|
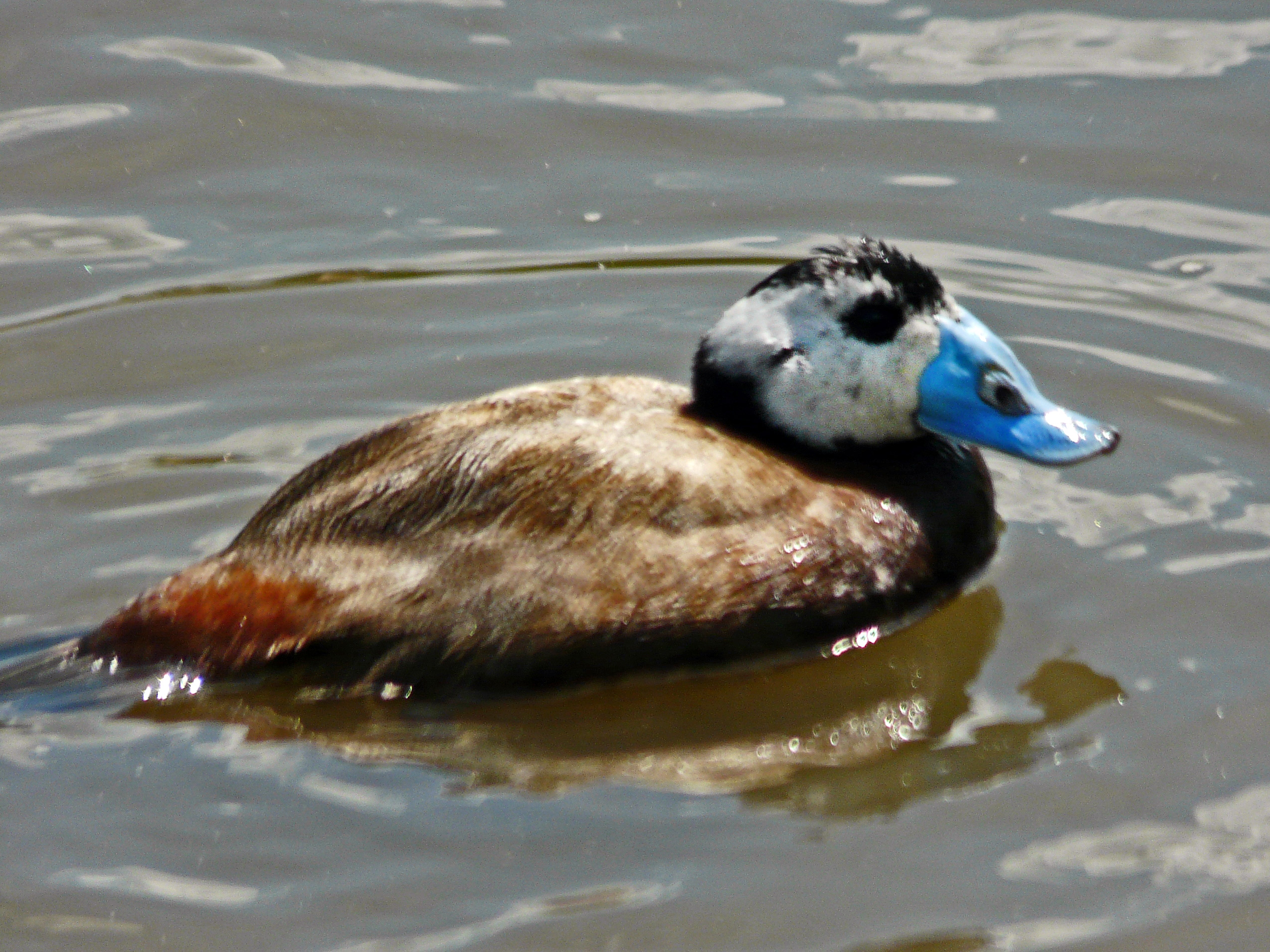
White-headed Duck
The white-headed duck (''Oxyura leucocephala'') is a small diving duck some long. The male has a white head with black crown, a blue bill, and reddish-grey plumage. The female has a dark bill and rather duller colouring. Its breeding habitat is lakes with open water and dense vegetation at the margin. It dives under water and feeds on aquatic vegetation as well as some animal matter. It is more likely to swim away from a perceived threat than to fly. This duck is known from Spain, North Africa, Western Asia and Central Asia. Populations are declining, mostly due to Habitat destruction, loss of habitat and pollution, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated the bird's status as "endangered species, endangered". Taxonomy and systematics The white-headed duck was originally described as ''Anas leucocephala'' by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli, Giovani Antonio Scopoli in 1769. It is currently in the genus Stiff-tailed duck, Oxyura. Other generic synonyms used in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Antonio Scopoli
Giovanni Antonio Scopoli (sometimes Latinisation of names, Latinized as Johannes Antonius Scopolius) (3 June 1723 – 8 May 1788) was an Italians, Italian physician and natural history, naturalist. His biographer Otto Guglia named him the "first anational European" and the "Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus of the Habsburg monarchy, Austrian Empire". Biography Scopoli was born at Cavalese in the Val di Fiemme, belonging to the Prince-Bishopric of Trent, Bishopric of Trent (today's Trentino), son of Francesco Antonio, military commissioner, and Claudia Caterina Gramola (1699-1791), a painter from a patrician family from Trentino. He obtained a degree in medicine at University of Innsbruck, and practised as a doctor in Cavalese and Venice.Newton, Alfred 1881. ''Scopoli's ornithological papers.'' The Willoughby SocietyScanned version/ref> Much of his time was spent in the Alps, Plant collecting, collecting plants and Entomology, insects, of which he made outstanding collections. He spent two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat (ecology)
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, habitat generalist species are able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species require a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior of a stem, a rotten log, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of West Asia
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of Europe
More than 900 species of birds have been observed in Europe. The avifauna of Europe is broadly similar to that of Asia north of the Himalayas and North Africa, both of which also belong to the Palearctic realm. There are also many groups shared with North America. On the other hand, many groups characteristic of the Afrotropical and Indomalayan realms are entirely absent from Europe, including jacanas, darters, trogons, hornbills, honeyguides, barbets (families Lybiidae in Africa and Megalaimidae in Asia), parrots, pittas, cuckooshrikes, broadbills (families Calyptomenidae and Eurylaimidae), drongos, monarch flycatchers, white-eyes, and estrildid finches (although parrots and estrildid finches have been introduced to Europe by humans). Two species that occurred in the European region until recently (post 1800) — the great auk and the Canary Islands oystercatcher — are now globally extinct, while one additional species — the slender-billed curlew — may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducks
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family (biology), family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and goose, geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form taxon; they do not represent a monophyletic group (the group of all descendants of a single common ancestral species), since swans and geese are not considered ducks. Ducks are mostly aquatic birds, and may be found in both fresh water and sea water. Ducks are sometimes confused with several types of unrelated water birds with similar forms, such as loons or divers, grebes, gallinules and coots. Etymology The word ''duck'' comes from Old English 'diver', a derivative of the verb 'to duck, bend down low as if to get under something, or dive', because of the way many species in the dabbling duck group feed by upending; compare with Dutch language, Dutch and German language, German 'to dive'. This word replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyurinae , a tribe of ducks in the family Anatidae
{{Disambiguation, geo ...
Oxyurinae may refer to: * Oxyuridae, a family of nematode worms * Oxyurini The Oxyurini are a tribe of the duck subfamily of birds, the Anatinae. It has been subject of considerable debate about its validity and circumscription. Some taxonomic authorities place the group in its own subfamily, the ''Oxyurinae''. Most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birding World
''Birding World'' was a monthly birdwatching, birding magazine published in the United Kingdom. It was the magazine of the Bird Information Service, based at Cley next the Sea, Norfolk. With the publication of issue No. 26/12 in January 2014, ''Birding World'' magazine ceased publication. History and profile Originally published in 1987 as ''Twitching'' volume 1, the magazine underwent a name-change to this name, in 1988 (also resetting its volume count back to 1). The editor was Steve Gantlett, and the assistant editor Richard Millington. It was aimed at birdwatcher, birders with an interest in the occurrence and identification of rare birds in the United Kingdom and the Western Palearctic. It also covered birding-related material from around the globe. The range of material published included: * papers on bird identification, often including proposed new identification characters for difficult groups of taxa * news articles on rare birds in Britain and elsewhere in the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gantlett, Steve
Stephen J. M. Gantlett is a British birder. He lives with his wife Sue in Cley-next-the-Sea, Norfolk. A qualified optician, SJMG retired from this profession in 1982 to become a full-time ornithologist. He was the editor of Birding World magazine until it ceased production in January 2014. He also co-runs Birdline, a telephone information service containing news of rare birds, with Richard Millington. Steve Gantlett is a twitcher. He is one of a small number of birders who have seen over 500 species in Britain. He is a former member of the British Birds Rarities Committee. Gantlett's specialism as an ornithologist is the advancement of bird identification. Among the areas of knowledge in which Gantlett has played a key role are the identification of orange-billed terns. He also found the UK's first Rock Sparrow at Cley on 14 June 1981 (with Richard Millington), still the only record in the UK. He has published papers on this subject in Birding World ''Birding World'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AEWA
The Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds, or African-Eurasian Waterbird Agreement (AEWA), is an independent international treaty developed under the auspices of the United Nations Environment Programme's Convention on Migratory Species. Background The Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds was drafted on 19 June 1995 in The Hague, Netherlands, in order to coordinate efforts to conserve bird species migrating between European and African nations. Description The AEWA is an independent treaty under the auspices of the Convention on Migratory Species, of the United Nations Environment Programme. The agreement focuses on bird species that depend on wetlands for at least part of their lifecycle and cross international borders in their migration patterns. As of 2023 it covered 255 species. As of July 2023, its scope covered territories in 119 Range States stretching from the Arctic to South Africa, encompassing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyura Jamaicensis
The ruddy duck (''Oxyura jamaicensis'') is a species of duck in the family Anatidae. The ruddy duck is one of six species within the stiff-tailed ducks (genus ''Oxyura''). Stiff-tailed ducks occupy heavily vegetated habitats in North and South America as well as the British Isles, France, and Spain. In the 1940s, the ruddy duck was introduced to the United Kingdom, where it has since established a growing population. Outside the Americas, the ruddy duck is considered a highly invasive species, prompting many countries to initiate culling projects to eradicate it from the native ecosystem. The generic name is derived from Ancient Greek ''oxus'' meaning "sharp", and ''oura'' meaning "tail". The specific name ''jamaicensis'' means "from Jamaica". The ruddy duck has also been nicknamed "butterball", a term used to describe an individual that is somewhat fat, due to its short and stout stature making activities like flying and walking upright awkward. Taxonomy The ruddy duck was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |