|
Wilms Tumor 1
Wilms tumor protein (WT33) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WT1'' gene on chromosome 11p. Function This gene encodes a transcription factor that contains four zinc finger motifs at the C-terminus and a proline / glutamine-rich DNA-binding domain at the N-terminus. It has an essential role in the normal development of the urogenital system, and it is mutated in a subset of patients with Wilms' tumor, the gene's namesake. Multiple transcript variants, resulting from alternative splicing at two coding exons, have been well characterized. There is also evidence for the use of non-AUG (CUG) translation initiation site upstream of, and in-frame with the first AUG, leading to additional isoforms. Structure The WT1 gene product shows similarity to the zinc fingers of the mammalian growth regulated early growth response protein 1 ( EGR1) and (EGR2) proteins. Clinical significance ''Mutations of Wilms' tumor suppressor gene1'' (WT1) are associated with embryon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties, but may still be harmful to health. The term benign in more general medical use characterizes a condition or growth that is not cancerous, i.e. does not spread to other parts of the body or invade nearby tissue. Sometimes the term is used to suggest that a condition is not dangerous or serious. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
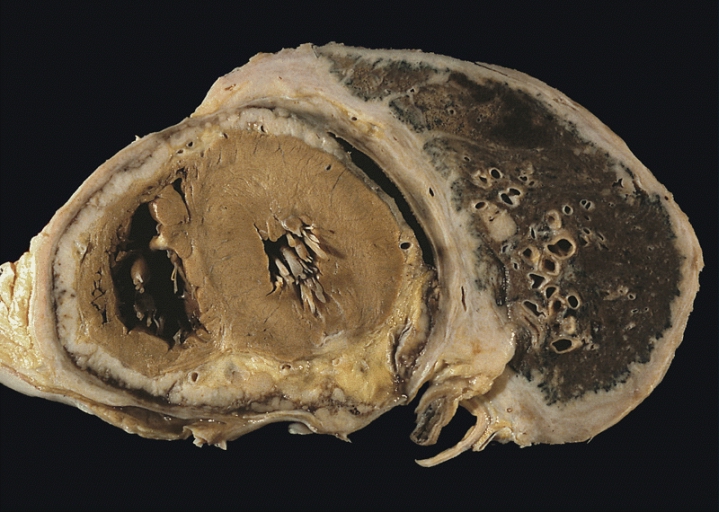
Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The area most commonly affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lining of the abdomen and rarely the sac surrounding the heart, or the sac surrounding each testis may be affected. Signs and symptoms of mesothelioma may include shortness of breath due to fluid around the lung, a swollen abdomen, chest wall pain, cough, feeling tired, and weight loss. These symptoms typically come on slowly. More than 80% of mesothelioma cases are caused by exposure to asbestos. The greater the exposure, the greater the risk. As of 2013, about 125 million people worldwide have been exposed to asbestos at work. High rates of disease occur in people who mine asbestos, produce products from asbestos, work with asbestos products, live with asbestos workers, or work in buildings containing asbestos. Asbestos exposure and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
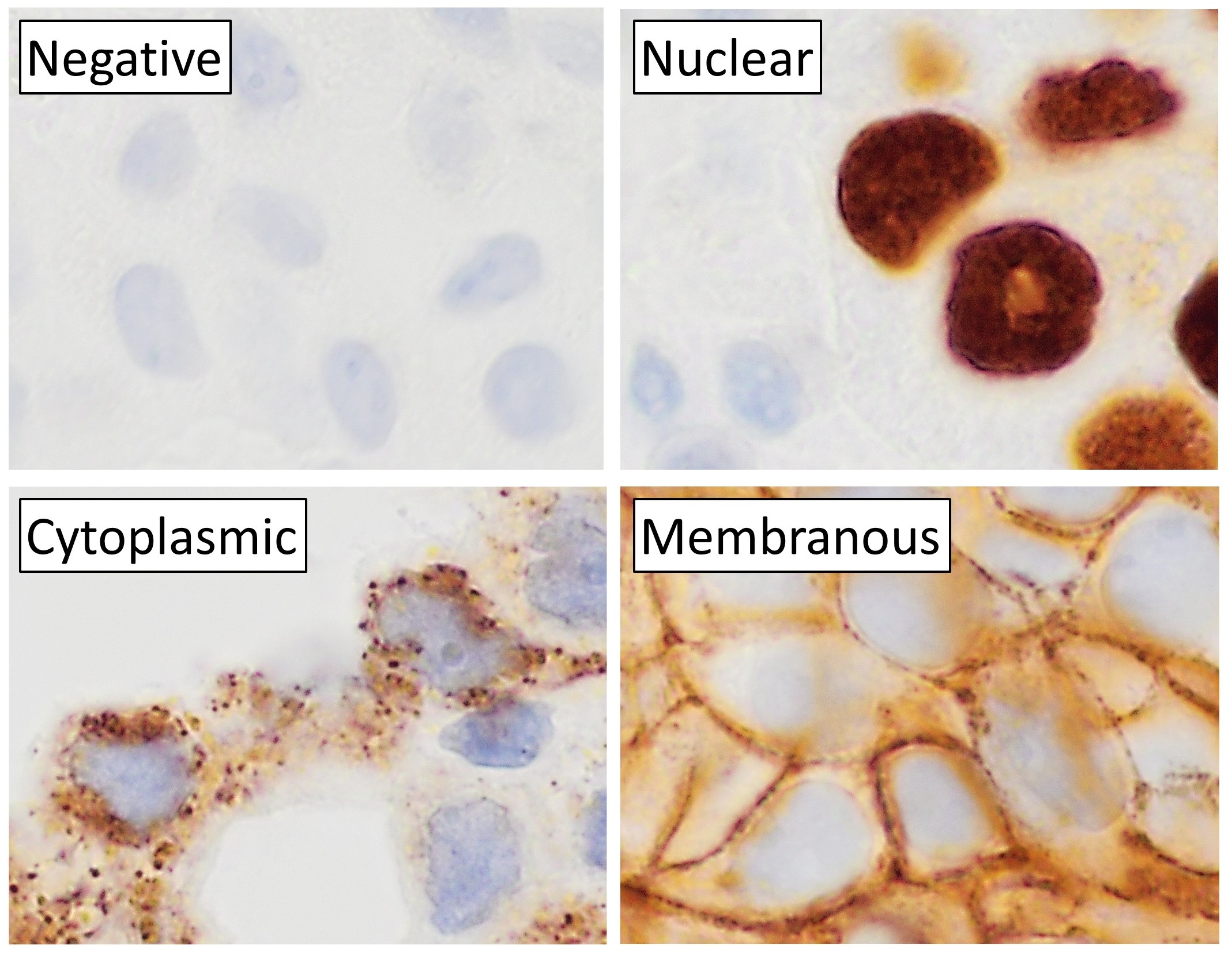
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Coons, Albert Hewett Coons, Ernst Berliner, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in Paraffin wax, paraffin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HtrA Serine Peptidase 2
Serine protease HTRA2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''HTRA2'' gene. This protein is involved in caspase-dependent apoptosis and in Parkinson's disease. Structure Gene The gene ''HTRA2'' encodes a serine protease. The human gene has 8 exons and locates at chromosome band 2p12. Protein Protein HtrA2, also known as Omi, is a mitochondrially-located serine protease. The human protein Serine protease HTRA2, mitochondrial is 49kDa in size and composed of 458 amino acids. The peptide fragment of 1-31 amino acid is the mitochondrial transition sequence, fragment 32-133 amino acid is propertied, and 134-458 is the mature protein Serine protease HTRA2, mitochondrial, and its theoretical pI of this protein is 6.12. HtrA2 shows similarities with DegS, a bacterial protease present in the periplasm of gram-negative bacteria. Structurally, HtrA2 is a trimeric molecule with central protease domains and a carboxy-terminal PDZ domain, which is characteristic of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include Fatigue, feeling tired, shortness of breath, Bruise, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include getting older, being male, smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a anemia, drop in red blood cells, thrombocytopenia, platelets, and normal leukopenia, white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IDH2
Isocitrate dehydrogenase ADP mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''IDH2'' gene. Isocitrate dehydrogenases are enzymes that catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. These enzymes belong to two distinct subclasses, one of which utilizes NAD(+) as the electron acceptor and the other NADP(+). Five isocitrate dehydrogenases have been reported: three NAD(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, which localize to the mitochondrial matrix, and two NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, one of which is mitochondrial and the other predominantly cytosolic. Each NADP(+)-dependent isozyme is a homodimer. The protein encoded by the IDH2 gene is the NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase found in the mitochondria. It plays a role in intermediary metabolism and energy production. This protein may tightly associate or interact with the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Somatic mosaic mutations of this gene have also been found as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IDH1
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''IDH1'' gene on chromosome 2. Isocitrate dehydrogenases catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. These enzymes belong to two distinct subclasses, one of which uses NAD+ as the electron acceptor and the other NADP+. Five isocitrate dehydrogenases have been reported: three NAD+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, which localize to the mitochondrial matrix, and two NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, one of which is mitochondrial and the other predominantly cytosolic. Each NADP+-dependent isozyme is a homodimer. The protein encoded by this gene is the NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase found in the cytoplasm and peroxisomes. It contains the PTS-1 peroxisomal targeting signal sequence. The presence of this enzyme in peroxisomes suggests roles in the regeneration of NADPH for intraperoxisomal reductions, such as the conversion of 2,4-dienoyl-CoAs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TET2
Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 (''TET2'') is a human gene. It resides at chromosome 4q24, in a region showing recurrent microdeletions and copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity (CN-LOH) in patients with diverse myeloid malignancies. Function ''TET2'' encodes a protein that catalysis, catalyzes the conversion of the modified DNA base methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. The first mechanistic reports showed tissue-specific accumulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, 5hmC) and the conversion of 5-Methylcytosine, 5mC to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, 5hmC by Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 1, TET1 in humans in 2009. In these two papers, Kriaucionis and Heintz provided evidence that a high abundance of 5hmC can be found in specific tissues and Tahiliani et al. demonstrated the Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 1, TET1-dependent conversion of 5-Methylcytosine, 5mC to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, 5hmC. A role for TET1 in cancer was reported in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Exclusivity
In logic and probability theory, two events (or propositions) are mutually exclusive or disjoint if they cannot both occur at the same time. A clear example is the set of outcomes of a single coin toss, which can result in either heads or tails, but not both. In the coin-tossing example, both outcomes are, in theory, collectively exhaustive, which means that at least one of the outcomes must happen, so these two possibilities together exhaust all the possibilities. However, not all mutually exclusive events are collectively exhaustive. For example, the outcomes 1 and 4 of a single roll of a six-sided die are mutually exclusive (both cannot happen at the same time) but not collectively exhaustive (there are other possible outcomes; 2,3,5,6). Logic In logic, two propositions \phi and \psi are mutually exclusive if it is not logically possible for them to be true at the same time; that is, \lnot (\phi \land \psi) is a tautology. To say that more than two propositions are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPC3
Glypican-3 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''GPC3'' gene. The ''GPC3'' gene is located on human X chromosome (Xq26) where the most common gene (Isoform 2, GenBank Accession No.: NP_004475) encodes a 70-kDa core protein with 580 amino acids. Three variants have been detected that encode alternatively spliced forms termed Isoforms 1 (NP_001158089), Isoform 3 (NP_001158090) and Isoform 4 (NP_001158091). Structure and function The protein core of GPC3 consists of two subunits, where the N-terminal subunit has a size of ~40 kDa and the C-terminal subunit is ~30 kDa. Six glypicans (GPC1-6) have been identified in mammals. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are human genes and their protein products, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associated) are gene nomenclature, maintained by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. One alternative symbol, FANCD1, recognizes its association with the FANC proteins, FANC protein complex. Orthologs, styled ''Brca2'' and Brca2, are common in other vertebrate species. May 2021 ''BRCA2'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (specifically, a caretaker gene), found in all humans; its protein, also called by the synonym breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein, is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA2'' and ''BRCA1'' are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosome, chromosomal damage with an important role in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |