computer forensics (also known as computer forensic science) is a branch of digital forensic science pertaining to evidence found in computers and digital storage media. The goal of computer forensics is to examine digital media in a forensically sound manner with the aim of identifying, preserving, recovering, analyzing and presenting facts and opinions about the digital information. Although it is most often associated with the investigation of a wide variety of computer crime, computer forensics may also be used in civil proceedings. The discipline involves similar techniques and principles to data recovery, but with additional guidelines and practices designed to create a legal audit trail. Evidence from computer forensics investigations is usually subjected to the same guidelines and practices of other digital evidence. It has been used in a number of high-profile cases and is accepted as reliable within U.S. and European court systems. Overview In the early 1980s per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
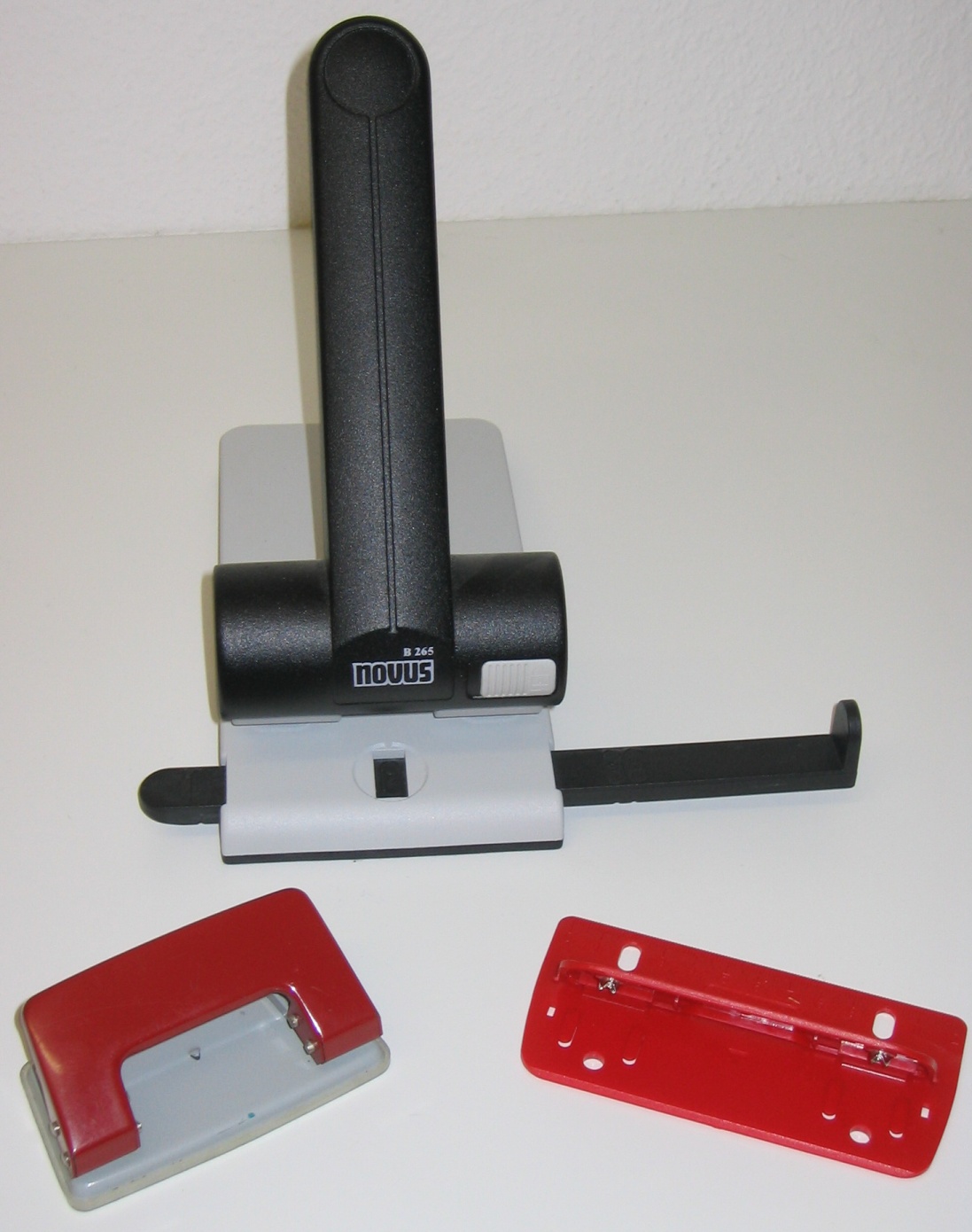
Hole Punch
A hole punch, also known as hole puncher, or paper puncher, is an office tool that is used to create holes in sheets of paper, often for the purpose of collecting the sheets in a binder or folder. A ''hole punch'' can also refer to similar tools for other materials, such as leather, cloth, or plastic or metal sheets. Mechanism The essential parts of a hole punch are the ''handle'', the ''punch head'', and the ''die''. The punch head is typically a cylinder, with a flat end called the ''face''. The die is a flat plate, with a hole matching the head. The head can move, while the die is fixed in place. Both head and die are usually made of a hard metal, with precise tolerances. One or more sheets of paper are inserted between the head and the die, with the flat face of the head parallel to the surface of the sheets. Moving the handle pushes the head straight through the sheets of paper. The hard edge of the punch vs the die cuts a hole in the paper, pushing the cut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
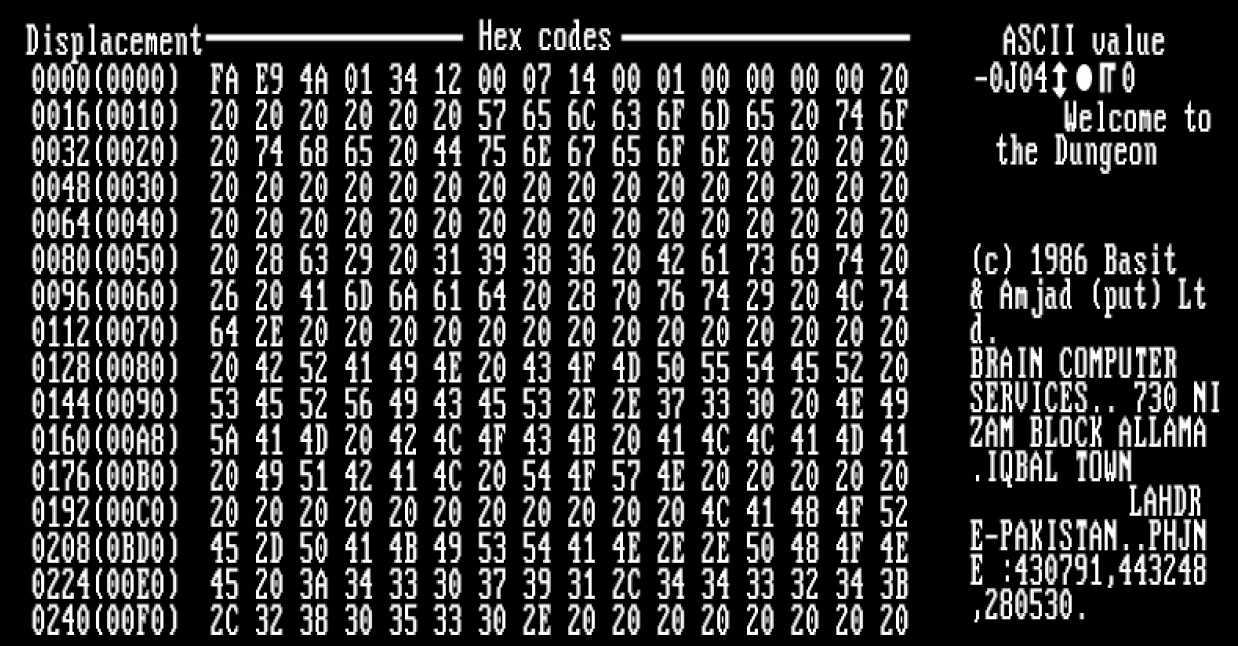
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. A computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems and to spread the virus. Viruses use complex anti-detection/stealth strategies to evade antivirus software. Motives for creating viruses can inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |