|
Wobblie
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), whose members are nicknamed "Wobblies", is an international labor union founded in Chicago, United States in 1905. The nickname's origin is uncertain. Its ideology combines general unionism with industrial unionism, as it is a general union, subdivided between the various industries which employ its members. The philosophy and tactics of the IWW are described as "revolutionary industrial unionism", with ties to socialist, syndicalist, and anarchist labor movements. In the 1910s and early 1920s, the IWW achieved many of its short-term goals, particularly in the American West, and cut across traditional guild and union lines to organize workers in a variety of trades and industries. At their peak in August 1917, IWW membership was estimated at more than 150,000, with active wings in the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zealand. However, the extremely high rate of IWW membership turnover during this era (es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Workers Of The World Philosophy And Tactics
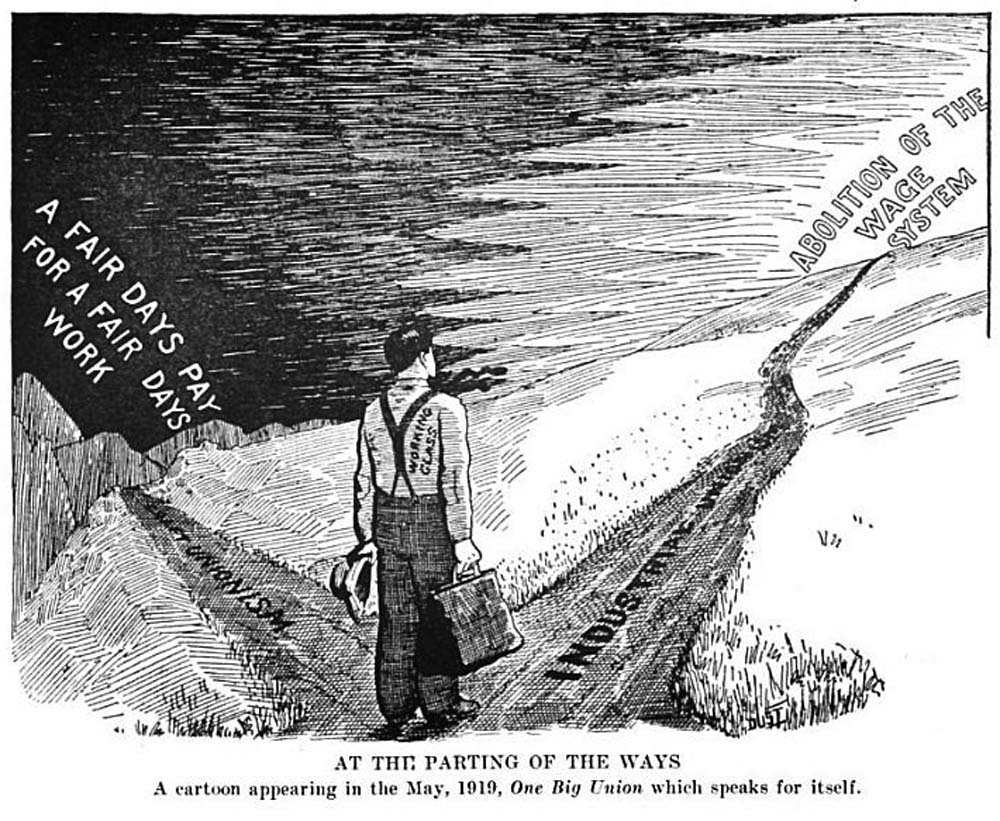
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which First Convention of the Industrial Workers of the World, was formed in Chicago in 1905 by militant unionists and their supporters due to anger over the conservatism, philosophy, and Craft unionism, craft-based structure of the American Federation of Labor (AFL). Throughout the early part of the 20th century, the philosophy and tactics of the IWW Labor federation competition in the U.S., were frequently in direct conflict with those of the AFL (forerunner of the AFL–CIO) concerning the best ways to organize workers, and how to best improve the society in which they toiled. The AFL had one guiding principle—"pure and simple trade unionism", often summarized with the slogan "A fair day's wage for a fair day's work, a fair day's pay for a fair day's work." The IWW embraced two guiding principles, fighting like the AFL for better wages, hours, and conditions, but also promoting an eventual, permanent solution t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Workers Of The World Organizational Evolution
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905. The IWW experienced a number of divisions and splits during its early history. When the office of the IWW president was abolished at the convention in 1906, deposed President Sherman and his supporters, many from the Socialist Party and the Western Federation of Miners, formed a rump IWW, which ceased to exist after about a year. Paul Frederick Brissenden, ''The I.W.W. A Study of American Syndicalism'', Columbia University, 1919, pages 174-184 After the 1908 convention of the original IWW, at which Socialist Labor Party (SLP) head Daniel DeLeon was barred from voting via credentials challenges, DeLeon and the SLP bolted to form another rump IWW, which came to be called the Detroit IWW. In 1915, the Detroit IWW changed its name to the Workers' International Industrial Union (WIIU). The WIIU continued its close relationship with the SLP, but ceased to exist in 1924. There was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndicalism
Syndicalism is a labour movement within society that, through industrial unionism, seeks to unionize workers according to industry and advance their demands through Strike action, strikes and other forms of direct action, with the eventual goal of gaining control over the means of production and the economy at large through social ownership. Syndicalist unions first emerged in Spain and North America in the 1870s, before rising to prominence in France and later emerging on other continents. Syndicalist movements were most predominant amongst the socialist movement during the interwar period that preceded the outbreak of World War II. Major syndicalist organizations included the General Confederation of Labour (France), General Confederation of Labor (CGT) in France, the Confederacion Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) in Spain, the Italian Syndicalist Union (USI), the Free Workers' Union of Germany (FAUD), and the Argentine Regional Workers' Federation (FORA). Although they did not re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Socialist Movement In The United States
The history of the socialist movement in the United States spans a variety of tendencies, including anarchists, communists, democratic socialists, social democrats, Marxists, Marxist–Leninists, Trotskyists and utopian socialists. It began with utopian communities in the early 19th century such as the Shakers, the activist visionary Josiah Warren and intentional communities inspired by Charles Fourier. In the 1860s, immigration from Europe of radical labor activists, particularly of German, Jewish, and Scandinavian backgrounds, led to the creation of the International Workingmen's Association in 1864 and Socialist Labor Party of America in 1877. In the 1870s, socialists of different tendencies were involved in early American labor organizations and struggles. These reached a high point in the 1886 Haymarket massacre in Chicago, which founded the International Workers' Day as the main labor holiday and made the eight-hour day an objective of workers organizations and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Unionism
Industrial unionism is a trade union organising method through which all workers in the same industry are organized into the same union, regardless of skill or trade, thus giving workers in one industry, or in all industries, more leverage in bargaining and in strike situations. De Leon believed that militarized Industrial unions would be the vehicle of class struggle. Industrial unionism contrasts with craft unionism, which organizes workers along lines of their specific trades. History in the United States Early history In 1893, the American Railway Union (ARU) was formed in the United States, by Eugene Debs and other railway union leaders, as an industrial union in response to the perceived limitations of craft unions. Debs himself gave an example of the inadequacies that his fellows at the time felt towards organising by craft. He recounts, that in 1888, a strike was called by train drivers and railway firemen on the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railways, but o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far-left Politics
Far-left politics, also known as extreme left politics or left-wing extremism, are politics further to the left on the left–right political spectrum than the standard political left. The term does not have a single, coherent definition; some scholars consider it to be the left of communist parties, while others broaden it to include the left of social democracy. In certain instances—especially in the news media—''far left'' has been associated with some forms of authoritarianism, anarchism, communism, and Marxism, or are characterized as groups that advocate for revolutionary socialism and related communist ideologies, or anti-capitalism and anti-globalization. Far-left terrorism consists of extremist, militant, or insurgent groups that attempt to realize their ideals through political violence rather than using democratic processes. Ideologies Far-left politics are the leftmost ideologies on the left of the left–right political spectrum. They are a hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Worker
The ''Industrial Worker'', "the voice of revolutionary industrial unionism", is the magazine of the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW, a.k.a., "Wobblies"). It is now released quarterly. The publication was printed and edited by union labor, and frequently distributed at radical bookstores, demonstrations, Strike action, strikes, and labor rallies. It covers industrial conditions, strikes, workplace organizing experiences, and features on labor history (discipline), labor history. It used to be released as a newspaper. The newspaper was first printed in journal format in Joliet, Illinois, in January 1906, incorporating ''The Voice of Labor'' (the newspaper from the former American Labor Union which had joined the IWW), and ''International Metal Worker''. It was edited by A. S. Edwards, and early contributors included Eugene V. Debs, Jack London, Daniel DeLeon, Bill Haywood, and James H. Walsh. It also included poetry by Covington Hall. When the group led by ousted President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Federation Of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutual support and disappointed in the Knights of Labor. Samuel Gompers was elected the full-time president at its founding convention and was re-elected every year except one until his death in 1924. He became the major spokesperson for the union movement. The A.F. of L. was the largest union grouping, even after the creation of the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) by unions that were expelled by the A.F. of L. in 1935. The A.F. of L. was founded and dominated by craft unions, especially in the building trades. In the late 1930s, craft affiliates expanded by organizing on an industrial union basis to meet the challenge from the CIO. The A.F. of L. and the CIO competed bitterly in the late 1930s but then cooperated during World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Politics
Radical politics denotes the intent to transform or replace the principles of a society or political system, often through social change, structural change, revolution or radical reform. The process of adopting radical views is termed radicalisation. The word derives from the Latin ("root") and Late Latin ("of or pertaining to the root, radical"). Historically, political use of the term referred exclusively to a form of progressive electoral reformism, known as Radicalism, that had developed in Europe during the 18th and 19th centuries. However, the denotation has changed since its 18th century coinage to comprehend the entire political spectrum, though retaining the connotation of "change at the root". History The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces usage of 'radical' in a political context to 1783. The ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' records the first political usage of 'radical' as ascribed to Charles James Fox, a British Whig Party parliamentarian who in 1797 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |