|
Wolffenstein–Böters Reaction
The Wolffenstein–Böters reaction is an organic reaction converting benzene to picric acid by a mixture of aqueous nitric acid and mercury(II) nitrate. The reaction, which involves simultaneous nitration and oxidation, was first reported by the German chemists Richard Wolffenstein and Oskar Böters in 1906. According to one series of studies the mercury nitrate first takes benzene to the corresponding nitroso compound and through the diazonium salt to the phenol. The presence of nitrite is essential for the reaction; picric acid formation is prevented when urea, a trap for nitrous acid, is added to the mixture. From then on the reaction proceeds as a regular aromatic nitration.''The Oxynitration of Benzene. I. Studies Relating to the Reaction Mechanisms''Marvin Carmack, Manuel M. Baizer, G. Richard Handrick, L. W. Kissinger, and Edward H. Specht J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1947; 69(4) pp 785 - 790; A conceptually related reaction is the Bohn–Schmidt reaction, dating to 1889, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, mechanistic organic photochemistry, photochemical reactions and organic redox reaction, redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions. The oldest organic reactions are combustion of organic fuels and saponification of fats to make soap. Modern organic chemistry starts with the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. In the history of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awards have been given for the invention of specific organic reactions such as the Grignard reaction in 1912, the Diels–Alder reaction in 1950, the Wittig reaction in 1979 and olefin metathesis in 2005. Classifications Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazonium Salt
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. The parent, compound where R is hydrogen, is diazenylium. Structure and general properties Arene derivatives According to X-ray crystallography the linkage is linear in typical diazonium salts. The bond distance in benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is 1.083(3) Å, which is almost identical to that for dinitrogen molecule (N≡N). The linear free energy constants σm and σp indicate that the diazonium group is strongly electron-withdrawing. Thus, the diazonio-substituted phenols and benzoic acids have greatly reduced p''K''a values compared to their unsubstituted counterparts. The p''K''a of phenolic proton of 4-hydroxybenzenediazonium is 3.4, versus 9.9 for phenol itself. In other words, the diazonium group raises the ionization constant ''K'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitration Reactions
In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group () into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters () between alcohols and nitric acid (as occurs in the synthesis of nitroglycerin). The difference between the resulting molecular structures of nitro compounds and nitrates () is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom (typically carbon or another nitrogen atom), whereas in nitrate esters (also called organic nitrates), the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom (nitrito group). There are many major industrial applications of nitration in the strict sense; the most important by volume are for the production of nitroaromatic compounds such as nitrobenzene. The technology is long-standing and mature. : Nitration reactions are notably used for the production of explosiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic organic compound with formula . Several isomers exist but these terms usually refer to 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein the ketone, keto groups are located on the central ring. It is used as a digester additive to Pulp (paper), wood pulp for papermaking. Many Anthraquinones, anthraquinone derivatives are generated by organisms or synthesised industrially for use as Anthraquinone dyes, dyes, pharmaceuticals, and Catalysis, catalysts. Anthraquinone is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly solubility, soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite. Synthesis There are several current industrial methods to produce 9,10-anthraquinone: # The oxidation of anthracene. Chromium(VI) is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Se and atomic number 34. It has various physical appearances, including a brick-red powder, a vitreous black solid, and a grey metallic-looking form. It seldom occurs in this elemental state or as pure ore compounds in Earth's crust. Selenium ( ) was discovered in 1817 by , who noted the similarity of the new element to the previously discovered tellurium (named for the Earth). Selenium is found in :Sulfide minerals, metal sulfide ores, where it substitutes for sulfur. Commercially, selenium is produced as a byproduct in the refining of these ores. Minerals that are pure selenide or selenate compounds are rare. The chief commercial uses for selenium today are glassmaking and pigments. Selenium is a semiconductor and is used in photocells. Applications in electronics, once important, have been mostly replaced with silicon semiconductor devices. Selenium is still used in a few types of Direct current, DC power surge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless, and Viscosity, viscous liquid that is Miscibility, miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not occur naturally due to its Dehydration reaction, strong affinity to water vapor; it is Hygroscopy, hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties, making it highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid but, to the contrary, dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is releas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohn–Schmidt Reaction
The Bohn–Schmidt reaction, a named reaction in chemistry, introduces a hydroxy group at an anthraquinone system. The anthraquinone must already have at least one hydroxy group. The reaction was first described in 1889 by René Bohn (1862–1922) and in 1891 by Robert Emanuel Schmidt (1864–1938), two German industrial chemists. René Bohn is one of the few industrial chemists after whom a reaction is named. In 1901, he made indanthrone from 2-aminoanthraquinone and thus laid the basis for a new group of dyes. Reaction mechanism The postulated reaction mechanism is explained below for the example of 2-hydroxyanthraquinone: The sulfuric acid protonates the keto group of the anthraquinone 1. This causes a shift of the electrons to the oxonium ion in molecule 2. This shift enables the sulfuric acid to attack the carbenium ion 3 which is formed. The sulfuric acid oxidizes the resulting hydroxyanthracenone 5, which is then Protonation, protonated and the reaction starts all ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor base (chemistry), alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably metabolic waste#Nitrogen wastes, nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
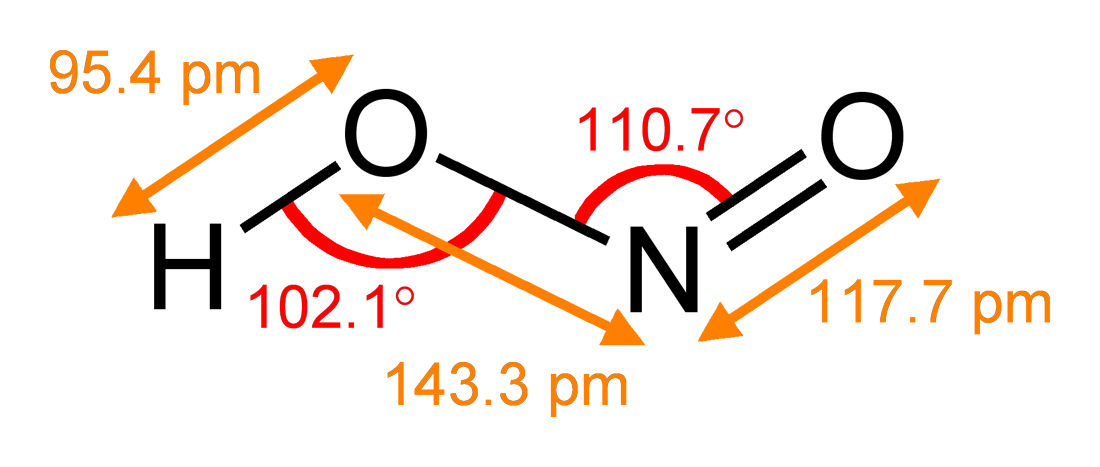
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. It is acutely toxic and is considered a health hazard. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds, and is a liquid when manufactured. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, explosives such as picric acid, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitroso
In organic chemistry, nitroso refers to a functional group in which the nitric oxide () group is attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as ''C''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosoalkanes; ), ''S''-nitroso compounds ( nitrosothiols; ), ''N''-nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines, ), and ''O''-nitroso compounds ( alkyl nitrites; ). Synthesis Nitroso compounds can be prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds or by the oxidation of hydroxylamines. Ortho-nitrosophenols may be produced by the Baudisch reaction. In the Fischer–Hepp rearrangement, aromatic 4-nitrosoanilines are prepared from the corresponding nitrosamines. Properties Nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer–dimer equilibrium. The azobenzene ''N'',''N'-''dioxide (Ar(–O)N+=+N(O–)Ar) dimers, which are often pale yellow, are generally favored in the solid state, whereas the deep-green monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |