|
Wirrina Cove
Wirrina Cove is a locality and holiday resort on the Fleurieu Peninsula, South Australia. It is located between the coastal towns of Second Valley, South Australia, Second Valley and Normanville, South Australia, Normanville on Yankalilla Bay. The holiday resort was developed from around 1972, and is located about south of Adelaide. There are various overlapping names associated with the Wirrina Cove area recorded as being used by the Kaurna people before the British colonisation of South Australia: Congeratinga (with a creek now given that name), also spelt Kongaratinga, Yarnauwingga, and Anacotilla. The location is also associated with the Dreamtime, Dreaming story of the creator ancestor Tjilbruke. Today, features at Wirrina cove include marina named Marina St. Vincent, the New Terry Hotel & Golf Resort, a variety of camping and other holiday accommodation at the Wirrina Cove Holiday Park other accommodation options. Little Gorge, near which the HMAS Hobart (D 39), HMAS ''Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Creek, South Australia
Deep Creek is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south coast of the Fleurieu Peninsula overlooking Backstairs Passage about south of the Adelaide city centre. Deep Creek's boundaries were created in August 1999 along with the selection of its name which is derived from the watercourse located within its extent. As of 2015, land use within the locality consists of land zoned both for primary production uses such as agriculture and zoned for Conservation (ethic), conservation purposes such as the protected area known as Deep Creek Conservation Park and the coastline overlooking Backstairs Passage. Deep Creek is located within the federal division of Mayo, the state electoral district of Mawson and the local government area of the District Council of Yankalilla. See also *Deep Creek (other) References Towns in South Australia Fleurieu Peninsula {{SouthAustralia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yankalilla Bay
Yankalilla Bay is a long, wide bay in south-eastern South Australia, on the Fleurieu Peninsula. It is on the south-eastern coast of the Gulf St Vincent, as it opens into the Southern Ocean. Three rivers discharge into the bay: the Bungala River, Yankalilla River (whose mouth is at Lady Bay) and Carrickalinga Creek. The rivers can adversely affect the ecology of the sea, in particular the health of the reef and seagrass. Normanville Beach and Carrickalinga Reef. Yankalilla Bay is known for being the site of the ship's graveyard of HMAS ''Hobart'', which was scuttled on 5 November 2002 off the coast between Wirrina Cove and Normanville to create a dive wreck and artificial reef An artificial reef (AR) is a human-created freshwater or marine benthic structure. Typically built in areas with a generally featureless bottom to promote Marine biology#Reefs, marine life, it may be intended to control #Erosion prevention, erosio .... Its official name is the Fleurieu Artificial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commemorative Plaque
A commemorative plaque, or simply plaque, or in other places referred to as a historical marker, historic marker, or historic plaque, is a plate of metal, ceramic, stone, wood, or other material, bearing text or an image in relief, or both, to commemorate one or more persons, an event, a former use of the place, or some other thing. Most such plaques are attached to a wall, stone, or other vertical surface. Many modern plaques and markers are used to associate the location where the plaque or marker is installed with the person, event, or item commemorated as a place worthy of visit. A monumental plaque or tablet commemorating a deceased person or persons, can be a simple form of church monument. Most modern plaques affixed in this way are commemorative of something, but not all. There are also purely religious plaques, and some signify ownership or affiliation of some sort. A plaquette is a small plaque, but in English, unlike many European languages, the term is not t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Spring
A spring is a natural exit point at which groundwater emerges from an aquifer and flows across the ground surface as surface water. It is a component of the hydrosphere, as well as a part of the water cycle. Springs have long been important for humans as a source of fresh water, especially in arid regions which have relatively little annual rainfall. Springs are driven out onto the surface by various natural forces, such as gravity and hydrostatic pressure. A spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater is known as a hot spring. The yield of spring water varies widely from a volumetric flow rate of nearly zero to more than for the biggest springs. Formation Springs are formed when groundwater flows onto the surface. This typically happens when the water table reaches above the surface level, or if the terrain depresses sharply. Springs may also be formed as a result of karst topography, aquifers or volcanic activity. Springs have also been observe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
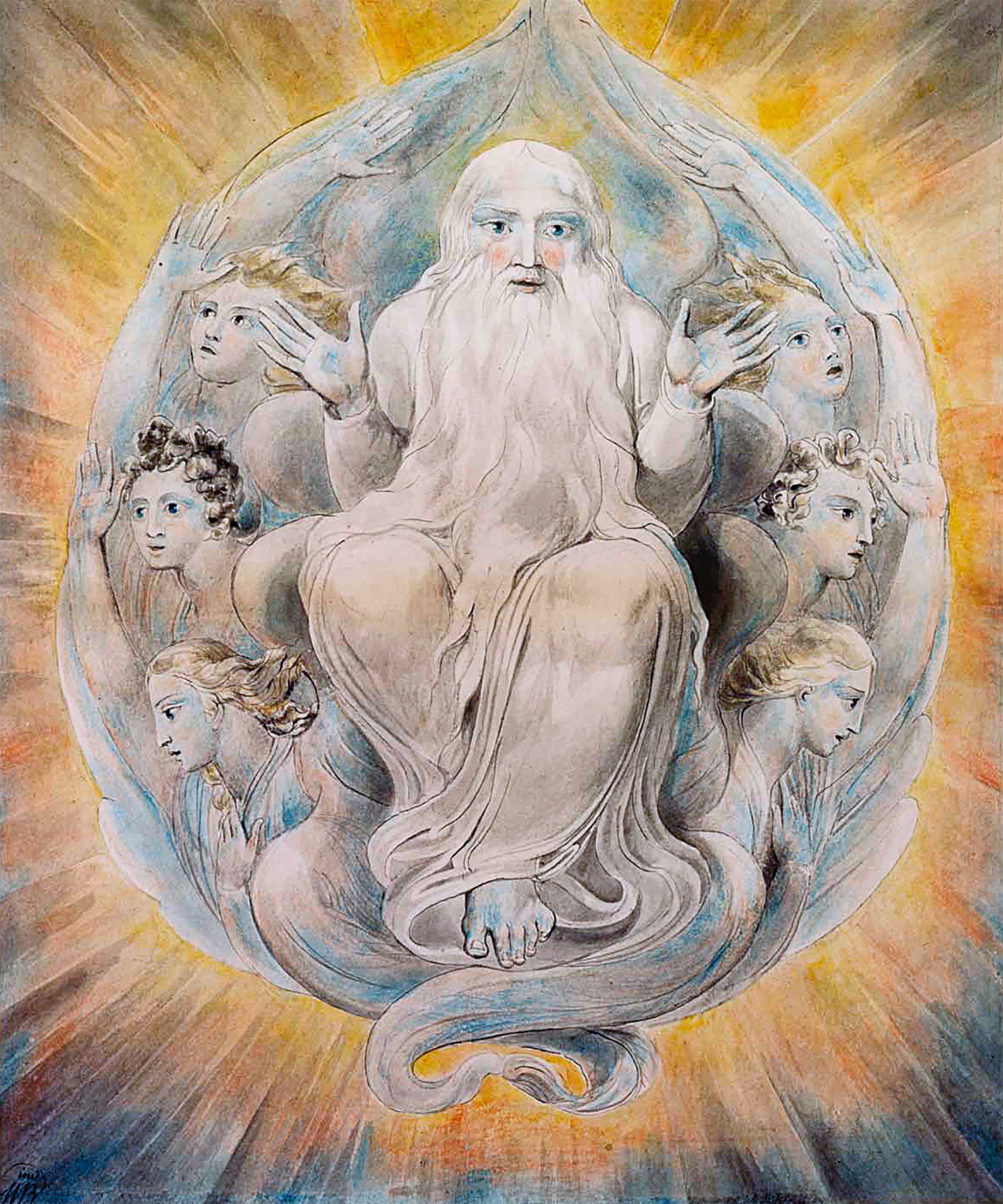
Creator Being
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a secondary creator from a primary transcendent being, identified as a primary creator.(2004) Sacred Books of the Hindus Volume 22 Part 2: Pt. 2, p. 67, R.B. Vidyarnava, Rai Bahadur Srisa Chandra Vidyarnava Monotheism Atenism Initiated by Pharaoh Akhenaten and Queen Nefertiti around 1330 BCE, during the New Kingdom period in ancient Egyptian history. They built an entirely new capital city ( Akhetaten) for themselves and worshippers of their sole creator god in a wilderness. His father used to worship Aten alongside other gods of their polytheistic religion. Aten, for a long time before his father's time, was revered as a god among the many gods and goddesses in Egypt. Atenism was countermanded by later pharaoh Tutankhamun, as chron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
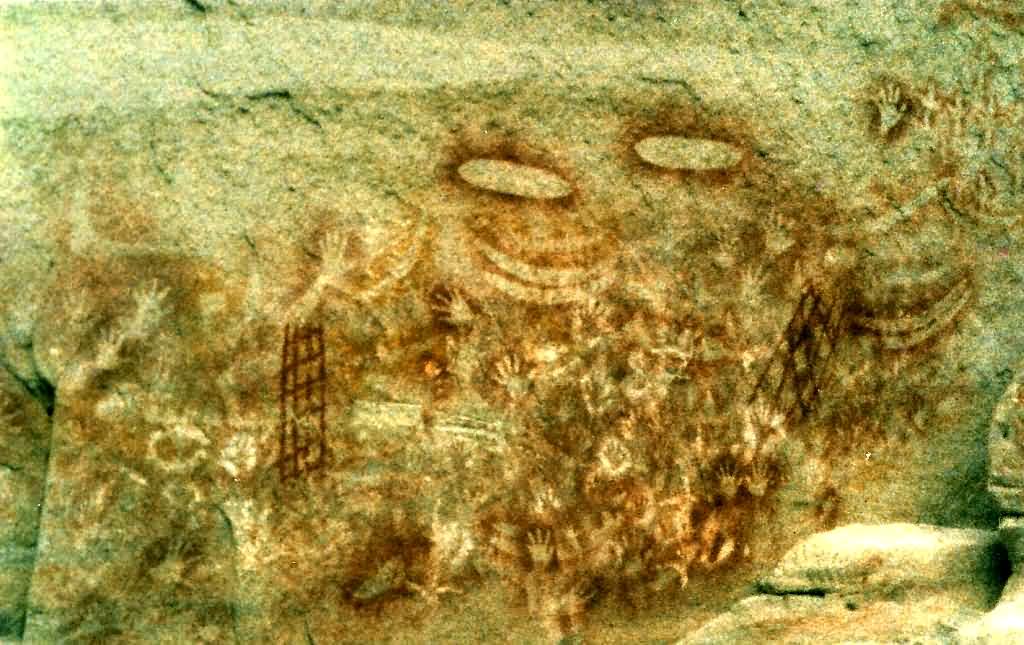
Aboriginal Australian Sacred Site
An Australian Aboriginal sacred site is a place deemed significant and meaningful by Aboriginal Australians based on their beliefs. It may include any feature in the landscape, and in coastal areas, these may lie underwater. The site's status is derived from an association with some aspect of social and cultural tradition, which is related to ancestral beings, collectively known as Dreamtime (or the Dreaming/s), who created both physical and social aspects of the world. The site may have its access restricted based on gender, clan or other Aboriginal grouping, or other factors. The sites are protected by various state- and territory-based legislation as part of Australian heritage laws, and the federal ''Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Heritage Protection Act 1984'' can be invoked as a "last resort" if the site is not considered adequately covered by legislation in the jurisdiction. The legislation also protects sites of archaeological, historical and cultural signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Owners
Native title is the set of rights, recognised by Australian law, held by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander groups or individuals to land that derive from their maintenance of their traditional laws and customs. These Aboriginal title rights were first recognised as a part of Australian common law with the decision of '' Mabo v Queensland (No 2)'' in 1992. The doctrine was subsequently implemented and modified via statute with the '' Native Title Act 1993''. The concept recognises that in certain cases there was and is a continued beneficial legal interest in land held by Indigenous peoples which survived the acquisition of radical title and sovereignty to the land by the Crown. Native title can co-exist with non-Aboriginal proprietary rights and in some cases different Aboriginal groups can exercise their native title rights over the same land. The Federal Court of Australia arranges mediation in relation to claims made by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide Plains
The Adelaide Plains (Kaurna name Tarndanya) is a plain in South Australia lying between the coast ( Gulf St Vincent) on the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges on the east. The southernmost tip of the plain is in the southern seaside suburbs of Adelaide around Brighton at the foot of the O'Halloran Hill escarpment with the south Hummocks Range and Wakefield River roughly approximating the northern boundary. Traditionally entirely occupied by the Kaurna (indigenous) people, the Adelaide Plains are crossed by a number of rivers and creeks, but several dry up during summer. The rivers (from south to north) include: the Onkaparinga/Ngangki, Sturt/Warri Torrens/Karra Wirra, Little Para, Gawler, Light/Yarralinka and Wakefield/Undalya. The plains are generally fertile with annual rainfall of about per year. The plain can be roughly divided into three parts. The southern area is now covered by the city of Adelaide, the capital of South Australia. The central area is considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
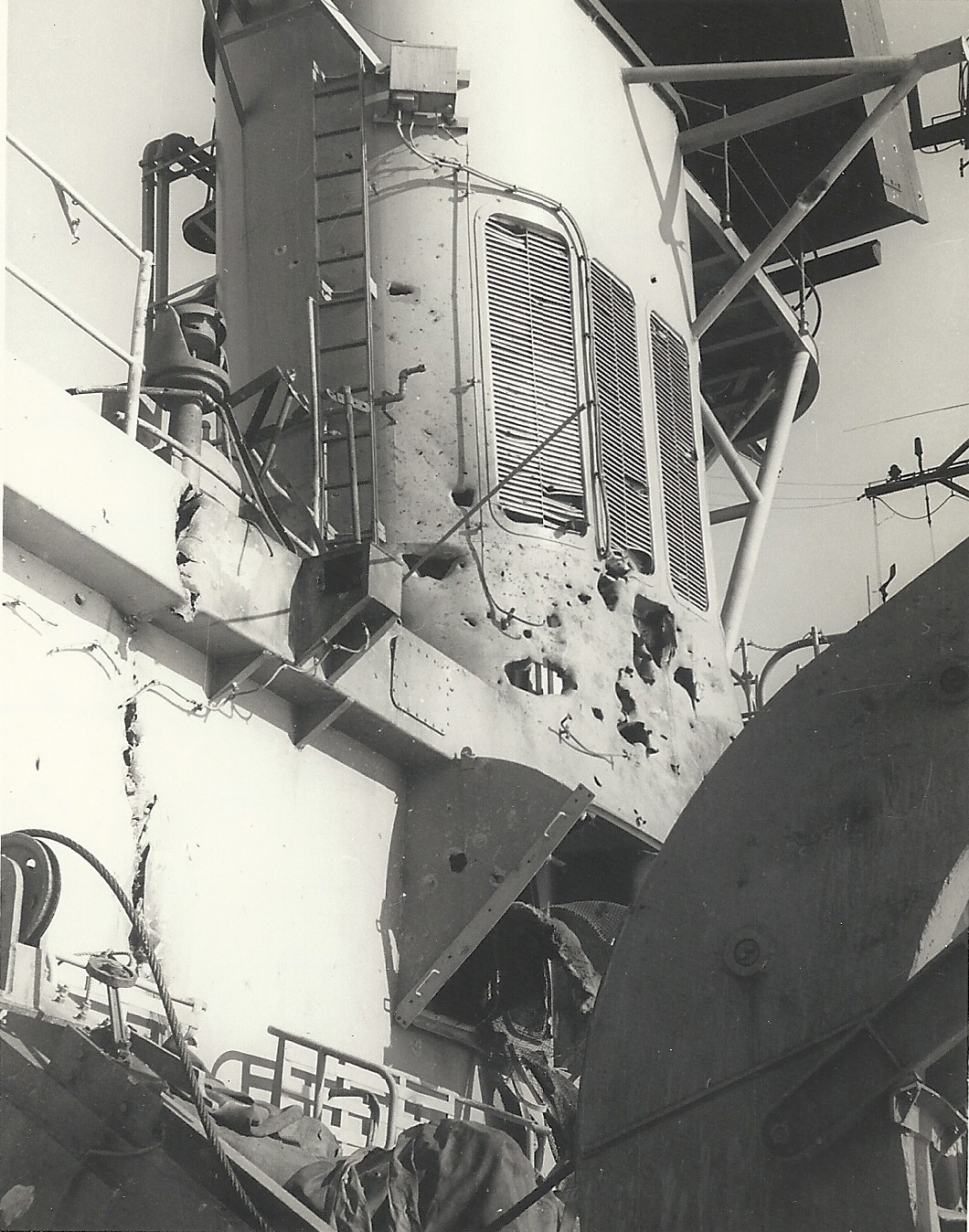
HMAS Hobart (D 39)
HMAS ''Hobart'' (D 39) was a guided missile destroyer of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). Built in the United States of America to a slight variant of the United States Navy (USN) , she was commissioned into the RAN in 1965. In March 1967, ''Hobart'' became the first RAN combat ship deployed to fight in the Vietnam War. This marked the start of consistent six-month deployments to the warzone, which continued until late 1971; ''Hobart'' was redeployed in 1969 and 1970. During the 1968 tour, the destroyer was attacked by a United States Air Force aircraft. After the Vietnam War, ''Hobart'' saw service during Operation Navy Help Darwin; the RAN disaster relief effort following Cyclone Tracy, was the first RAN ship to dock at in Western Australia, and completed a round-the-world voyage in 1976. The ship was modernised during the late 1970s. ''Hobart'' was decommissioned in 2000, and sunk as a dive wreck off South Australia. Design and construction ''Hobart'' was one of three gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marina
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : "related to the sea") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats. A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ships or cargo from freighters. The word ''marina'' may also refer to an inland wharf on a river or canal that is used exclusively by non-industrial pleasure craft such as canal narrowboat A narrowboat is a particular type of Barge, canal boat, built to fit the narrow History of the British canal system, locks of the United Kingdom. The UK's canal system provided a nationwide transport network during the Industrial Revolution, b ...s. Emplacement Marinas may be located along the banks of rivers connecting to lakes or seas and may be inland. They are also located on coastal harbors (natural or man made) or coastal lagoons, either as stand alone facilities or within a port complex. History In the 19th century, the few existing pleasure craft share ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjilbruke
Tjilbruke (also Tjirbruki, Tjilbruki, Tjirbruke, Tjirbuk or Tjirbuki,) is an important creation ancestor for the Kaurna people of the Adelaide plains in the Australian state of South Australia. Tjilbruke was a Kaurna man, who appeared in Kaurna Dreaming dating back about 11,000 years. The Tjilbruke Dreaming Track or Tjilbruke Dreaming Trail is a major Dreaming trail, which connects sites from within metropolitan Adelaide southwards as far as Cape Jervis, some of which are Aboriginal sacred sites of great significance. Man and creator-being The Tjilbruke Dreaming pre-dates European contact, probably arising when the "Adelaide plains tribe", the Kaurna, settled the area at least 2,000 years BP (as evidenced by archaeological finds at Hallett Cove, where Kaurna campsites succeeded those of the Kartan people of Kangaroo Island, who had been there tens of thousands of years earlier). ''Kaurna Yerta Parngkarra'' (Kaurna tribal country) stretches from Cape Jervis in the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreamtime
The Dreaming, also referred to as Dreamtime, is a term devised by early anthropologists to refer to a religio-cultural worldview attributed to Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology, Australian Aboriginal mythology. It was originally used by Francis James Gillen, Francis Gillen, quickly adopted by his colleague Walter Baldwin Spencer, and thereafter popularised by A. P. Elkin, who later revised his views. The Dreaming is used to represent Aboriginal concepts of "Everywhen", during which the land was inhabited by ancestral figures, often of heroic proportions or with supernatural abilities. The term is based on a rendition of the Arandic languages, Arandic word , used by the Aranda people, Aranda (Arunta, Arrernte) people of Central Australia, although it has been argued that it is based on a misunderstanding or mistranslation. Some scholars suggest that the word's meaning is closer to "Eternity, eternal, uncreated". Anthropologist William Edward Hanley Stanner, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |