|
White Clipper
A white clipper (or white limiter) is a circuit in professional video products that limits the maximum amplitude of the luminance part of the analogue video signal to 1 volt. It is essential for both analogue recording and transmission of video material. Video signal The standard video signal (or more precisely composite video signal Composite video, also known as CVBS (composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync), is an analog video format that combines image information—such as brightness (luminance), color (chrominance), and synchronization, int ...) is a signal with a maximum level of 1 volt into 75 Ω. In this signal 0.3 volt corresponds to black and 1 volt corresponds to white. The 0.0 volt to 0.3 volt range is reserved for the sync pulses. Video circuits are designed around these limits. These limits apply to recording on analogue video tape and analogue transmission as well as in analogue to digital video converters. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminance (video)
In video, luma (Y') represents the brightness in an image (the "black-and-white" or achromatic portion of the image). Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image, while the chroma components represent the color information. Converting R′G′B′ sources (such as the output of a three-CCD camera) into luma and chroma allows for chroma subsampling: because human vision has finer spatial sensitivity to luminance ("black and white") differences than chromatic differences, video systems can store and transmit chromatic information at lower resolution, optimizing perceived detail at a particular bandwidth. Luma versus relative luminance Luma is the weighted sum of gamma-compressed R′G′B′ components of a color video—the ''prime symbols'' ′ denote gamma compression. The word was proposed to prevent confusion between luma as implemented in video engineering and relative luminance as used in color science (i.e. as defined by CIE). Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analogue Video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems, which, in turn, were replaced by flat-panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities, and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcasts, magnetic tape, optical discs, computer files, and network streaming. Etymology The word ''video'' comes from the Latin verb ''video,'' meaning to see or ''videre''. And as a noun, "that which is displayed on a (television) screen," History Analog video Video developed from facsimile systems developed in the mid-19th century. Early mechanical video scanners, such as the Nipkow disk, were patented as early as 1884, however, it took several decades b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Video Signal
Composite video, also known as CVBS (composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync), is an analog video format that combines image information—such as brightness (luminance), color (chrominance), and synchronization, into a single signal transmitted over one channel. It is most commonly used for standard-definition television, and is sometimes referred to as ''SD video''. The signal is typically carried on a yellow RCA connector, with separate connectors used for left and right audio channels. In professional equipment, a BNC connector is often used instead. Other connector types may appear in compact consumer devices like digital cameras. Composite video supports several line resolutions, including 405-line, 525-line, and 625-line interlaced formats. It exists in three major regional variants based on analog color encoding standards: NTSC, PAL, and SECAM. The same format can also be used to transmit monochrome (black-and-white) video. Signal component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proportion to a property, primarily the instantaneous amplitude, of a message signal, such as an audio signal. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and Run-length limited#FM: .280.2C1.29 RLL, computing. In Analog signal, analog frequency modulation, such as radio broadcasting of voice and music, the instantaneous frequency deviation, i.e. the difference between the frequency of the carrier and its center frequency, has a functional relation to the modulating signal amplitude. Digital data can be encoded and transmitted with a type of frequency modulation known as frequency-shift keying (FSK), in which the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is shifted among a set of frequencies. The frequencies m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCIR System B
CCIR System B (originally known as the "Gerber Standard") was the 625-line VHF analog broadcast television system which at its peak was adopted by more than one hundred countries, either with PAL or SECAM colour. It is usually associated with CCIR System G for UHF broadcasts. System B was the first internationally accepted 625-line broadcasting standard in the world. A first 625-line system with a 8 MHz channel bandwidth was proposed at the CCIR Conference in Stockholm in July 1948 (based on 1946-48 studies in the Soviet Union by Mark KrivosheevOn the beginning of broadcast in 625-lines 60 year s ago, ''625'' magazine (in Russian). ). At a CCIR Geneva meeting in July 1950 Dr. Gerber (a Swiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCIR System M
CCIR System M, sometimes called 525–line, NTSC, NTSC-M, or CCIR-M, is the analog broadcast television system approved by the FCC (upon recommendation by the National Television System Committee - NTSC) for use in the United States since July 1, 1941, replacing the 441-line TV system introduced in 1938. It is also known as EIA standard 170. System M comprises a total of 525 interlaced lines of video, of which 486 contain the image information, at 30 frames per second. Video is amplitude modulated and audio is frequency modulated, with a total bandwidth of 6 MHz for each channel, including a guard band. It was also adopted in the Americas and Caribbean; Myanmar, Philippines, South Korea, Taiwan and Japan (here with minor differences, informally referred to as ''System J)''. System M doesn't specify a color system, but NTSC color encoding was normally used, with some exceptions: NTSC-J in Japan, PAL-M in Brazil and SECAM-M in Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam (see '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrominance
Chrominance (''chroma'' or ''C'' for short) is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture (see YUV color model), separately from the accompanying Luma (video), luma signal (or Y' for short). Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B-Y, B′ − Y′ (blue − luma) and V = R-Y, R′ − Y′ (red − luma). Each of these different components may have scale factors and offsets applied to it, as specified by the applicable video standard. In composite video signals, the U and V signals modulate a color subcarrier signal, and the result is referred to as the chrominance signal; the Phase (waves), phase and amplitude of this modulated chrominance signal correspond approximately to the hue and Saturation (color theory), saturation of the color. In digital-video and still-image color spaces such as Y′CbCr, the luma and chrominance components are digita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTSC
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170. In 1953, a second NTSC standard was adopted, which allowed for color television broadcast compatible with the existing stock of black-and-white receivers. It is one of three major color formats for analog television, the others being PAL and SECAM. ''NTSC color'' is usually associated with the System M; this combination is sometimes called NTSC II. The only other broadcast television system to use NTSC color was the System J. Brazil used System M with PAL color. Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos used System M with SECAM color – Vietnam later started using PAL in the early 1990s. The NTSC/System M standard was used in most of the Americas (except Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay), Myanmar, South Korea, Taiwan, Philippines, Japan, and some Pacific Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Clipping
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on television and computer screens is created by a mixture of red, blue, and green light. The color white can be given with white pigments, especially titanium dioxide. In ancient Egypt and ancient Rome, priestesses wore white as a symbol of purity, and Romans wore white togas as symbols of citizenship. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance a white unicorn symbolized chastity, and a white lamb sacrifice and purity. It was the royal color of the kings of France as well as the flag of monarchist France from 1815 to 1830, and of the monarchist movement that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War (1917–1922). Greek temples and Roman temples were faced with white marble, and beginning in the 18th century, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zener Diode
A Zener diode is a type of diode designed to exploit the Zener effect to affect electric current to flow against the normal direction from anode to cathode, when the voltage across its terminals exceeds a certain characteristic threshold, the ''Zener voltage''. Zener diodes are manufactured with a variety of Zener voltages, including variable devices. Some types have an abrupt, heavily doped p–n junction with a low Zener voltage, in which case the reverse conduction occurs due to electron quantum tunnelling in the short distance between p and n regions. Diodes with a higher Zener voltage have more lightly doped junctions, causing their mode of operation to involve avalanche breakdown. Both breakdown types are present in Zener diodes with the Zener effect predominating at lower voltages and avalanche breakdown at higher voltages. Zener diodes are used to generate low-power stabilized supply rails from higher voltages and to provide reference voltages for circuits, especially sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band-pass Filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range. It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''. Description In electronics and signal processing, a filter is usually a two-port circuit or device which removes frequency components of a signal (an alternating voltage or current). A band-pass filter allows through components in a specified band of frequencies, called its ''passband'' but blocks components with frequencies above or below this band. This contrasts with a high-pass filter, which allows through components with frequencies above a specific frequency, and a low-pass filter, which allows through components with frequencies below a specific frequency. In digital signal processing, in which signals represented by digital numbers are processed by computer programs, a band-pass filter is a computer algorithm that performs the same function. The term band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
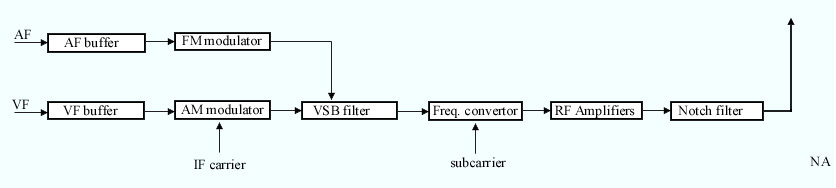
TV Transmitter
A television transmitter is a transmitter that is used for terrestrial (over-the-air) television broadcasting. It is an electronic device that radiates radio waves that carry a video signal representing moving images, along with a synchronized audio channel, which is received by television receivers ('televisions' or 'TVs') belonging to a public audience, which display the image on a screen. A television transmitter, together with the broadcast studio which originates the content, is called a television station. Television transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to a certain frequency channel and power level. They transmit on frequency channels in the VHF and UHF bands. Since radio waves of these frequencies travel by line of sight, they are limited by the horizon to reception distances of 40–60 miles depending on the height of transmitter station. Television transmitters use one of two different technologies: ''analog'', in which the picture and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |