|
Wilcox Solar Observatory
The Wilcox Solar Observatory (WSO) is a solar observatory in Stanford, California that is used to produce daily observations of the magnetic and velocity field at the Sun's surface. It began daily observations of the Sun's mean magnetic field in May 1975. Formerly known as the Stanford Solar Observatory, it is operated by Stanford University and is located south of the Stanford University campus. It would later be named after solar physicist John M. Wilcox. WSO has historically been funded by NASA Heliophysics, the National Science Foundation, and the Office of Naval Research. WSO uses a Littrow spectrograph together with a Babcock magnetograph on the 5250 Å iron-1 spectral line, which it compares to the close by and magnetically insensitive iron-1 line at 5124 Å, to estimate the line-of-sight photospheric magnetic field to within 0.04 gauss Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; german: Gauß ; la, Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Observatory
A solar observatory is an observatory that specializes in monitoring the Sun. As such, they usually have one or more solar telescopes. The Einstein Tower was a solar observatory in the Albert Einstein Science Park in Potsdam, Germany. Solar observatories study phenomena associated with the Sun. The Sun, being the closest star to earth, allows a unique chance to study stellar physics with high-resolution. It was, until the 1990s, the only star whose surface had been resolved. General topics that interest a solar astronomer are its 11-year periodicity (i.e., the Solar Cycle), sunspots, magnetic field activity (see solar dynamo), solar flares, coronal mass ejections, differential rotation, and plasma physics. Some examples * Huairou Solar Observing Station * Solar observatories in space * National Solar Observatory See also * Coronagraph * Heliometer * Helioscope * List of solar telescopes This is a list of solar telescopes built in various countries around the world. A so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford, California
Stanford is a census-designated place (CDP) in the northwest corner of Santa Clara County, California, United States. It is the home of Stanford University. The population was 21,150 at the 2020 census. Stanford is an unincorporated area of Santa Clara County and is adjacent to the city of Palo Alto. The place is named after Stanford University. Most of the Stanford University campus and other core University owned land is situated within the census-designated place of Stanford though the Stanford University Medical Center, the Stanford Shopping Center, and the Stanford Research Park are officially part of the city of Palo Alto. Its resident population consists of the inhabitants of on-campus housing, including graduate student residences and single-family homes and condominiums owned by their faculty inhabitants but located on leased Stanford land. A residential neighborhood adjacent to the Stanford campus, College Terrace, featuring streets named after universities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity Field
In continuum mechanics the flow velocity in fluid dynamics, also macroscopic velocity in statistical mechanics, or drift velocity in electromagnetism, is a vector field used to mathematically describe the motion of a continuum. The length of the flow velocity vector is the flow speed and is a scalar. It is also called velocity field; when evaluated along a line, it is called a velocity profile (as in, e.g., law of the wall). Definition The flow velocity ''u'' of a fluid is a vector field : \mathbf=\mathbf(\mathbf,t), which gives the velocity of an '' element of fluid'' at a position \mathbf\, and time t.\, The flow speed ''q'' is the length of the flow velocity vector :q = \, \mathbf \, and is a scalar field. Uses The flow velocity of a fluid effectively describes everything about the motion of a fluid. Many physical properties of a fluid can be expressed mathematically in terms of the flow velocity. Some common examples follow: Steady flow The flow of a fluid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun's Surface
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. The term itself is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos, photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the deepest region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Composition of the Sun The Sun is composed primarily of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland Stanford, Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a List of United States senators from California, U.S. senator and former List of governors of California, governor of California who made his fortune as a Big Four (Central Pacific Railroad), railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a Mixed-sex education, coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John M
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
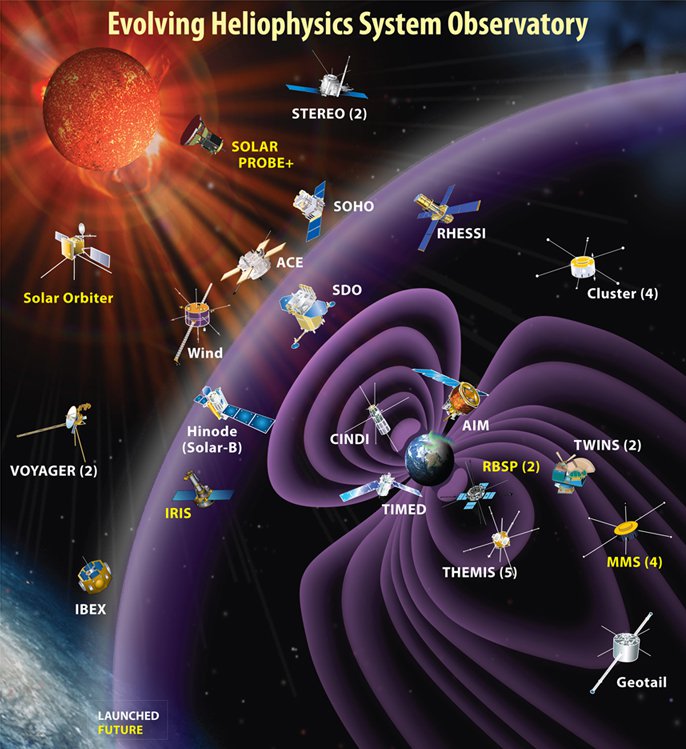
NASA Heliophysics
Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from Attic Greek ''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System. NASA defines heliophysics as "(1) the comprehensive new term for the science of the Sun - Solar System Connection, (2) the exploration, discovery, and understanding of Earth's space environment, and (3) the system science that unites all of the linked phenomena in the region of the cosmos influenced by a star like our Sun." Heliophysics concentrates on the Sun's effects on Earth and other bodies within the Solar System, as well as the changing conditions in space. It is primarily concerned with the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, and upper atmosphere of the Earth and other planets. Heliophysics combines the science of the Sun, corona, heliosphere and geospace, and encompasses a wide variety of astronomical phenomena, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. With an annual budget of about $8.3 billion (fiscal year 2020), the NSF funds approximately 25% of all federally supported basic research conducted by the United States' colleges and universities. In some fields, such as mathematics, computer science, economics, and the social sciences, the NSF is the major source of federal backing. The NSF's director and deputy director are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate, whereas the 24 president-appointed members of the National Science Board (NSB) do not require Senate confirmation. The director and deputy director are responsible for administration, planning, budgeting and day-to-day operations of the foundation, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Naval Research
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) is an organization within the United States Department of the Navy responsible for the science and technology programs of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps. Established by Congress in 1946, its mission is to plan, foster, and encourage scientific research to maintain future naval power and preserve national security. It carries this out through funding and collaboration with schools, universities, government laboratories, nonprofit organizations, and for-profit organizations, and overseeing the Naval Research Laboratory, the corporate research laboratory for the Navy and Marine Corps. NRL conducts a broad program of scientific research, technology and advanced development. ONR Headquarters is in the Ballston neighborhood of Arlington, Virginia. ONR Global has offices overseas in Santiago, Sao Paulo, London, Prague, Singapore, and Tokyo. Overview ONR was authorized by an Act of Congress, Public Law 588, and subsequently approved by Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littrow Spectrograph
In optics, a Littrow prism or Littrow spectrograph or Littrow mirror is a retro-reflecting dispersing prism arranged in such a way that an incident light beam which enters at the Brewster angle undergoes minimal deviation and hence maximum dispersion. Littrow prisms are typically 30°/60°/90° prisms, with a reflective film coating on the surface opposite the 60° angle. It was devised by Otto von Littrow (1843—1864). Typically Littrow prisms are used in lasers at the end of an optical cavity to offer fine adjustment of the laser's output frequency by altering the angle of incidence. Before the ready availability of diffraction gratings Littrow prisms were used widely in spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter .... They are still used in some UV instruments and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Magnetogram
In solar observation, a magnetogram is a pictorial representation of the spatial variations in strength of the solar magnetic field. Solar magnetograms are produced by solar magnetographs. Some magnetographs only measure the absolute value of the magnetic field strength while others are capable of measuring the 3-dimensional magnetic field. The latter are referred to as '' vector magnetographs''. The measurements are usually done based on the Zeeman effect. The first magnetograph was constructed by George Ellery Hale George Ellery Hale (June 29, 1868 – February 21, 1938) was an American solar astronomer, best known for his discovery of magnetic fields in sunspots, and as the leader or key figure in the planning or construction of several world-lead ... in 1908. References Magnetic devices {{Sun-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |