|
WinChip
The WinChip series is a discontinued CPU electrical consumption, low-power Socket 7-based x86 central processing unit, processor that was designed by Centaur Technology and marketed by its parent company Integrated Device Technology, IDT. Overview Design The design of the WinChip was quite different from other processors of the time. Instead of a large gate count and die (integrated circuit), die area, IDT, using its experience from the RISC processor market, created a small and electrically efficient processor similar to the Intel 80486, 80486, because of its single Pipeline (computing), pipeline and Out of Order execution#In-order processors, in-order execution microarchitecture. It was of much simpler design than its Socket 7 competitors, such as AMD K5/AMD K6, K6, which were superscalar and based on dynamic translation to buffered micro-operations with advanced instruction reordering (Out of Order execution, out of order execution). Use WinChip was, in general, designed to per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Socket 7
Super Socket 7, also referred to as Super 7, is a hardware-level extension of the Socket 7 Zero insertion force, ZIF socket specification for x86 processors. It was released in May 1998. Compatible motherboards and chipsets use a standard Socket 7 connection for the CPU, while adding certain features including a maximum 100 Megahertz, MHz front-side bus and support for Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP graphics cards. Super Socket 7 was used by Advanced Micro Devices, AMD AMD K6-2, K6-2 and AMD K6-III, K6-III processors, some of the final Cyrix M-II processors, some of the final Integrated Device Technology, IDT WinChip, WinChip 2 processors, and Rise Technology, Rise mP6 processors. It is backward compatibility, backward compatible with Socket 7 CPUs, meaning a Socket 7 CPU can be used with a Super Socket 7 motherboard, but a Super Socket 7 CPU cannot operate at full speed in a Socket 7 motherboard. Socket 5 CPUs are pin-compatible with Super Socket 7, but not all motherboards d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 5
Socket 5 was created for the second generation of Intel P5 (microarchitecture), P5 Pentium (brand), Pentium processors operating at speeds from 75 to 133 MHz as well as certain Pentium OverDrive and Pentium MMX processors with core voltage 3.3 V. It superseded the earlier Socket 4. It was released in March 1994. Consisting of 320 pins, this was the first socket to use a staggered pin grid array, or SPGA, which allowed the chip's pins to be spaced closer together than earlier sockets. Socket 5 was replaced by Socket 7 in 1995. External linksDifferences between Socket 5 and Socket 7(archived) See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of AMD microprocessors References {{earlysock CPU sockets, Socket 005 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrix III
Cyrix III is an x86-compatible Socket 370 CPU. VIA Technologies launched the processor in February 2000. VIA had purchased both Centaur Technology and Cyrix. Cyrix III was to be based upon a core from one of the two companies. History The Cyrix III was launched in late February 2000. It was initially based on the Joshua core, and was available in two performance ratings of 500 and 533 MHz, with the PR500 being $84 per unit and the PR533 $99. National Semiconductor would be the producer of the chips. 650 and 677 MHz versions of the Cyrix III were available starting January 2001. The 650 MHz version would cost $55 per chip while the 677 would be $60 and both were based on the Samuel core. The 700 MHz version of the Cyrix III was available on January 19, 2001. The price would be $62 per chip in bulk quantities. This was the last III chip released using the Samuel core, as the Samuel II was expected to be released in March. Just a month later in February 2001, Cyrix III chips ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel P5
The Pentium (also referred to as the i586 or P5 Pentium) is a microprocessor introduced by Intel on March 22, 1993. It is the first CPU using the Pentium, Pentium brand. Considered the fifth generation in the x86 (8086) compatible line of processors, succeeding the i486, its implementation and microarchitecture was internally called ''P5''. Like the Intel i486, the Pentium is instruction set compatible with the 32-bit i386. It uses a very similar microarchitecture to the i486, but was extended enough to implement a dual integer instruction pipelining, pipeline design, as well as a more advanced floating-point unit (FPU) that was noted to be ten times faster than its predecessor. The Pentium was succeeded by the Pentium Pro in November 1995. In October 1996, the Pentium MMX was introduced, complementing the same basic microarchitecture of the original Pentium with the MMX (instruction set), MMX instruction set, larger caches, and some other enhancements. Intel discontinued the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Device Technology
Integrated Device Technology, Inc. (IDT), was an American semiconductor company headquartered in San Jose, California. The company designed, manufactured, and marketed low-power, high-performance mixed-signal semiconductor products for the advanced communications, computing, and consumer industries. The company marketed its products primarily to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Founded in 1980, the company began as a provider of complementary metal-oxide semiconductors (CMOS) for the communications business segment and computing business segments. The company focused on three major areas: communications infrastructure (wireless and wired), high-performance computing, and advanced power management. Between 2018 and 2019, IDT was acquired by Renesas Electronics. Business segments The communications segment produces communication clocks, serial RapidIO products for wireless base station infrastructure applications, radio frequency products, digital logic products, first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IA-32
IA-32 (short for "Intel Architecture, 32-bit", commonly called ''i386'') is the 32-bit version of the x86 instruction set architecture, designed by Intel and first implemented in the i386, 80386 microprocessor in 1985. IA-32 is the first incarnation of x86 that supports 32-bit computing; as a result, the "IA-32" term may be used as a Metonymy, metonym to refer to all x86 versions that support 32-bit computing. Within various programming language directives, IA-32 is still sometimes referred to as the "i386" architecture. In some other contexts, certain iterations of the IA-32 ISA are sometimes labelled ''i486'', ''i586'' and ''i686'', referring to the instruction supersets offered by the i486, 80486, the P5 (microarchitecture), P5 and the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitectures respectively. These updates offered numerous additions alongside the base IA-32 set including X87, floating-point capabilities and the MMX (instruction set), MMX extensions. Intel was historically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaur Technology
Centaur Technology was an x86 CPU design company started in 1995 and subsequently a wholly owned subsidiary of VIA Technologies. In 2015, the documentary ''Rise of the Centaur'' covered the early history of the company. The company was broken up in 2021. History Centaur Technologies Inc. was founded in April 1995 by Glenn Henry, Terry Parks, Darius Gaskins, and Al Sato. The funding was provided by Integrated Device Technology, Inc (IDT). The business goal was to develop compatible x86 processors that were less expensive than Intel processors and consumed less power. There were two main elements of the plan: # a new design, developed from scratch, of an x86 processor core optimized differently from Intel's cores; # a novel management approach designed to achieve high productivity. While funded by IDT, three different Centaur designs were shipped under the marketing name of WinChip. In September 1999, Centaur was purchased from IDT by VIA Technologies, a Taiwanese company. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
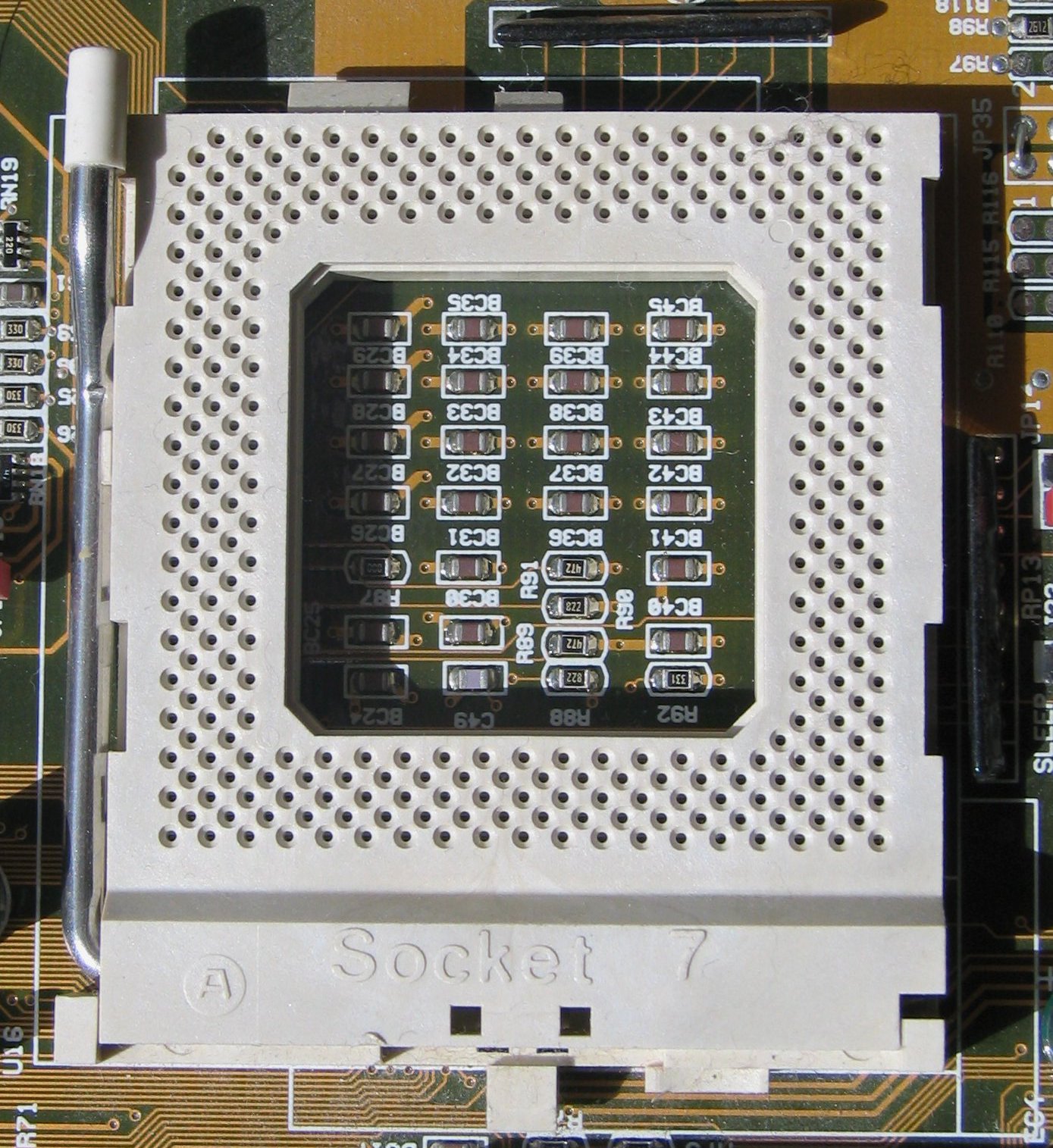
Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. It was released in June 1995. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others. Socket 7 was the only socket that supported a wide range of CPUs from different manufacturers and a wide range of speeds. Differences between Socket 5 and Socket 7 are that Socket 7 has an extra pin and is designed to provide dual split rail voltage, as opposed to Socket 5's single voltage. However, not all motherboard manufacturers supported the dual voltage on their boards initially. Socket 7 is backwards compatible; a Socket 5 CPU can be inserted and used on a Socket 7 motherboard. Processors that used Socket 7 are the AMD K5 and K6, the Cyrix 6x86 and 6x86MX, the IDT WinChip, the Intel P5 Pentium (2.5–3.5 V, 75–200 MHz), the Pentium MMX (166–233 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrix
Cyrix Corporation was a microprocessor developer that was founded in 1988 in Richardson, Texas, as a specialist supplier of floating point units for 286 and 386 microprocessors. The company was founded by Tom Brightman and Jerry Rogers. Terry Rogers was also serving as the company Chief Executive Officer and president up until December 9, 1996, when he stepped down from this role, but remained on the Board of Directors. In 1992, Cyrix introduced its own i386 compatible processors, the 486SLC and 486DLC. These had higher performance than the Intel parts, but a lower price. They were primarily marketed to users looking to upgrade existing machines. Their release sparked a lengthy series of lawsuits with Intel while their foundry partner IBM was releasing the same designs under their own branding. The combination of these events led Cyrix to begin losing money, and the company merged with National Semiconductor on 11 November 1997. National released Cyrix's latest designs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PR Rating
The PR (performance rating, P-rating, or Pentium rating) system was a figure of merit developed by AMD, Cyrix, IBM Microelectronics and SGS-Thomson in the mid-1990s as a method of comparing their x86 processors to those of rival Intel. The idea was to consider instructions per cycle (IPC) in addition to the clock speed, so that the processors become comparable with Intel's Pentium that had a higher clock speed with overall lower IPC. Branding The first use of the PR system was in 1995, when AMD used it to assert that their AMD 5x86 processor was as fast as a Pentium running at 75 MHz. The designation "P75" was added to the chip to denote this. Later that year, Cyrix also adopted the PR system for its 6x86 and 6x86MX line of processors. These processors were faster than Pentiums of the same speed in some benchmarks, so Cyrix gave them a Performance Rating faster than their clock speed. Some AMD K5 models also use the PR system. AMD initially branded its AMD K6 processors with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front Side Bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge. Depending on the implementation, some computers may also have a back-side bus that connects the CPU to the cache. This bus and the cache connected to it are faster than accessing the system memory (or RAM) via the front-side bus. The speed of the front side bus is often used as an important measure of the performance of a computer. The original front-side bus architecture was replaced by HyperTransport, Intel QuickPath Interconnect, and Direct Media Interface, followed by Intel Ultra Path Interconnect and AMD's Infinity Fabric. History The term came into use by Intel Corporation about the time the Pentium Pro and Pentium II products were announced, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out Of Order Execution
In computer engineering, out-of-order execution (or more formally dynamic execution) is an instruction scheduling paradigm used in high-performance central processing units to make use of instruction cycles that would otherwise be wasted. In this paradigm, a processor executes instructions in an order governed by the availability of input data and execution units, rather than by their original order in a program. In doing so, the processor can avoid being idle while waiting for the preceding instruction to complete and can, in the meantime, process the next instructions that are able to run immediately and independently. History Out-of-order execution is a restricted form of dataflow architecture, which was a major research area in computer architecture in the 1970s and early 1980s. Early use in supercomputers The first machine to use out-of-order execution was the CDC 6600 (1964), designed by James E. Thornton, which uses a scoreboard to avoid conflicts. It permits an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |