|
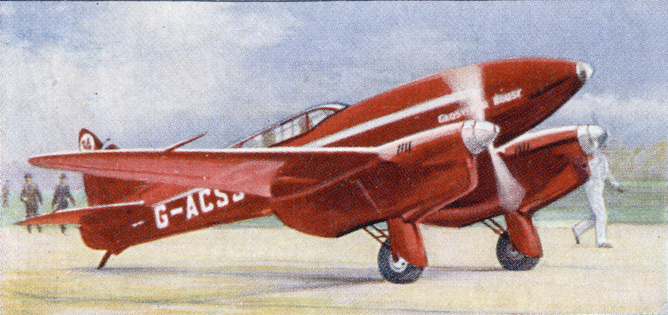
Wilson Airways
Florence Kerr Wilson OBE (1879 – September 1966) was a pioneer of aviation in East Africa. She founded and operated Wilson Airways Ltd., which operated from airfields in Nairobi from 1929 until the airline was absorbed by the Kenyan military in 1939 at the outbreak of World War II. She was made an officer of the Order of the British Empire (civil division) in 1933 for her service to civil aviation. She died at her home in Kenya on September 29, 1966. The Wilson Airport in Nairobi was named for her in 1962. Early life Florence Kerr Fernie was born in England at Blundellsands, near Liverpool, in 1879. Her family were wealthy ship owners. In 1902 she married William Herbert Wilson (1866–1928), who became a Major in the British Army. After World War I the couple emigrated to Kenya and took up farming. Major Wilson died in 1928. Wilson Airways Early in 1929, Florence Kerr Wilson had to travel to the UK for business; instead of taking a long sea voyage, she arranged to fly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the region is recognized in the United Nations Statistics Division United Nations geoscheme for Africa, scheme as encompassing 18 sovereign states and 4 territories. It includes the Horn of Africa to the North and Southeastern Africa to the south. Definitions In a narrow sense, particularly in English-speaking contexts, East Africa refers to the area comprising Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, largely due to their shared history under the Omani Empire and as parts of the British East Africa Protectorate and German East Africa. Further extending East Africa's definition, the Horn of Africa—comprising Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia—stands out as a distinct geopolitical entity within East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Campbell Black
Tom Campbell Black (December 1899 – 19 September 1936) was an English aviator. He was the son of Alice Jean McCullough and Hugh Milner Black. He became a world-famous aviator when he and C. W. A. Scott won the London to Melbourne Centenary Air Race in 1934. Early years Tom Campbell Black attended Brighton College and the records for the period summer 1915 to summer 1917 indicate that he entered Hampden House, May 1915, was appointed House Prefect, January 1917 and played Second XI Football, 1915 to 1916 and 1916 to 1917. Campbell Black attended Army Class II and entered the RN College at Greenwich and attained a commission in the R.N.A.S. (Naval Air Service). He served first as a pilot in the Naval Air Service and later in the RAF during the Great War, rising to the rank of captain. Arriving in Africa as a soldier settler in 1922, he joined his brother, Frank Milner Black, who had been stationed as a soldier in Kenya and decommissioned in 1920. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Pioneers
Aviation pioneers are people directly and indirectly responsible for the creation and advancement of human flight capability, including people who worked to achieve manned flight before the invention of aircraft, as well as others who achieved significant "firsts" in aviation after heavier-than-air flight became routine. Pioneers of aviation have contributed to the development of aeronautics Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design process, design, and manufacturing of air flight-capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. While the term originally referred ... in one or more ways: through science and theory, theoretical or applied design, by constructing models or experimental prototypes, the mass production of aircraft for commercial and government request, achievements in flight, and providing financial resources and publicity to expand the field of aviation. Table key Pioneer type * Science: C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1966 Deaths
Events January * January 1 – In a coup, Colonel Jean-Bédel Bokassa takes over as military ruler of the Central African Republic, ousting President David Dacko. * January 3 – 1966 Upper Voltan coup d'état: President Maurice Yaméogo is deposed by a military coup in the Republic of Upper Volta (modern-day Burkina Faso). * January 10 ** Pakistani–Indian peace negotiations end successfully with the signing of the Tashkent Declaration, a day before the sudden death of Indian prime minister Lal Bahadur Shastri. ** Georgia House of Representatives, The House of Representatives of the US state of Georgia refuses to allow African-American representative Julian Bond to take his seat, because of his anti-war stance. * January 15 – 1966 Nigerian coup d'état: A bloody military coup is staged in Nigeria, deposing the civilian government and resulting in the death of Prime Minister Abubakar Tafawa Balewa. * January 17 ** The Nigerian coup is overturned by another faction of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1879 Births
Events January * January 1 ** The Specie Resumption Act takes effect. The United States Note is valued the same as gold, for the first time since the American Civil War. ** Brahms' Violin Concerto is premiered in Leipzig with Joseph Joachim as soloist and the composer conducting. * January 11 – The Anglo-Zulu War begins. * January 22 – Anglo-Zulu War – Battle of Isandlwana: A force of 1,200 British soldiers is wiped out by over 20,000 Zulu warriors. * January 23 – Anglo-Zulu War – Battle of Rorke's Drift: Following the previous day's defeat, a smaller British force of 140 successfully repels an attack by 4,000 Zulus. February * February 3 – Mosley Street in Newcastle upon Tyne (England) becomes the world's first public highway to be lit by the electric incandescent light bulb invented by Joseph Swan. * February 8 – At a meeting of the Royal Canadian Institute, engineer and inventor Sandford Fleming first proposes the global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Airways
Imperial Airways was an early British commercial long-range airline, operating from 1924 to 1939 and principally serving the British Empire routes to South Africa, India, Australia and the Far East, including Malaya and Hong Kong. Passengers were typically businessmen or colonial administrators, and most flights carried about 20 passengers or fewer. Accidents were frequent: in the first six years, 32 people died in seven incidents. Imperial Airways never achieved the levels of technological innovation of its competitors and was merged into the British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) in 1939. BOAC in turn merged with the British European Airways (BEA) in 1974 to form British Airways. Background The establishment of Imperial Airways occurred in the context of facilitating British colonialism by making travel to and from the colonies quicker than travel by ship. Air travel would speed up both colonial government and trade. The launch of the airline followed a burst of air ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Charter
Air charter is the business of renting an entire aircraft (i.e., chartering) as opposed to individual aircraft seats (i.e., purchasing a ticket through a traditional airline). Regulation Charter – also called air taxi or ad hoc – flights require certification from the associated country's civil aviation authority. The regulations are differentiated from typical commercial/passenger service by offering a non-scheduled service. Analogous regulations generally also apply to air ambulance and cargo operators, which are often also ad hoc for-hire services. United States In the United States, these flights are regulated under FAA Part 135. There are some cases where a charter operator can sell scheduled flights, but only in limited quantities. As of 2021, the FAA had made it a priority to crack down on unauthorised charter flights, according to industry experts. Types of service There are several business models which offer air charter services from the traditional cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot Licensing And Certification
Pilot licensing or certification refers to permits for operating aircraft. Flight crew licences are issued by the civil aviation authority of each country, which must establish that the holder has met minimum knowledge and experience before issuing licences. The licence, along with the required class or type rating, allows a pilot to fly aircraft registered in the licence issuing state. Regulators The International Civil Aviation Organization's "Annex 1 – Personnel Licensing" acts as the international minimum standard for licensing. However, states can deviate from these standards by notifying ICAO about the changes. In the United States, pilot certification is regulated by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), a branch of the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT). A pilot is certified under the authority of Parts 61 and 141 of Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations, also known as the Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White People In Kenya
White people in Kenya or White Kenyans are those born in or resident in Kenya who descend from Europeans and/or identify themselves as White. There is currently a minor but relatively prominent White community in Kenya, mainly descended from British, but also to a lesser extent Italian and Greek, migrants dating from the colonial period. History The Age of Discovery first led to European interaction with the region of present-day Kenya. The coastal regions were seen as a valuable foothold in eastern trade routes, and Mombasa became a key port for ivory. The Portuguese established a presence in the region for two hundred years between 1498 and 1698, before losing control of the coast to the Sultanate of Oman when Fort Jesus was captured. European exploration of the interior commenced in 1844 when two German missionaries, Johann Ludwig Krapf and Johannes Rebmann, ventured inland with the aim of spreading Christianity. The region soon sparked the imagination of other advent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson Airways
Florence Kerr Wilson OBE (1879 – September 1966) was a pioneer of aviation in East Africa. She founded and operated Wilson Airways Ltd., which operated from airfields in Nairobi from 1929 until the airline was absorbed by the Kenyan military in 1939 at the outbreak of World War II. She was made an officer of the Order of the British Empire (civil division) in 1933 for her service to civil aviation. She died at her home in Kenya on September 29, 1966. The Wilson Airport in Nairobi was named for her in 1962. Early life Florence Kerr Fernie was born in England at Blundellsands, near Liverpool, in 1879. Her family were wealthy ship owners. In 1902 she married William Herbert Wilson (1866–1928), who became a Major in the British Army. After World War I the couple emigrated to Kenya and took up farming. Major Wilson died in 1928. Wilson Airways Early in 1929, Florence Kerr Wilson had to travel to the UK for business; instead of taking a long sea voyage, she arranged to fly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major (British Army)
Major (Maj) is a military rank which is used by both the British Army and Royal Marines. The rank is superior to captain and subordinate to lieutenant colonel. The insignia for a major is a crown. The equivalent rank in the Royal Navy is lieutenant commander, and squadron leader in the Royal Air Force. History By the time of the Napoleonic wars, an infantry battalion usually had two majors, designated the "senior major" and the "junior major". The senior major effectively acted as second-in-command and the majors often commanded detachments of two or more companies split from the main body. The second-in-command of a battalion or regiment is still a major. File:British-Army-Maj(1856-1867)-Collar Insignia.svg, 1856 to 1867 major's collar rank insignia File:British-Army-Maj(1867-1880)-Collar Insignia.svg, 1867 to 1880 major's collar rank insignia File:British&Empire-Army-Maj(1881-1902).svg, 1881 to 1902 major's shoulder rank insignia During World War I, majors wore the follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |