|
Wimshurst Influence Machine
The Wimshurst machine or Wimshurst influence machine is an electrostatic generator, a machine for generating high voltages developed between 1880 and 1883 by British inventor James Wimshurst (1832–1903). It has a distinctive appearance with two large contra-rotating discs mounted in a vertical plane, two crossed bars with metallic brushes, and a spark gap formed by two metal spheres. Description These machines belong to a class of electrostatic generators called influence machines, which separate electric charges through electrostatic induction, or ''influence'', not depending on friction for their operation. Earlier machines in this class were developed by Wilhelm Holtz (1865 and 1867), August Toepler (1865), J. Robert Voss (1880), and others. The older machines are less efficient and exhibit an unpredictable tendency to switch their polarity, while the Wimshurst machine has neither defect. In a Wimshurst machine, the two insulated discs and their metal sectors rota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyden Jar
A Leyden jar (or Leiden jar, or archaically, Kleistian jar) is an electrical component that stores a high-voltage electric charge (from an external source) between electrical conductors on the inside and outside of a glass jar. It typically comprises a glass jar with metal foil cemented to the inside and the outside surfaces, and a metal terminal projecting vertically through the jar lid to make contact with the inner foil. It was the original form of the capacitor (also called a ''condenser''). Its invention was a discovery made independently by German cleric Ewald Georg von Kleist on 11 October 1745 and by Dutch scientist Pieter van Musschenbroek of Leiden (Leyden), Netherlands, in 1745–1746. The Leyden jar was used to conduct many early experiments in electricity, and its discovery was of fundamental importance in the study of electrostatics. It was the first means of accumulating and preserving electric charge in large quantities that could be discharged at the experi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power (physics)
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. Power is a Scalar (physics), scalar quantity. Specifying power in particular systems may require attention to other quantities; for example, the power involved in moving a ground vehicle is the product of the aerodynamic drag plus traction (engineering), traction force on the wheels, and the velocity of the vehicle. The output power of a Engine, motor is the product of the torque that the motor generates and the angular velocity of its output shaft. Likewise, the power dissipated in an electrical element of a electrical circuit, circuit is the product of the electric current, current flowing through the element and of the voltage across the element. Definition Power is the Rate (mathematics), rate with respect to time at which work is done or, more generally, the rate of change of total mechanical energy. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Instruments
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing with electrical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Generators
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies slow-moving or stationary electric charges. Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word (), meaning 'amber', was thus the root of the word ''electricity''. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of plastic wrap to one's hand after it is removed from a package, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and photocopier and laser printer operation. The electrostatic model accurately predicts electrical phenomena in "classical" cases where the velocities are low and the system is macroscopic so no quantum effects are involved. It also plays a role in quantum mechanics, where additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van De Graaff Generator
A Van de Graaff generator is an electrostatic generator which uses a moving belt to accumulate electric charge on a hollow metal globe on the top of an insulated column, creating very high electric potentials. It produces very high voltage direct current (DC) electricity at low current levels. It was invented by American physicist Robert J. Van de Graaff in 1929. The potential difference achieved by modern Van de Graaff generators can be as much as 5 megavolts. A tabletop version can produce on the order of 100 kV and can store enough energy to produce visible electric sparks. Small Van de Graaff machines are produced for entertainment, and for physics education to teach electrostatics; larger ones are displayed in some science museums. The Van de Graaff generator was originally developed as a particle accelerator for physics research, as its high potential can be used to accelerate subatomic particles to great speeds in an evacuated tube. It was the most powerful type of ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelletron
A Pelletron is a type of electrostatic generator, structurally similar to a Van de Graaff generator. Pelletrons have been built in many sizes, from small units producing voltages up to 500 kilovolts (kV) and beam energies up to 1 electronvolt, megaelectronvolt (MeV) of kinetic energy, to the largest system, which has reached a DC voltage of over 25 megavolts and produced ion beams with energies over 900 MeV. According to the review paper of F. Hinterberger the pelletron was first developed in the mid 1960s by Prof. Raymond Herb. In 1965 Ray together with J. A. Ferry and T. Pauly founded the National Electrostatics Corporation, to manufacture pelletrons as a solution to the problems of ever larger Van de Graaff machines required at that time for particle physic research. As in the Van de Graaff machine, electric charge is moved by a mechanical transportation system. The charge is carried on a chain of 'pellets' (conductive tubes connected by links made of insulating mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin Water Dropper
The Kelvin water dropper, invented by Scottish scientist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) in 1867, is a type of electrostatic generator. Kelvin referred to the device as his water-dropping condenser. The apparatus is variously called the Kelvin hydroelectric generator, the Kelvin electrostatic generator, or Lord Kelvin's thunderstorm. The device uses falling water to generate voltage differences by electrostatic induction occurring between interconnected, oppositely Electric charge, charged systems. This eventually leads to an electric arc discharging in the form of a spark. It is used in physics education to demonstrate the principles of electrostatics. Description A typical setup is shown in Fig. 1. A reservoir of water or other conducting liquid (top, grey) is connected to two hoses that release two falling streams of drops, which land in two buckets or containers (bottom, blue and red). Each stream passes (without touching) through a metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
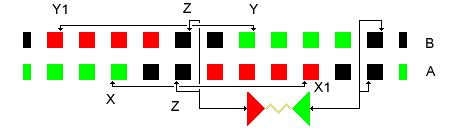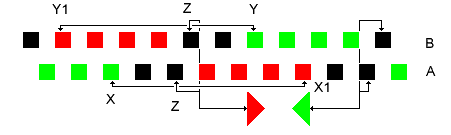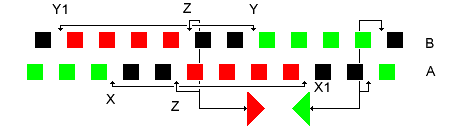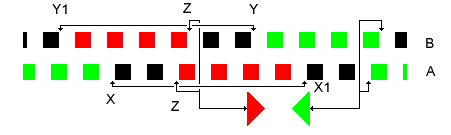
Wimshurst Machine Charge Cycle
Wimshurst is an English surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Henry Wimshurst (1804–1884), English shipbuilder * James Wimshurst (1832–1903), English inventor, engineer and shipwright **Wimshurst machine, an electrostatic generator *Ken Wimshurst Kenneth Pinkney Wimshurst (23 March 1938 – 6 July 2017) was an English footballer who played as a right half. He made over 300 Football League appearances in the years after the Second World War. Career Ken Wimshurst played locally for South ... (1938–2017), English footballer and manager {{surname, Wimshurst English-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induction Coil
An induction coil or "spark coil" ( archaically known as an inductorium or Ruhmkorff coil after Heinrich Rühmkorff) is a type of transformer used to produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage direct current (DC) supply. p.98 To create the flux changes necessary to induce voltage in the secondary coil, the direct current in the primary coil is repeatedly interrupted by a vibrating mechanical contact called an interrupter. Invented in 1836 by the Irish-Catholic priest Nicholas Callan, also independently by American inventor Charles Grafton Page, the induction coil was the first type of transformer. It was widely used in x-ray machines, spark-gap radio transmitters, arc lighting and quack medical electrotherapy devices from the 1880s to the 1920s. Today its only common use is as the ignition coils in internal combustion engines and in physics education to demonstrate induction. Construction and function An induction coil consists of two coils of insulated wire wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Generator
An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is an electric generator, electrical generator that produces ''static electricity'', or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current. The knowledge of static electricity dates back to the earliest civilizations, but for millennia it remained merely an interesting and mystifying phenomenon, without a theory to explain its behavior and often confused with magnetism. By the end of the 17th century, researchers had developed practical means of generating electricity by friction, but the development of electrostatic machines did not begin in earnest until the 18th century, when they became fundamental instruments in the studies about the new science of electricity. Electrostatic generators operate by using manual (or other) power to transform mechanical work into electric energy, or using electric currents. Manual electrostatic generators develop electrostatic electrical charge, charges of opposite signs rendered to two co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast to other sources of ionizing radiation, X-rays are only produced as long as the X-ray tube is energized. X-ray tubes are also used in CT scanners, airport luggage scanners, X-ray crystallography, material and structure analysis, and for industrial inspection. Increasing demand for high-performance computed tomography (CT) scanning and angiography systems has driven development of very high-performance medical X-ray tubes. History X-ray tubes evolved from experimental Crookes tubes with which X-rays were first discovered on November 8, 1895, by the German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen. The first-generation ''cold cathode'' or ''Crookes'' X-ray tubes were used until the 1920s. These tubes work by ionisation of residual gas within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |