|
William George MacCallum
William George MacCallum (18 April 1874 – 3 February 1944) was a Canadian-American physician and pathologist. He was of Scottish descent and was born in Dunnville village in Canada, where his father was a physician. He was educated at the University of Toronto. He graduated with BA in 1894. Initially inclined towards Greeks as academic career, his father influenced him to enter medicine. He joined the second year of the first batch of medicine course in the Johns Hopkins Medical School, and became one of the first graduates of the institute in 1897. He was appointed assistant resident of pathology of the medical school in 1897, resident pathologist in 1901, soon after Associate Professor, and full Professor in 1908. Between 1909 and 1917 he held a twin position of Professor of Pathology at Columbia University and the NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital. From 1917 to 1943 he held the Chair of Pathogy at Johns Hopkins University. MacCallum discovered the existence of two forms (now k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunnville
Dunnville is an unincorporated community located near the mouth of the Grand River in Haldimand County, Ontario, Canada, near the historic Talbot Trail. It was formerly an incorporated town encompassing the surrounding area with a total population of 12,000. History Dunnville was the site of a Cayuga settlement called ''Detgahnegaha'gó:wah''. The European settlement was originally built as the entrance to the Welland "feeder" canal, and the town once boasted several water-powered mills and a once-bustling canal port. The feeder canal closed in the late 1880s, and the last mill was destroyed and replaced with a condominium complex. There is an impassable dam at Dunnville which regulates the level of the Grand River at Port Maitland, which, in the 19th century, also helped regulate the level of the Welland Canal (from 1829 to 1887 when the third canal began to intake its water directly from Lake Erie). Dunnville was incorporated as a village in 1860 and then as a town in 1900. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Medicine
A Doctor of Medicine (abbreviated MD, from the Latin language, Latin ) is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the ''MD'' denotes a professional degree of physician. This generally arose because many in 18th-century medical professions trained in Scotland, which used the MD degree nomenclature. In England, however, Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) was used: in the 19th century, it became the standard in Scotland too. Thus, in the United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Ireland and other countries, the MD is a research doctorate, honorary degree, honorary doctorate or applied clinical degree restricted to those who already hold a professional degree (Bachelor's/Master's/Doctoral) in medicine. In those countries, the equivalent professional degree to the North American, and some others' usage of MD is still typically titled Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery. History The fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-largest metropolitan area in the country at 2.84 million residents. The city is also part of the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area, which had a population of 9.97 million in 2020. Baltimore was designated as an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851. Though not located under the jurisdiction of any county in the state, it forms part of the central Maryland region together with the surrounding county that shares its name. The land that is present-day Baltimore was used as hunting ground by Paleo-Indians. In the early 1600s, the Susquehannock began to hunt there. People from the Province of Maryland established the Port of Baltimore in 1706 to support the tobacco trade with Europe and established the Town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest William Goodpasture
Ernest William Goodpasture (October 17, 1886 – September 20, 1960) was an American pathologist and physician. Goodpasture advanced the scientific understanding of the pathogenesis of infectious diseases, parasitism, and a variety of rickettsial and viral infections. Together with colleagues at Vanderbilt University, he invented methods for growing viruses and rickettsiae in chicken embryos and fertilized chicken eggs. This enabled the development of vaccines against influenza, chicken pox, smallpox, yellow fever, typhus, Rocky mountain spotted fever, and other diseases. He also identified and described what would become known as Goodpasture syndrome.Valentini, Rudolph PPediatric Anti-GBM Disease (Goodpasture Syndrome). Accessed 8-28-2009. Education and professional career Goodpasture was born in Clarksville, Tennessee, in 1886. He received his B.A. from Vanderbilt University in 1908. In 1912, Goodpasture graduated from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine with an M.D. degr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan gram-negative cell wall, cell wall sandwiched between an inner (Cytoplasm, cytoplasmic) Cell membrane, membrane and an Bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous Antibiotic, antibiotics (including penicillin), Detergent, detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pylorus
The pylorus ( or ) connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pyloric canal'' ends as the ''pyloric orifice'', which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the ''pyloric sphincter''. The word ''pylorus'' comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word ''pylorus'' in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" () and is thus linguistically related to the word " pylon". Structure The pylorus is the furthest part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum. It is divided into two parts, the ''antrum'', which connects to the body of the stomach, and the ''pyloric canal'', which connects to the duodenum. Antrum The antrum also called the ''gastric antrum'' or the ''pyloric antrum'' is the initial portion of the pyloric region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
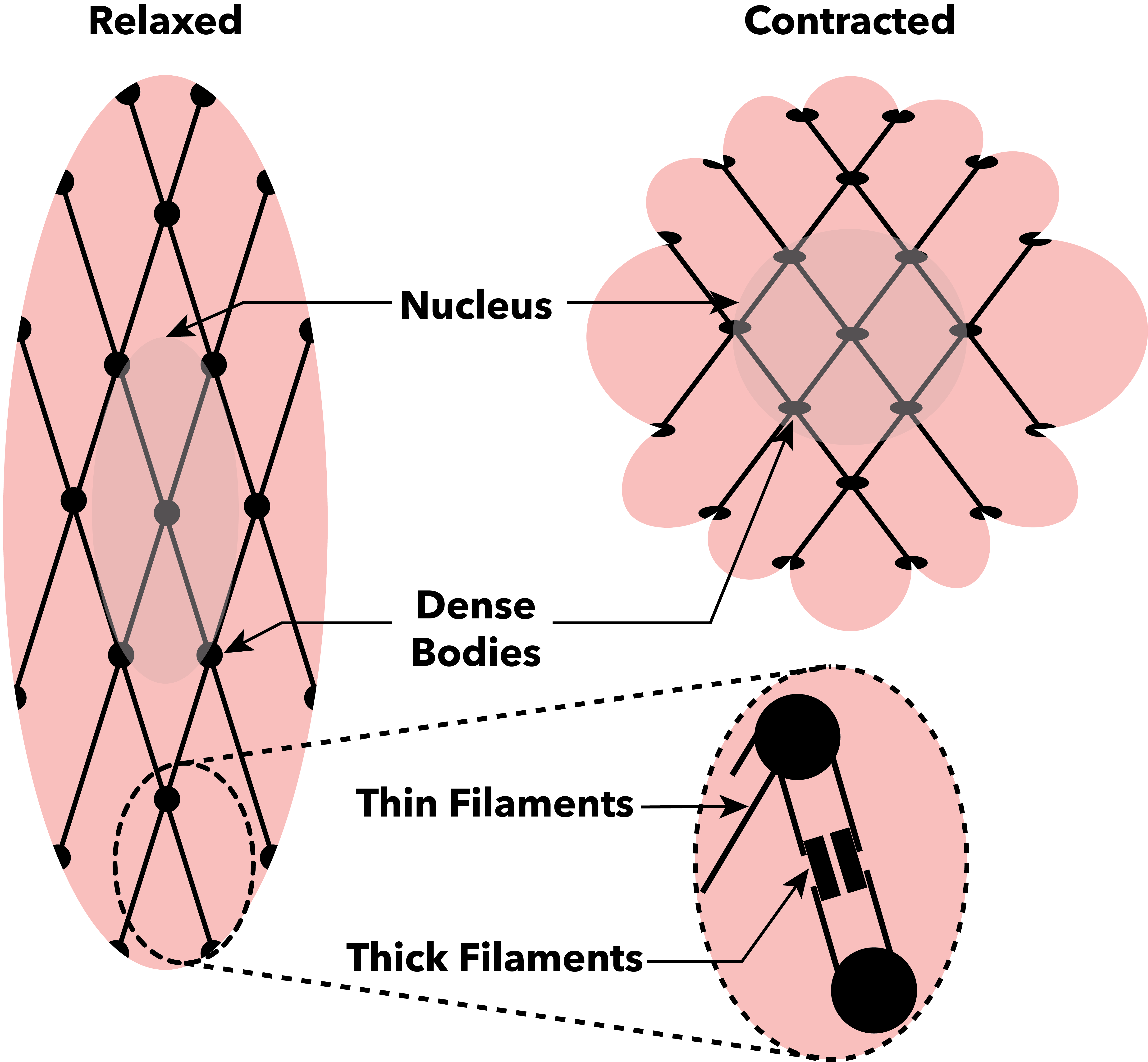
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the change in action of two types of Myofilament, filaments: thin and thick filaments. The major constituent of thin filaments is a chain formed by helical coiling of two strands of actin, and thick filaments dominantly consist of chains of the Motor protein, motor-protein myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils - the basic functional organelles in the skeletal muscle system. In vertebrates, Muscle cell#Muscle contraction in striated muscle, skele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossils of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name comes from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceuticals for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetany
Tetany or tetanic seizure is a medical sign consisting of the involuntary contraction of muscles, which may be caused by disorders that increase the action potential frequency of muscle cells or of the nerves that innervate them. Cramp, Muscle cramps caused by the disease tetanus are not classified as tetany; rather, they are due to a lack of inhibition to the neurons that supply muscles. Tetanic contractions (physiologic tetanus) have a broad range of muscle contraction types, of which tetany is only one. Signs and symptoms Tetany is characterized by contraction of distal muscles of the hands (carpal spasm with extension of interphalangeal joints and adduction and flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joints) and feet (pedal spasm) and is associated with tingling around the mouth and distally in the limbs. Causes * The usual cause of tetany is a deficiency of calcium. An excess of phosphate (high phosphate-to-calcium ratio) can also trigger the spasms. * Underfunction of the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parathyroid Gland
Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes parathyroid hormone in response to low blood calcium, which plays a key role in regulating the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones. Parathyroid glands share a similar blood supply, venous drainage, and lymphatic drainage to the thyroid glands. Parathyroid glands are derived from the epithelial lining of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouch (embryology), pharyngeal pouches, with the superior glands arising from the fourth pouch and the inferior glands arising from the higher third pouch. The relative position of the inferior and superior glands, which are named according to their final location, changes because of the migration of embryological tissues. Hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism, characterized by alterations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |