|
Worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateria, bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limb (anatomy), limbs, and usually no eyes. Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete worms (bristle worms); for the African giant earthworm, ''Microchaetus rappi''; and for the marine nemertean worm (bootlace worm), ''Lineus longissimus''. Various types of worm occupy a small variety of parasitism, parasitic niches, living inside the bodies of other animals. Free-living worm species do not live on land but instead live in marine or freshwater environments or underground by burrowing. In biology, "worm" refers to an obsolete taxon, ''Vermes'', used by Carl Linnaeus, Carolus Linnaeus and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck for all non-arthropod invertebrate animals, now seen to be paraphyletic. The name stems from the Old English word ''wikt:wyrm, wyrm''. Most animals called "worms" are invertebrates, but the term is also use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguis Fragilis
The common slow worm (''Anguis fragilis'') is a species of legless lizard native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple, steelworm, and hazelworm. The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a blindsnake (although the slow worm's eyes are functional). The common slow worm, i.e. the species ''Anguis fragilis'', is often called simply "slow worm", though all species of the species complex comprising the genus ''Anguis'' are also called "slow worms". Common slow worms are semifossorial (burrowing) lizards that spend much of their time hiding underneath objects. The skin of slow worms is smooth, with scales that do not overlap. Like many other lizards, they autotomize, meaning that they have the ability to shed their tails to escape predators. While the tail regrows, it does not reach its original length. In the UK, slow worms are commonly encountered in gardens and allotments, where they can be enco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
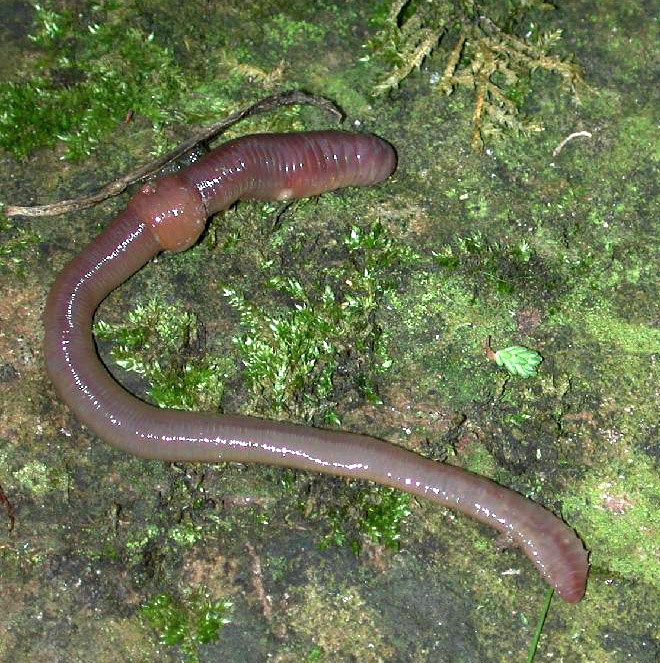
Annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lineus Longissimus
The bootlace worm (''Lineus longissimus'') is a species of ribbon worm and one of the longest known animals, with specimens up to long being reported. Its mucus is highly toxic. Taxonomy The bootlace worm is in the phylum Nemertea or ribbon worms. It is the most common nemertean found along the coasts of Great Britain, Britain. Description Bootlace worms may grow very long but are usually only in width. The body is brown with lighter (longitudinal) stripes. Its mucus contains a relatively strong neurotoxin which it uses as a defense against predators. When handled, it produces large amounts of thick mucus with a faint pungent smell, reminiscent of iron or sewage. This toxic mucus has been shown to kill crabs and cockroaches, and could have applications as an agricultural insecticide. In 1864, William M'Intosh described a specimen that had washed ashore in the aftermath of a severe storm by St Andrews, Scotland, which was more than long, longer than the longest known lion's ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases. They are classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa. Unlike the flatworms, nematodes have a tubular digestive system, with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species are uncertain. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity suggested there are over 25,000. Estimates of the total number of extant species are su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetognatha
The Chaetognatha or chaetognaths (meaning ''bristle-jaws'') are a phylum of predatory marine worms that are a major component of plankton worldwide. Commonly known as arrow worms, they are mostly pelagic; however about 20% of the known species are benthic, and can attach to algae and rocks. They are found in all marine waters, from surface tropical waters and shallow tide pools to the deep sea and polar regions. Most chaetognaths are transparent and are torpedo shaped, but some deep-sea species are orange. They range in size from . Chaetognaths were first recorded by the Dutch naturalist Martinus Slabber in 1775. As of 2021, biologists recognize 133 modern species assigned to over 26 genera and eight families. Despite the limited diversity of species, the number of individuals is large. Arrow worms are strictly related to and possibly belonging to Gnathifera, a clade of protostomes that do not belong to either Ecdysozoa or Lophotrochozoa. Anatomy Chaetognaths are transpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biological evolution occurred and proceeded in accordance with Naturalism (philosophy), natural laws. Lamarck fought in the Seven Years' War against Prussia, and was awarded a commission for bravery on the battlefield. Posted to Monaco, Lamarck became interested in natural history and resolved to study medicine.#Packard, Packard (1901), p. 15. He retired from the army after being injured in 1766, and returned to his medical studies. Lamarck developed a particular interest in botany, and later, after he published the three-volume work ''Flore françoise'' (1778), he gained membership of the French Academy of Sciences in 1779. Lamarck became involved in the Jardin des Plantes and was appointed to the Chair of Botany in 1788. When the French Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform (worm-shaped) or serpentine (snake-shaped) amphibians with small or sometimes nonexistent eyes. They mostly live hidden in soil or in streambeds, and this cryptic lifestyle renders caecilians among the least familiar amphibians. Modern caecilians live in the tropics of South America, South and Central America, Africa, and southern Asia. Caecilians feed on small subterranean creatures, such as earthworms. The body is cylindrical and often darkly coloured, and the skull is bullet-shaped and strongly built. Caecilian heads have several unique adaptations, including fused cranial and jaw bones, a two-part system of jaw muscles, and a Chemoreceptor, chemosensory tentacle in front of the eye. The skin is slimy and bears ringlike markings or grooves and may contain scales. Modern caecilians are a clade, the Order (biology), order Gymnophiona (or Apoda ), one of the three living amphibian groups alongside Anura (frogs) and Urodela (sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
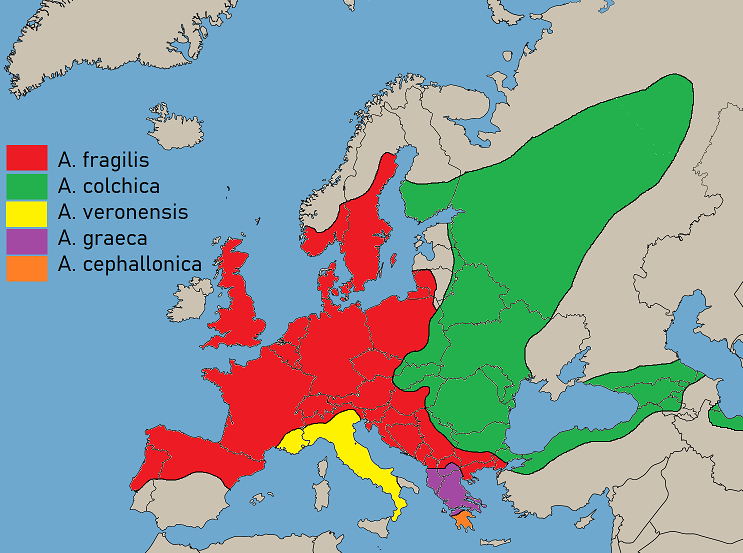
Anguis
Slow wormsThe "slow-" in slowworm is distinct from the English adjective ''slow'' ("not fast"); the word comes from Old English ''slāwyrm'', where ''slā-'' means "slowworm" and ''wyrm'' means "serpent, reptile". () (also called blindworms and hazelworms) are a small genus (''Anguis'') of snake-like legless lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus contains five extant living species, including the Anguis fragilis, common slow worm (''A. fragilis''), the Anguis colchica, eastern slow worm (''A. colchica''), the Anguis graeca, Greek slow worm (''A. graeca''), the Peloponnese slow worm (''A. cephalonnica''), and the Anguis veronensis, Italian slow worm (''A. veronensis''). There are also known fossil species. Description Slow worms are typically grey-brown, with the females having a coppery sheen and two lateral black stripes, and the males displaying Electric blue (color), electric blue spots, particularly in the breeding season. They viviparous, give birth to live young, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maggot
A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, hoverflies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies. Etymology "Maggot" is not a technical term and should not be taken as such; in many standard textbooks of entomology, it does not appear in the index at all. In many non-technical texts, the term is used for insect larvae in general. Other sources have coined their own definitions; for example: "The term applies to a grub when all trace of limbs has disappeared" and "Applied to the footless larvae of Diptera".Smith, John. BExplanation of terms used in entomology Brooklyn Entomological Society, 1906. Additionally, in ''Flies: The Natural History and Diversity of Diptera'', the author claims maggots "are larvae of higher Brachycera (Cyclorrhapha)." Maggot-like fly larvae are of significance in ecology and medicine; among other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermes
Vermes ("vermin/vermes") is an obsolete taxon used by Carl Linnaeus and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck for non-arthropod invertebrate animals. Linnaeus In Linnaeus's ''Systema Naturae'', the Vermes had the rank of class (biology), class, occupying the 6th (and last) slot of his animal systematics. It was divided into the following order (biology), orders, all except the Lithophyta containing (in modern terms) organisms from a variety of phyla: * Intestina, including horsehair worms, earthworms, roundworms, liver flukes, leeches, hagfishes, and shipworms * Mollusca, including slugs, sea slugs, polychaetes, sea mouse, sea mice, priapulids, salps, jellyfish, starfish, and sea urchins * Testacea, including chitons, barnacles, clams, cockle (bivalve), cockles, nautiluses, snails and serpulidae, serpulid worms * Lithophyta, including various corals * Zoophyta, including bryozoans, coralline algae, ''Hydra (genus), Hydra'', sea pens, tapeworms, and ''Volvox'' Apart from the Mollusca, unders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemertea
Nemertea is a phylum of animals also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms, consisting of about 1300 known species. Most ribbon worms are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. Many have patterns of yellow, orange, red and green coloration. The foregut, stomach and intestine run a little below the midline of the body, the anus is at the tip of the tail, and the mouth is under the front. A little above the gut is the , a cavity which mostly runs above the midline and ends a little short of the rear of the body. All species have a proboscis which lies in the rhynchocoel when inactive but wikt:eversion, everts to emerge just above the mouth to capture the animal's prey with venom. A highly extensible muscle in the back of the rhynchocoel pulls the proboscis in when an attack ends. A few species with stubby bodies Filter feeders, filter feed and have suckers at the front and back ends, with which they attach to a Hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |