|
Wenchang Satellite Launch Center
The Wenchang Space Launch Site ( zh, 文昌航天发射场, links=no) is a rocket launch site located in Wenchang on the island of Hainan, in China. Formally a suborbital test center, it currently serves as China's southernmost spaceport. The site was selected for its low latitude, 19° north of the equator, allowing for larger payloads to be launched. It is capable of launching the Long March 5, the heaviest Chinese rocket. Unlike launch facilities on the mainland, Wenchang uses its seaport for deliveries. The construction of the site was complete by October 2014. The first launch took place on 25 June 2016. Due to construction delays, the initial launch of the CZ-5 booster from Wenchang, originally expected to start in 2014 was postponed and took place on 3 November 2016. The CZ-5B (maximum payload to LEO) variant was expected to be completed circa 2018 but the maiden flight took place on 5 May 2020. A CZ-5 carrier rocket was already shipped from North China's Tian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenchang
Wenchang ( postal: Mencheong; ; Hainanese spellings: Boon Siou) is a county-level city in the northeast of Hainan Island in China. Covering an area of , the city has a coastline of , and is divided into 17 towns. The city is a major target for typhoons in the northwestern Pacific, and experiences the most frequent and severe typhoon-induced storm surges in the South China Sea. The city is a major ancestral home of Chinese diaspora, with the local dish Wenchang chicken as an origin of Hainanese chicken rice in Southeast Asia. Since 2016, the city has also been home to China’s newest spaceport. History Wenchang was elevated from a county to a city on November 7, 1995. Its population was recorded as 86,551 in 1999, with an estimated increase to 115,000 by 2006. Maps published by the Republic of China in Taiwan still depict Wenchang as a county within its Guangdong province. In 2016, Wenchang Space Launch Site was put in use, which is China's latest spaceport. Geography Locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 5
Chang'e 5 () was the fifth lunar exploration mission in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program of CNSA, and China's first lunar sample-return mission. Like its predecessors, the spacecraft is named after the Chinese moon goddess, Chang'e. It launched at 20:30 UTC on 23 November 2020, from Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on Hainan Island, landed on the Moon on 1 December 2020, collected ~ of lunar samples (including from a core ~1 m deep), and returned to the Earth at 17:59 UTC on 16 December 2020. Chang'e 5 was the first lunar sample-return mission since the Soviet Union's Luna 24 in 1976. New lunar minerals, including Changesite-(Y) and two different structures of the titanium compound Ti2O, were identified from the samples returned from the mission, making China the third country to discover a new lunar mineral. The mission also made China the third country to return samples from the Moon after the United States and the Soviet Union. Overview The Chinese Lunar Expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianhe (space Station Module)
''Tianhe'' (), officially the ''Tianhe'' core module (), is the first module to launch of the Tiangong space station. It was launched into orbit on 29 April 2021, as the first launch of the final phase of Tiangong program, part of the China Manned Space Program ( Project 921). ''Tianhe'' follows the earlier projects Salyut, Skylab, Mir, International Space Station, Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2 space stations. It is the first module of a third-generation Chinese modular space station. Other examples of modular station projects include the Soviet/Russian Mir and the International Space Station. Operations will be controlled from the Beijing Aerospace Flight Control Center. In 2018, a fullscale mockup of ''Tianhe'' was publicly presented at China International Aviation & Aerospace Exhibition in Zhuhai. In October 2020, China selected 18 new astronauts ahead of the space station construction to participate in the country's space station project. Functions and systems The core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Mars Injection
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun itself are in such orbits, as are many artificial probes and pieces of debris. The moons of planets in the Solar System, by contrast, are not in heliocentric orbits, as they orbit their respective planet (although the Moon has a convex orbit around the Sun). The barycenter of the Solar System, while always very near the Sun, moves through space as time passes, depending on where other large bodies in the Solar System, such as Jupiter and other large gas planets, are located at that time. A similar phenomenon allows the detection of exoplanets by way of the radial-velocity method. The ''helio-'' prefix is derived from the Greek word "ἥλιος", meaning "Sun", and also Helios, the personification of the Sun in Greek mythology. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
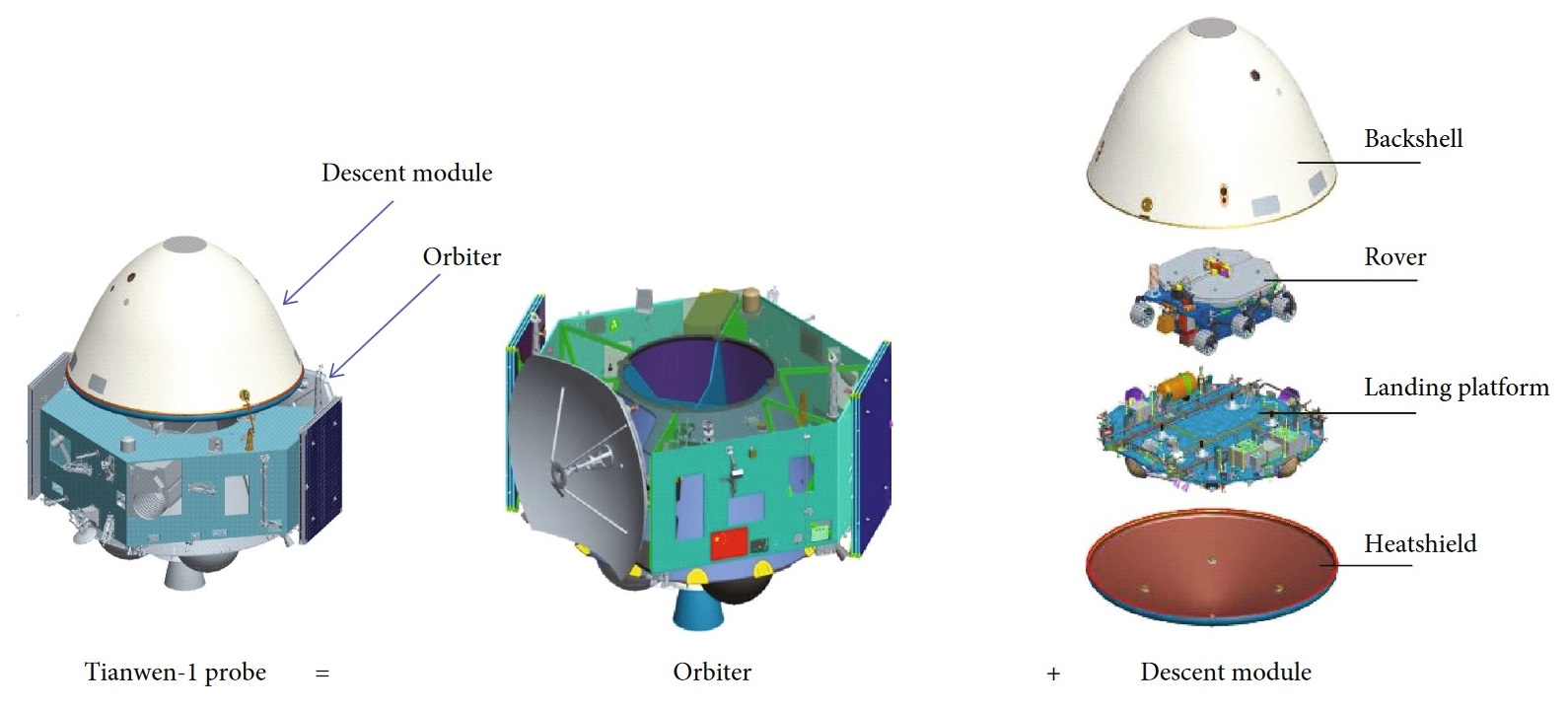
Tianwen-1
-1 ( zh , s = 天问一号) (also referred to as TW-1) is an interplanetary mission by the China National Space Administration (CNSA) which sent a robotic spacecraft to Mars, consisting of 6 spacecraft: an orbiter, two deployable cameras, lander, remote camera, and the ' rover. The spacecraft, with a total mass of nearly five tons, is one of the heaviest probes launched to Mars and carries 14 scientific instruments. It is the first in a series of planned missions undertaken by CNSA as part of its Planetary Exploration of China program. The mission's scientific objectives include: investigation of Martian surface geology and internal structure, search for indications of current and past presence of water, and characterization of the space environment and the atmosphere of Mars. The mission was launched from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on 23 July 2020 on a Long March 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. After seven months of transit through the inner Solar System, the spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shijian
Shijian (, Abbreviation, abbr. "SJ") is a series of satellites built and operated by the China, People's Republic of China. Some Shijian-series satellites have drawn significant concerns from the United States government and space observers who cite unannounced launches, undisclosed sub-satellites deployed in orbit, unusual orbital maneuvers, and demonstrated rendezvous proximity operations (RPO) including the close inspection and towing of other satellites. Little is known about the series and what differentiates it from other experimental satellite series launched by China such as the Chuangxin () series or Shiyan () series. The China Aerospace Studies Institute of the United States Air Force asserts that Shiyan (satellite), Shiyan-series satellites play an earlier role in the systems development process testing various new technologies on a single bus while Shijian-series satellites are used to develop the best operational practices and optimize the technologies previously te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiden Flight
The maiden flight, also known as first flight, of an aircraft is the first occasion on which it leaves the ground under its own power. The same term is also used for the first launch of rockets. In the early days of aviation it could be dangerous, because the exact handling characteristics of the aircraft were generally unknown. The maiden flight of a new type is almost invariably flown by a highly experienced test pilot. Maiden flights are usually accompanied by a chase plane, to verify items like altitude, airspeed, and general airworthiness. A maiden flight is only one stage in the development of an aircraft type. Unless the type is a pure research aircraft (such as the X-15), the aircraft must be tested extensively to ensure that it delivers the desired performance with an acceptable margin of safety. In the case of civilian aircraft, a new type must be certified by a governing agency (such as the Federal Aviation Administration in the United States) before it can enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongjiao, Xiangxiang
Dongjiao Township () is a rural township in Xiangxiang City, Hunan Province, People's Republic of China. Cityscape The township is divided into 30 villages, which include the following areas: Xin Village, Huzhou Village, Huating Village, Dingtuo Village, Wangtang Village, Changfeng Village, Shanghau Village, Daqiao Village, Yangshu Village, Xinjiang Village, Xintang Village, Shijiang Village, Shizhu Village, Wangxing Village, Sanxiang Village, Xinyan Village, Xibei Village, Luogongqiao Village, Taopeng Village, Xiangshao Village, Xianghong Village, Bixing Village, Zhetang Village, Tianyuan Village, Jinxing Village, Xinyuan Village, Yongfeng Village, Fengquan Village, Hujian Village, Zhangu Village, Hengxin Village, Hengzhou Village, and Shichong Village (新村、浒洲村、花亭村、定托村、王塘村、长丰村、上花村、大桥村、杨树村、新江村、新塘村、石江村、石竹村、旺兴村、三湘村、新研村、西北村、罗公桥村、炭棚村、� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohu
Sohu, Inc. () is a Chinese Internet company headquartered in the Sohu Internet Plaza in Haidian District, Beijing. Sohu and its subsidiaries offer advertising, a search engine (Sogou.com), on-line multiplayer gaming (ChangYou.com) and other services. History Sohu was founded as Internet Technologies China (ITC) in 1996 by Charles Zhang after he completed his PhD from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and received venture capital funding from colleagues he met there. The following year, Zhang changed the name of ITC to Sohoo in homage to Yahoo! after meeting its cofounder, Jerry Yang; the name was soon after changed to Sohu to differentiate it from the American company. Sohu has been listed on NASDAQ since 2000 through a variable interest entity (VIE) based in Delaware. Sohu's Sogou.com search engine was in talks to be sold in July 2013 to Qihoo for around $1.4 billion. On September 17, 2013, it was announced that Tencent has invested $448 million for a minority sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Military Commission (People's Republic Of China)
Central Military Commission may refer to: * Central Military Commission (China), the highest national defense organization in the People's Republic of China. * Central Military Commission of the Communist Party of Vietnam, the highest body in Vietnam on military policy and heads the People's Army of Vietnam (PVAN). * Central Military Commission of the Workers' Party of Korea, an organ of the Central Committee of the Workers' Party of Korea. See also * Civilian control of the military in communist states {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Council Of The People's Republic Of China
The State Council of the People's Republic of China, also known as the Central People's Government, is the chief administrative authority and national cabinet. It is constitutionally the highest administrative organ of the country and the executive organ of the National People's Congress, the highest organ of state power. It is composed of a premier, vice-premiers, state councilors, ministers, chairpersons of commissions, an auditor-general, the governor of the People's Bank of China, and a secretary-general. The premier of the State Council is responsible for the State Council and exercises overall leadership of its work. The secretary-general of the State Council, under the leadership of the premier, is responsible for handling the daily work of the State Council and heads the General Office of the State Council. The executive meeting of the State Council, consisting of the premier, vice-premiers, state councilors, and the secretary-general, is held two to three times a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |