|
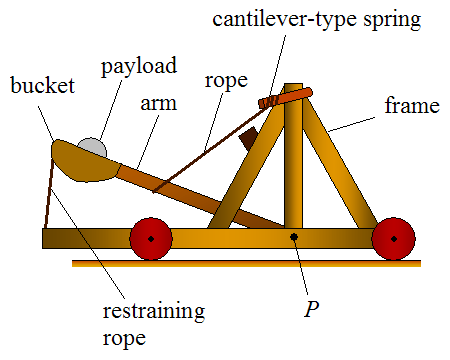
West Spring Gun
The West Spring Gun was a bomb-throwing catapult used by British, Canadian and Australian forces during World War I. It was designed to throw a hand grenade in a high trajectory into enemy trenches. Description It consisted of a metal frame supporting a throwing arm powered by 24 metal springs. It was invented by Captain Allen West in 1915 and manufactured by the Reason Manufacturing Company of Brighton, which was granted a patent for the device on 19 October of that year. Although called a catapult, it was a hybrid of a ballista and a trebuchet. It required a crew of five - three to compress the springs, one to load the bomb, and one to fire as soon as the fuse was lit or the grenade pin was pulled. In tests, it could throw Mills bomb about or a projectile about with a flight time of 6 or 7 seconds. In the field it generally threw a Jam Tin Grenade, No. 15 Ball grenade, No. 21 "Spherical" grenade or No. 28 chemical grenade, equipped with a slightly longer fuse (typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored potential energy to propel its payload. Most convert Tension (mechanics), tension or Torsion (mechanics), torsion energy that was more slowly and manually built up within the device before release, via springs, bows, twisted rope, elastic, or any of numerous other materials and mechanisms which allow the catapult to launch a projectile such as rocks, cannon balls, or debris. During wars in the ancient times, the catapult was usually known to be the strongest heavy weaponry. In modern times the term can apply to devices ranging from a simple hand-held implement (also called a "slingshot") to a mechanism for Aircraft catapult, launching aircraft from a ship. The earliest catapults date to at least the 7th century BC, with Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jam Tin Grenade
The double cylinder, Nos. 8 and No. 9 hand grenades, also known as the "jam tins", are a type of improvised explosive device used by the British and Commonwealth forces, notably the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) in World War I. The jam tin, or bully beef tin, was one of many grenades designed by ANZACs in the early part of the First World War in response to a lack of equipment suited to trench warfare. The grenade was an inner can of explosive with an outer can of metal fragments or bearing balls. The heavier pattern No. 9 grenade contained more high explosive and more metal fragments. The fuse was ignited by a friction device or a cigarette. Initially when demand for grenades was at its greatest, engineers were encouraged to improvise their own grenades from the tins containing the soldier's ration of jam, hence the name. Incidents with the improvised form and the supply of superior grenades led to official withdrawal of the design. Jam tin grenades were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I British Infantry Weapons
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectile Weapons
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion (physics), motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found in warfare and sports (for example, a thrown Baseball (ball), baseball, kicked ball (association football), football, fired bullet, shot arrow, stone released from catapult). In ballistics, mathematical equations of motion are used to analyze projectile trajectory, trajectories through launch, flight, and terminal ballistics, impact. Motive force Blowguns and pneumatic rifles use compressed gases, while most other guns and cannons utilize expanding gases liberated by sudden chemical reactions by propellants like smokeless powder. Light-gas guns use a combination of these mechanisms. Railguns utilize electromagnetic fields to provide acceleration along the entire length of the device, greatly increasing the muzzle veloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian War Memorial
The Australian War Memorial (AWM) is a national war memorial, war museum, museum and archive dedicated to all Australians who died as a result of war, including peacekeeping duties. The AWM is located in Campbell, Australian Capital Territory, Campbell, a suburb of the Australian capital city of Canberra. The grounds include five buildings and a sculpture garden. Most of the museum galleries and commemorative areas are contained in the Memorial Building. Plans to build a national war memorial and museum were initiated shortly after the First World War, with the AWM formally established through federal legislation in 1925. Designs for the AWM were created by Emil Sodersten and John Crust, although the onset of the Great Depression delayed its construction. Work on the Memorial Building progressed in the mid-1930s, and the AWM was officially opened to the public in 1941. Several structures designed by Denton Corker Marshall were built on the grounds from the 1980s to 2000s, to hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial War Museum
The Imperial War Museum (IWM), currently branded "Imperial War Museums", is a British national museum. It is headquartered in London, with five branches in England. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, it was intended to record the civil and military war effort and sacrifice of the United Kingdom and its Empire during the First World War. The museum's remit has since expanded to include all conflicts in which British or Commonwealth forces have been involved since 1914. As of 2012, the museum aims "to provide for, and to encourage, the study and understanding of the history of modern war and 'wartime experience'." Originally housed in the Crystal Palace at Sydenham Hill, the museum opened to the public in 1920. In 1924, it moved to space in the Imperial Institute in South Kensington and in 1936 it acquired a permanent home at the former Bethlem Royal Hospital in Southwark, which serves as its headquarters. The outbreak of the Second World War saw the museum expand bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes Mortar
The Stokes mortar was a British trench mortar designed by Sir Wilfred Stokes KBE that was issued to the British and U.S. armies, as well as the Portuguese Expeditionary Corps, during the latter half of the First World War. The 3-inch trench mortar is a smooth-bore, muzzle-loading weapon for high angles of fire. Although it is called a 3-inch mortar, its bore is actually 3.2 inches or 81 mm. Design The Stokes mortar was a simple weapon, consisting of a smoothbore metal tube fixed to a base plate (to absorb recoil) with a lightweight bipod mount. When a mortar bomb was dropped into the tube, an impact sensitive primer in the base of the bomb would make contact with a firing pin at the base of the tube, and ignite the propellant charge in the base, launching the bomb towards the target. The warhead itself was detonated by an impact fuse on reaching the target. The barrel is a seamless drawn-steel tube necked down at the breech or base end. To the breech end is fitted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2 Inch Medium Mortar
The 2 inch medium trench mortar, also known as the 2-inch howitzer, and nicknamed the "toffee apple" or "plum pudding" mortar, was a British smooth bore muzzle loading (British ordnance terms#SBML, SBML) medium trench mortar in use in World War I from mid-1915 to mid-1917. The designation "2-inch" refers to the mortar barrel, into which only the bomb shaft but not the bomb itself was inserted; the spherical bomb itself was actually in diameter and weighed , hence this weapon is more comparable to a standard mortar of approximately bore. Background and predecessors As the Western Front in France and Belgium stagnated into trench warfare in late 1914, British forces found themselves with no means of replying to the German ''minenwerfers'' (trench mortars) which were lobbing both small and large (over ) high-explosive shells into their frontline trenches from short range. British commanders requested an accurate short-range weapon which was manually portable in the trenches, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Ypres
The Second Battle of Ypres was fought from 22 April – 25 May 1915, during the First World War, for control of the tactically-important high ground to the east and the south of the Flanders, Flemish town of Ypres, in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of Chemical weapon, poison gas on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front. Background The Germans, German chemist Walther Nernst, who in 1914 was a volunteer driver, proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas. The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by the 4th Army (German Empire), 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Canadian Division
The 1st Canadian Division (French: ) is a joint operational command and control formation based at CFB Kingston, and falls under Canadian Joint Operations Command. It is a high-readiness unit, able to move on very short notice, and is staffed and equipped to meet Canada's military objectives to counter any potential threat. Formed during the First World War in August 1914, the 1st Canadian Division was a formation of the Canadian Expeditionary Force. The division contained a cavalry squadron and a Bicycle infantry, cyclist company, three infantry brigades (the 1st, 2nd and 3rd Canadian Infantry Brigades, each of four battalions), representing all parts of Canada, three field artillery brigades (roughly equivalent to modern regiments) armed with 18-pounders and engineers, together with elements of the Army Service Corps and the Army Medical Corps. The total war establishment of the division was 17,873 all ranks, with 4,943 horses. During its service in the First World War, the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |