|
Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment
The Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE) was a space telescope with a 50cm diameter mirror for spectroscopy and polarimetry in the ultraviolet spectral range. It was used in conjunction with other telescopes on the shuttle missions STS-35 (ASTRO-1 in December 1990) and STS-67 (ASTRO-2 in March 1995). WUPPE was developed at the University of Wisconsin A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Uni ... and designed to record spectra in the wavelength range of 140 to 330 nm with a resolution of 0.6 nm while simultaneously measuring polarization degree and direction as a function of wavelength. During the two shuttle missions, a total of 260 measurements of 186 heavenly objects (mainly stars) were captured. The measurements of WUPPE have, among other things, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
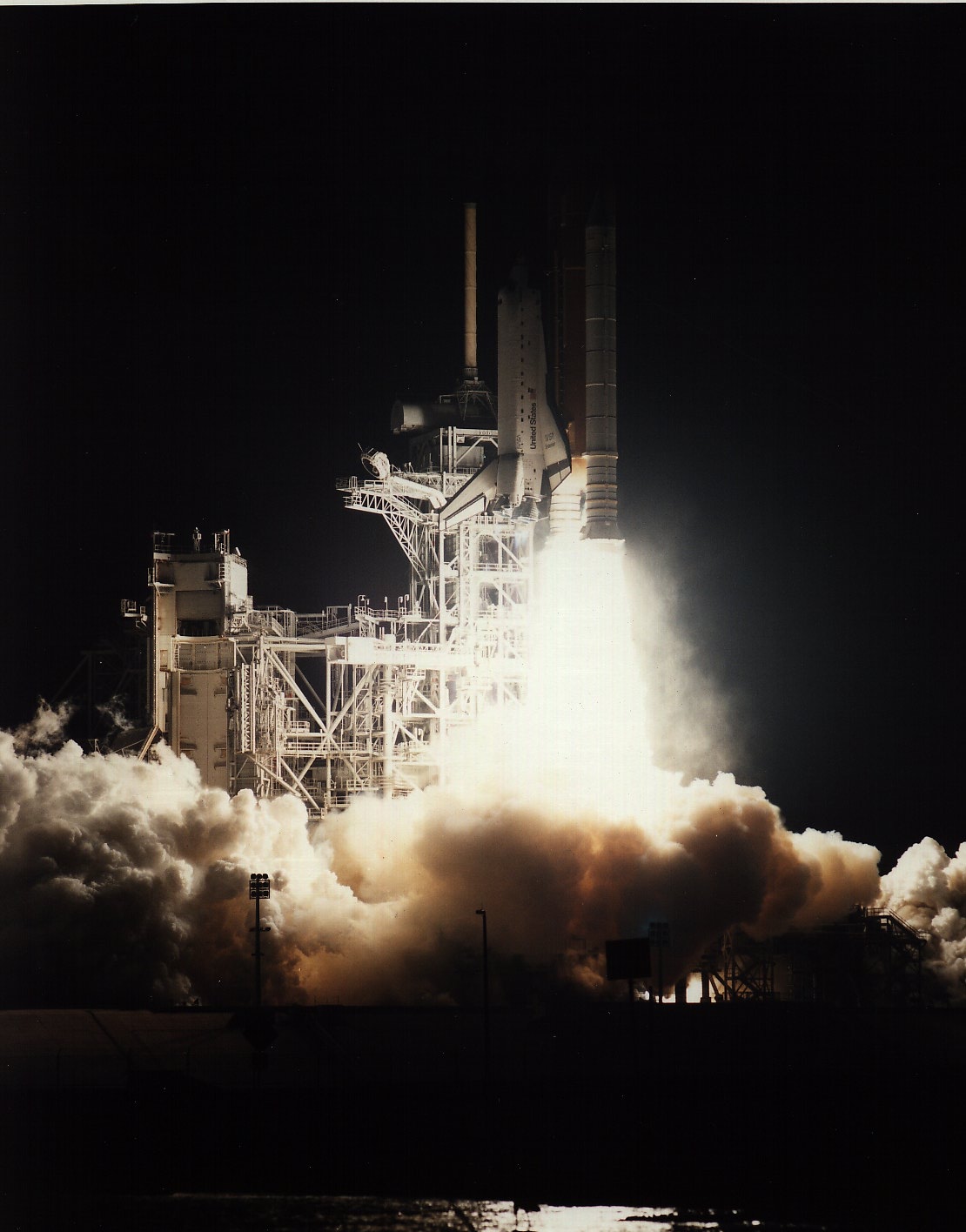
STS-35 Astro-1 Flight
STS-35 was the tenth flight of Space Shuttle ''Columbia'', the 38th shuttle mission. It was devoted to astronomical observations with ASTRO-1, a Spacelab observatory consisting of four telescopes. The mission launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on December 2, 1990. Crew Prior to the ''Challenger'' disaster, this mission was slated to launch in March 1986 as STS-61-E. Jon A. McBride was originally assigned to command this mission, which would have been his second spaceflight. He chose to retire from NASA in May 1989 and was replaced as mission commander by Vance D. Brand. In addition, Richard N. Richards (as pilot) and David C. Leestma (as mission specialist), were replaced by Guy S. Gardner and John M. Lounge respectively. Fifty-nine-year-old Brand was the oldest astronaut to fly into space until F. Story Musgrave, 61 on STS-80 in 1996, and U.S. Senator John H. Glenn Jr., 77 when he flew on STS-95 in 1998. Crew seat assignments Preparations and lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Spectroscopy
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the electromagnetic spectrum, spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including Visible light astronomy, visible light, Ultraviolet astronomy, ultraviolet, X-ray astronomy, X-ray, Infrared astronomy, infrared and Radio astronomy, radio waves that radiant energy, radiate from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance and luminosity. Spectroscopy can show the velocity of motion towards or away from the observer by measuring the Doppler effect, Doppler shift. Spectroscopy is also used to study the physical properties of many other types of celestial objects such as planets, nebulae, Galaxy, galaxies, and Active galactic nucleus, active galactic nuclei. Background Astronomical spectroscopy is used to measure three major bands of radiation in the electromagnetic spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarimetry
Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the polarization of transverse waves, most notably electromagnetic waves, such as radio or light waves. Typically polarimetry is done on electromagnetic waves that have traveled through or have been reflected, refracted or diffracted by some material in order to characterize that object. Plane polarized light: According to the wave theory of light, an ordinary ray of light is considered to be vibrating in all planes of right angles to the direction of its propagation. If this ordinary ray of light is passed through a nicol prism, the emergent ray has its vibration only in one plane. Applications Polarimetry of thin films and surfaces is commonly known as ellipsometry. Polarimetry is used in remote sensing applications, such as planetary science, astronomy, and weather radar. Polarimetry can also be included in computational analysis of waves. For example, radars often consider wave polarization in post-processing to im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-35
STS-35 was the tenth flight of Space Shuttle ''Columbia'', the 38th shuttle mission. It was devoted to astronomical observations with ASTRO-1, a Spacelab observatory consisting of four telescopes. The mission launched from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on December 2, 1990. Crew Prior to the ''Challenger'' disaster, this mission was slated to launch in March 1986 as STS-61-E. Jon A. McBride was originally assigned to command this mission, which would have been his second spaceflight. He chose to retire from NASA in May 1989 and was replaced as mission commander by Vance D. Brand. In addition, Richard N. Richards (as pilot) and David C. Leestma (as mission specialist), were replaced by Guy S. Gardner and John M. Lounge respectively. Fifty-nine-year-old Brand was the oldest astronaut to fly into space until F. Story Musgrave, 61 on STS-80 in 1996, and U.S. Senator John H. Glenn Jr., 77 when he flew on STS-95 in 1998. Crew seat assignments Preparations and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-67
STS-67 was a human spaceflight mission using that launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida on March 2, 1995. Crew Crew seat assignments Mission highlights Ultraviolet Imaging Experiments Astro-2 was the second dedicated Spacelab mission to conduct astronomical observations in the ultraviolet spectral regions (the first was the Astro-1 mission flown on STS-35). The Astro-2 Spacelab consisted of three unique instruments – the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) and the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE). These took measurements from objects within the Solar System as well as individual stars, nebulae, supernova remnants, galaxies and active extragalactic objects. The data supplemented the data obtained from the Astro-1 mission. The purpose of the UIT was to observe UV radiation from space (most UV radiation is absorbed by Earth's atmosphere and cannot be studied from the ground). The data collected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Galactic Nucleus
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that emits a significant amount of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum, with characteristics indicating that this luminosity is not produced by the stars. Such excess, non-stellar emissions have been observed in the radio waves, radio, microwave, infrared, visible spectrum, optical, ultra-violet, X-ray and gamma ray wavebands. A galaxy hosting an AGN is called an active galaxy. The non-stellar radiation from an AGN is theorized to result from the accretion (astrophysics), accretion of matter by a supermassive black hole at the center of its host galaxy. Active galactic nuclei are the most luminous persistent sources of electromagnetic radiation in the universe and, as such, can be used as a means of discovering distant objects; their evolution as a function of cosmic time also puts constraints on cosmology, models of the cosmos. The observed characteristics of an AGN depend on several properties s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |