|
Why Evolution Is True
''Why Evolution is True'' is a popular science book by American biologist Jerry Coyne. It was published in 2009, dubbed "Darwin Year" as it marked the bicentennial of Charles Darwin and the hundred and fiftieth anniversary of the publication of his '' On the Origin of Species By Means of Natural Selection.'' Coyne examines the evidence for evolution, some of which was known to Darwin (biogeography) and some of which has emerged in recent years (molecular biology). The book was a ''New York Times'' bestseller, and reviewers praised the logic of Coyne's arguments and the clarity of his prose. It was reprinted as part of the Oxford Landmark Science series. Summary Chapter One, "What is Evolution?", gives a brief overview of Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection as theory and fact. He writes that the "process is remarkably simple. It requires only that individuals of a species vary genetically in their ability to survive and reproduce in their environment. Given this, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerry Coyne
Jerry Allen Coyne (born December 30, 1949) is an American biologist and skeptic known for his work on speciation and his commentary on intelligent design. A professor emeritus at the University of Chicago in the Department of Ecology and Evolution, he has published numerous papers on the theory of evolution. His concentration is speciation and ecological and evolutionary genetics, particularly as they involve the fruit fly, '' Drosophila''. In 2023 he became a fellow with the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry. He is the author of the text ''Speciation'' and the bestselling non-fiction book '' Why Evolution Is True''. Coyne maintains a website and writes for his blog, also called ''Why Evolution Is True''. He is a hard determinist. Coyne gained attention outside of the scientific community as a public critic of religion. As a proponent of New Atheism, he is often cited with atheists such as Richard Dawkins and Sam Harris. He is the author of the book '' Faith Versus Fact''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinornithosaurus
''Sinornithosaurus'' (derived from a combination of Latin and Ancient Greek, Greek, meaning 'Chinese bird-lizard') is a genus of Feathered dinosaurs, feathered dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the early Cretaceous Period (geology), Period (late Barremian) of the Yixian Formation in what is now China. It was the fifth non–avian feathered dinosaurs, feathered dinosaur genera, genus discovered by 1999. The original specimen was collected from the Sihetun locality of western Liaoning. It was found in the Jianshangou beds of the Yixian Formation, dated to 124.5 million years ago. Additional specimens have been found in the younger Dawangzhangzi bed, dating to around 122 million years ago. Xu Xing described ''Sinornithosaurus'' and performed a phylogenetic analysis which demonstrated that it is basal, or primitive, among the dromaeosaurs. He has also demonstrated that features of the skull and shoulder are very similar to ''Archaeopteryx'' and other Avialae, avialans. Together these two fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
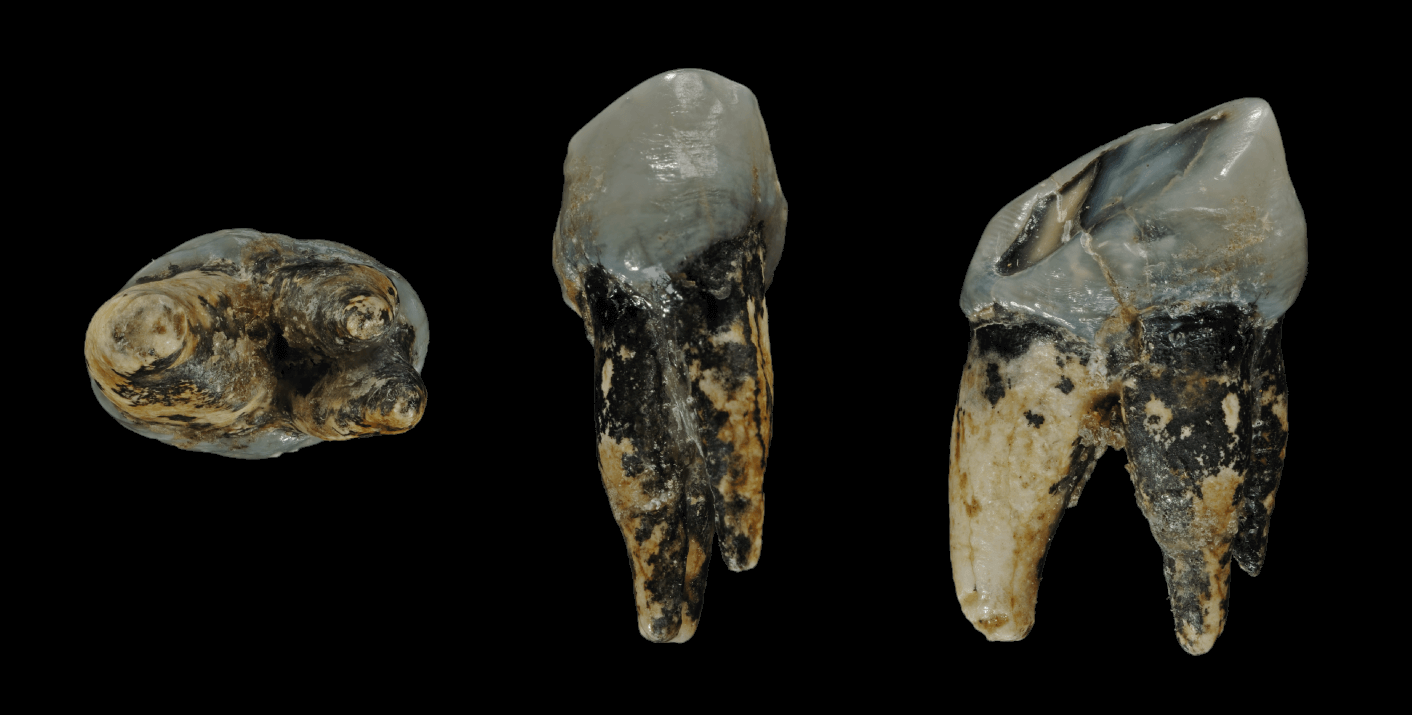
List Of Human Evolution Fossils
The following tables give an overview of notable finds of Hominini, hominin fossils and Skeleton, remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the Chimpanzee–human last common ancestor, human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roughly 7 to 8 million years ago. As there are thousands of fossils, mostly fragmentary, often consisting of single bones or isolated teeth with complete skulls and skeletons rare, this overview is not complete, but shows some of the most important findings. The fossils are arranged by approximate age as determined by radiometric dating and/or incremental dating and the species name represents current consensus; if there is no clear scientific consensus the other possible classifications are indicated. The early fossils shown are not considered ancestors to ''Homo sapiens'' but are closely related to ancestors and are therefore important to the study of the lineage. After 1.5 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of The Horse
The evolution of the horse, a mammal of the family Equidae, occurred over a geologic time scale of 50 million years, transforming the small, dog-sized, forest-dwelling '' Eohippus'' into the modern horse. Paleozoologists have been able to piece together a more complete outline of the evolutionary lineage of the modern horse than of any other animal. Much of this evolution took place in North America, where horses originated but became extinct about 10,000 years ago, before being reintroduced in the 15th century. The horse belongs to the order Perissodactyla ( odd-toed ungulates), the members of which one will share hooved feet and an odd number of toes on each foot, as well as mobile upper lips and a similar tooth structure. This means that horses share a common ancestry with tapirs and rhinoceroses. The perissodactyls arose in the late Paleocene, less than 10 million years after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. This group of animals appears to have been origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predictive Power
The concept of predictive power, the power of a scientific theory to generate testable predictions, differs from ''explanatory power'' and ''descriptive power'' (where phenomena that are already known are retrospectively explained or described by a given theory) in that it allows a prospective test of theoretical understanding. Examples A classic example of the predictive power of a theory is the discovery of Neptune as a result of predictions made by mathematicians John Couch Adams and Urbain Le Verrier, based on Newton's theory of gravity. Another example of the predictive power of theories or models is Dmitri Mendeleev's use of his periodic table to predict previously undiscovered chemical elements and their properties. Though largely correct, he misjudged the relative atomic masses of tellurium and iodine. Moreover, Charles Darwin used his knowledge of evolution by natural selection to predict that since a plant ('' Angraecum sesquipedale'') with a long spur in its flower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorudon
''Dorudon'' ("spear-tooth") is a genus of extinct basilosaurid ancient whales that lived alongside ''Basilosaurus'' 41.03 to 33.9 million years ago in the Eocene. It was a small whale, with ''D. atrox'' measuring long and weighing . ''Dorudon'' lived in warm seas around the world and fed on small fish and mollusks. Fossils have been found along the former shorelines of the Tethys Sea in present-day Egypt and Pakistan, as well as in the United States, New Zealand and Western Sahara. Taxonomic history described ''Dorudon serratus'' based on a fragmentary maxilla and a few teeth found in South Carolina. He concluded that the teeth must have belonged to a mammal since they were two-rooted, that they must have been teeth from a juvenile since they were hollow, and also noted their similarity to the teeth then described for ''Zeuglodon'' (''Basilosaurus''). When exploring the type locality, Gibbes discovered a lower jaw and twelve caudal vertebrae, which he felt obliged to assign to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilosaurus
''Basilosaurus'' (meaning "king lizard") is a genus of large, predatory, prehistoric archaeocete whale from the late Eocene, approximately 41.3 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). First described in 1834, it was the first archaeocete and prehistoric whale known to science. Fossils attributed to the type species ''B. cetoides'' were discovered in the southeastern United States. They were originally thought to be of a giant reptile, hence the suffix "-saurus", Ancient Greek for "lizard". The animal was later found to be an early marine mammal, prompting attempts at renaming the creature, which failed as the rules of zoological nomenclature dictate using the original name given. The second species named in 1904, ''B. isis'', lived in the region currently known as the Mediterranean Sea, with fossils found in North Africa and Jordan. ''Basilosaurus'' is thought to have been one of the largest animals of the Paleogene, with the type species ''B. cetoides'' measuring around long and we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodhocetus
''Rodhocetus'' (from ''Rodho'', the geological anticline at the type locality, and ''cetus'', Latin for whale) is an extinct genus of protocetid early whale known from the Lutetian of Pakistan. The best-known protocetid, ''Rodhocetus'' is known from two partial skeletons that taken together give a complete image of an Eocene whale that had short limbs with long hands and feet that were probably webbed and a sacrum that was immobile with four partially fused sacral vertebrae. It is one of several extinct whale genera that possess land mammal characteristics, thus demonstrating the evolutionary transition from land to sea. Description left, Size of ''Rodhocetus'' relative to a human. ''Rodhocetus'' was a small whale measuring long. Throughout the 1990s, a close relationship between cetaceans and mesonychians, an extinct group of cursorial, wolf-like ungulates, was generally accepted based on morphological analyses. In the late 1990s, however, cladistic analyses based on molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
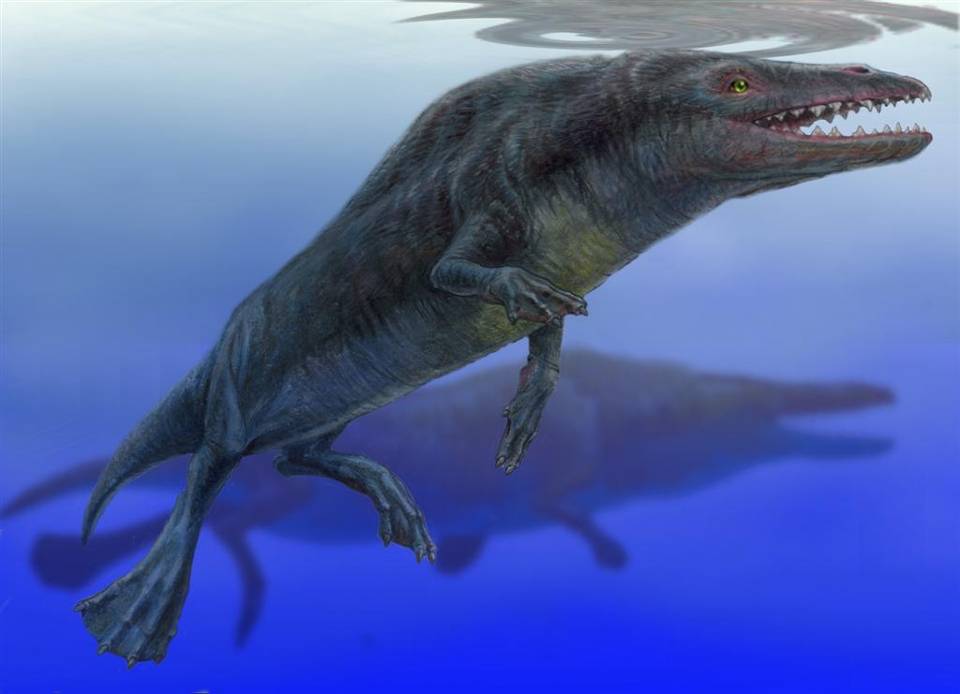
Ambulocetus
''Ambulocetus'' (Latin ''ambulare'' "to walk" + ''cetus'' "whale") is a genus of early Semiaquatic, amphibious cetacean from the Kuldana Formation in Pakistan, roughly 48 or 47 million years ago during the Early Eocene (Lutetian). It contains one species, ''Ambulocetus natans'' (Latin ''natans'' "swimming"), known solely from a near-complete skeleton. ''Ambulocetus'' is among the best-studied of Eocene cetaceans, and serves as an instrumental find in the study of evolution of cetaceans, cetacean evolution and their transition from land to sea, as it was the first cetacean discovered to preserve a suite of adaptations consistent with an amphibious lifestyle. ''Ambulocetus'' is classified in the group Archaeoceti—the ancient forerunners of modern cetaceans whose members span the transition from land to sea—and in the family (biology), family Ambulocetidae, which includes ''Himalayacetus'' and ''Gandakasia'' (also from the Eocene of the Indian subcontinent). ''Ambulocetus'' ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakicetus
''Pakicetus'' (meaning 'whale from Pakistan') is an extinct genus of amphibious cetacean of the family Pakicetidae, which was endemic to the Indian Subcontinent during the Ypresian (early Eocene) period, about 50 million years ago. It was a wolf-like mammal, about long, and lived in and around water where it ate fish and other animals. The name Pakicetus comes from the fact that the first fossils of this extinct amphibious whale were discovered in Pakistan. The vast majority of paleontologists regard it as the most basal whale, representing a transitional stage between land mammals and whales. It belongs to the even-toed ungulates with the closest living non-cetacean relative being the hippopotamus. Description Based on the sizes of specimens, and to a lesser extent on composite skeletons, species of ''Pakicetus'' are thought to have been to in length. ''Pakicetus'' looked very different from modern cetaceans, and its body shape more resembled those of land-dwelling h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indohyus
''Indohyus'' (Meaning "India's pig" from the Greek words ''Indos'', "from India" and ''hûs'', "pig") is an extinct genus of artiodactyl known from Eocene fossils in Asia. This small chevrotain-like animal found in the Himalayas is among the closest known non-cetacean relatives of whales. Discovery The fossils were discovered among rocks that had been collected in 1971 in Kashmir by the Indian geologist A. Ranga Rao who found a few teeth and parts of a jawbone; when he died, however, many rocks had yet to be broken open. Ranga Rao's widow gave the rocks to Hans Thewissen, who was working on them. When his technician accidentally broke one of the skulls they had found, Thewissen recognised the ear structure of the auditory bulla, formed from the ectotympanic bone in a shape which is highly distinctive, found only in the skulls of cetaceans both living and extinct, including '' Pakicetus''. Paleobiology About the size of a fox, this omnivorous pig-like creature shared some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even-toed Ungulate
Artiodactyls are placental mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla ( , ). Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes (the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof). The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, most perissodactyls bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two orders is that many artiodactyls (except for Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine (as perissodactyls do). Molecular biology, along with new fossil discoveries, has found that cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) fall within this taxonomic branch, being most closely related to hippopotamuses. Some modern taxonomists thus apply the name Cetartiodactyla () to this group, while others opt to include cetaceans within the existing name of Artiodactyla. Some researchers use "even-toed ungulates" to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |