|
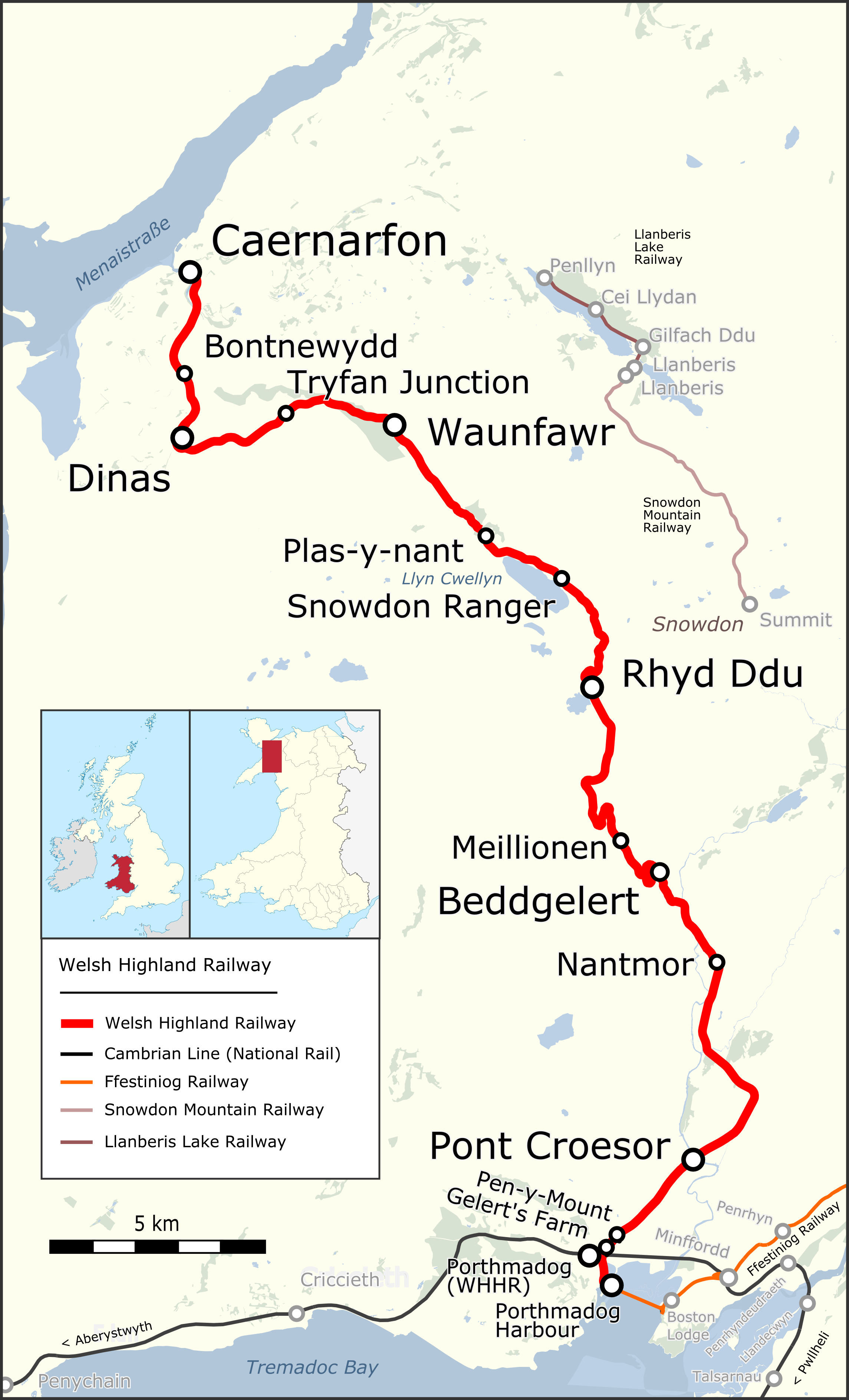
Welsh Highland Railway
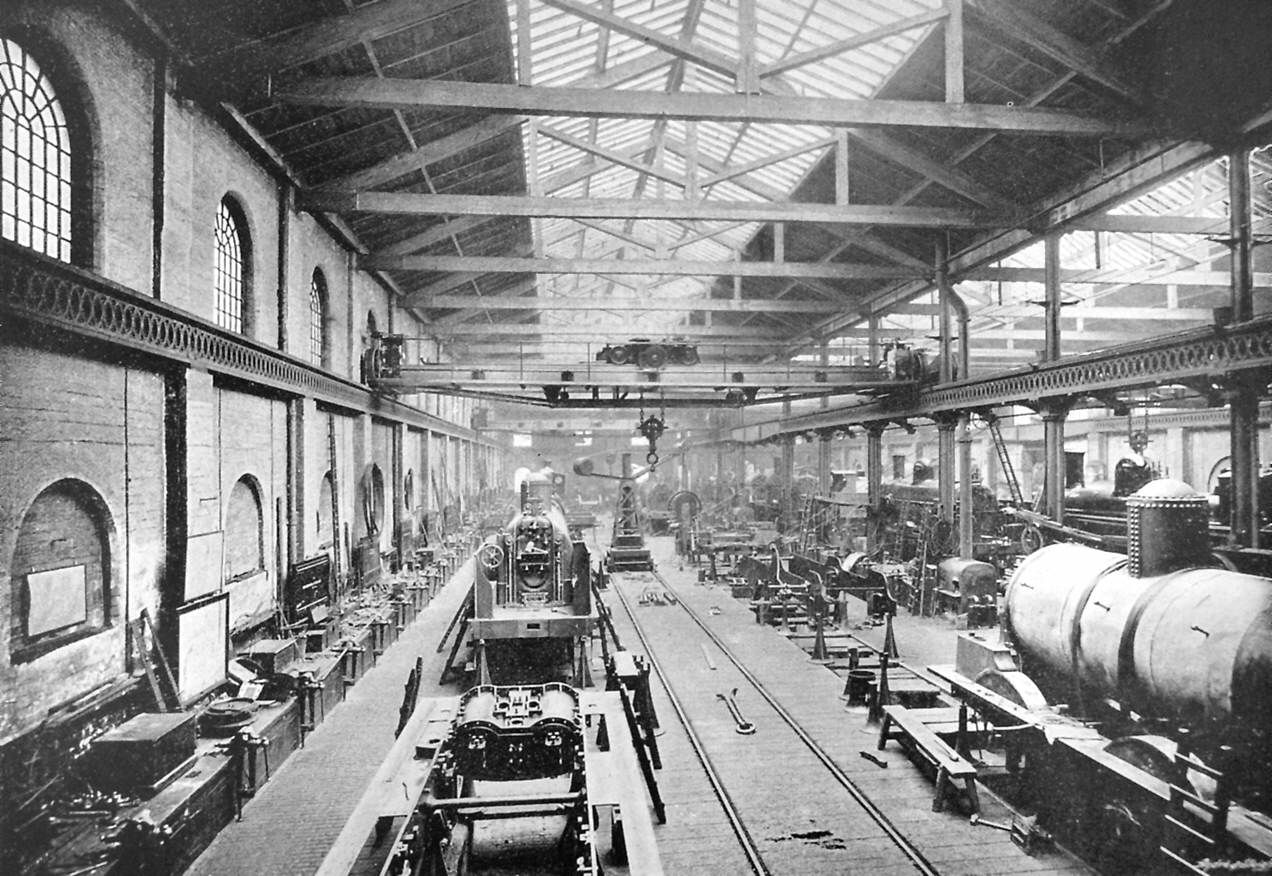
The Welsh Highland Railway (WHR; ) is a restored Narrow-gauge railway, narrow-gauge heritage railway in the Welsh county of Gwynedd. It runs from Caernarfon to Porthmadog, and passes through a number of popular tourist destinations including Beddgelert and the Aberglaslyn Pass. At Porthmadog it connects with the Ffestiniog Railway and to the Welsh Highland Heritage Railway. In Porthmadog it uses the United Kingdom's Porthmadog cross town link, only mixed gauge flat rail crossing. The restoration, which had the civil engineering mainly built by contractors and the track mainly built by volunteers, received a number of awards. Originally running from , near Caernarfon, to ,Boyd (1972), pages=283 the current line includes an additional section from Dinas to Caernarfon. The original line also had a branch to and the Slate industry in Wales, slate quarries around Moel Tryfan, which has not been restored. (This branch forms a footpath "rail trail", the lower section of which has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
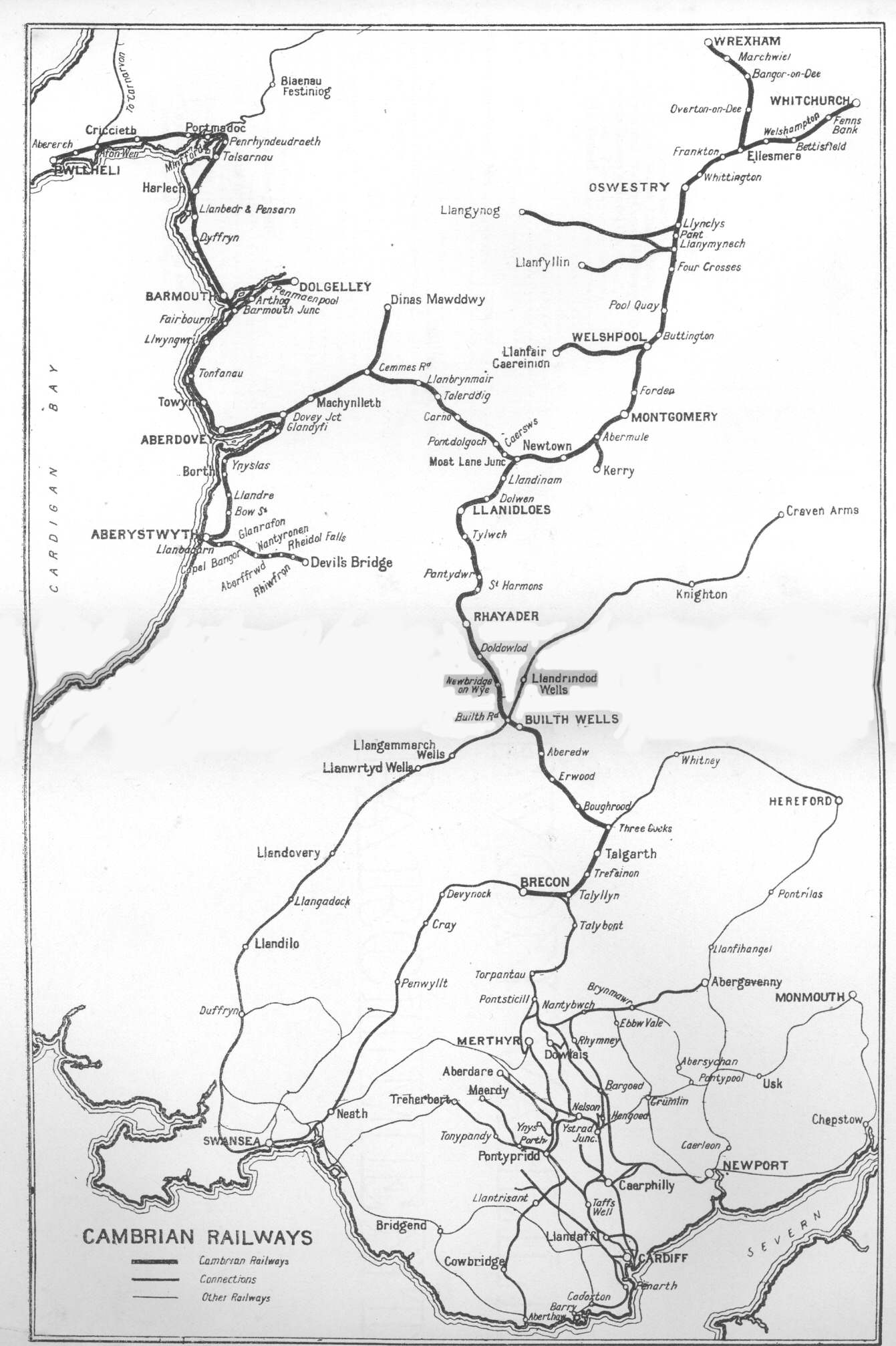
Cambrian Railways
The Cambrian Railways owned of Railway track, track over a large area of mid Wales. The system was an amalgamation of a number of railways that were incorporated in 1864, 1865 and 1904. The Cambrian connected with two larger railways with connections to the northwest of England via the London and North Western Railway, and the Great Western Railway for connections between London and Wales. The Cambrian Railways amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1922 as a result of the Railways Act 1921. The name is continued today in the route known as the Cambrian Line. History Creation of the Cambrian Railways: 1864 The Cambrian Railways Company was created on 25 July 1864 when the (27 & 28 Vict. c. cclxii) received royal assent. The company was formed by amalgamating most of the railway companies in mid Wales: the Oswestry and Newtown Railway, the Llanidloes and Newtown Railway, the Newtown and Machynlleth Railway and the Oswestry, Ellesmere and Whitchurch Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nant Gwynant
Nant Gwynant (also spelt Nantgwynant) is a valley in northern Wales. The A498 road descends into the valley in about two miles (3 km) from Pen-y-Gwryd; it follows the Nant Cynnyd, the Afon Glaslyn and alongside Llyn Gwynant, then beside the Nant Gwynant river to Llyn Dinas and passing below Dinas Emrys to Beddgelert. The road continues through the Aberglaslyn Pass to Porthmadog. History and geography Early references The earliest contemporary reference to a route down the valley comes from John Leland, antiquarian to King Henry VIII, who travelled to Wales in 1538. In describing Nant Gwynant, he wrote: "The trees were so thick that a man on a white horse could not be seen from Llyn y Dinas to Pen y Gwryd." In 1802 Williams Williams described it as “a road, or rather a mere right of passage”. He continued: "Through this charming valley, like all other mountainous unimproved roads, the road is very bad, circuitous, and winding, and absolutely impassable when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyd Ddu Railway Station
Rhyd Ddu is a station on the narrow gauge Welsh Highland Railway, which was built in 1881 as the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways Moel Tryfan Undertaking to carry dressed slate to Dinas Junction on the LNWR. It has also previously been named both "Snowdon" and "South Snowdon". "Rhyd Ddu" is Welsh for "Black Ford". A station for Snowdon In the late 1880s, the construction of a railway up Snowdon from Llanberis was being seriously discussed. The NWNGR company renamed the station "Snowdon" as part of an effort to promote tourist traffic on their railway, especially amongst those who wanted to climb Wales' highest mountain. Some in Llanberis thought this misleading, but as contemporary literature pointed out - Visitors were by now alighting at this halt in droves, and nearby Beddgelert consequently received many more visitors. Horse-drawn road vehicles provided the link to Beddgelert, the connections being included in the railway's timetable. It was largely as a consequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowdon Ranger Railway Station
Snowdon Ranger is a station on the narrow gauge Welsh Highland Railway, which was built in 1878 as the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways Moel Tryfan Undertaking, to carry dressed slate to Dinas Junction on the LNWR. The station was originally known as Quellyn Lake but was renamed after the path to the Summit of Snowdon popularised by, and named after, the local mountain guide, "The Snowdon Ranger", who went by that name for many years and was encountered by George Borrow during his 1854 walking trip. Certainly the name "Snowdon Ranger" was in common use on company timetables from as early as 1879, and that of the adjacent Snowdon Ranger Hotel from at least 1869. Passenger services ceased on 26 September 1936 and the station was reopened in 2003 following the complete reconstruction of the railway from Waunfawr to Rhyd Ddu. The train services are operated by the Festiniog Railway Company's Welsh Highland Railway subsidiary. Snowdon Ranger is currently operated as an unstaffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llyn Cwellyn
Llyn Cwellyn (''Llyn Quellyn'' in some antiquated texts) is a reservoir in North Wales which supplies drinking water to parts of Gwynedd and Anglesey. It lies on the Afon Gwyrfai in Nant y Betws between Moel Eilio and Mynydd Mawr in the northern part of Snowdonia National Park. It has an area of , and is over deep. It is considered relatively oligotrophic. At the southern end is the small village of Rhyd Ddu. Although it is now dammed at the northern end - below the Castell Cidwm ridge, near the village of Betws Garmon - this has not substantially increased the size of the natural glacial moraine lake that has existed since the last ice age. The lake is very deep and is one of the few lakes in Wales to support a natural population of Arctic char. The lake is also home to brown trout and there are otters that are regularly seen at the Castell Cidwm end. The lake has shared ownership between Lawrence Jones (businessman), owner of the Castell Cidwm estate at the northern en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waunfawr
Waunfawr (''gwaun'' + ''mawr'', ") is a village and community, SE of Caernarfon, near the Snowdonia National Park, Gwynedd, in Wales. Description Waunfawr is in the Gwyrfai valley, on the A4085 road from Caernarfon to Beddgelert. It contains the Waunfawr railway station on the Welsh Highland Railway between Caernarfon and Porthmadog. Waunfawr was historically part of the parish of Llanbeblig, which also included the borough of Caernarfon. The Local Government Act 1894 directed that parishes could no longer straddle borough boundaries, and so the part of the parish of Llanbeblig outside the borough of Caernarfon was made a separate parish called Waenfawr. The official spelling was changed from Waenfawr to Waunfawr in 1957. Rural parishes such as Waunfawr were converted into communities in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972. The community had a population of 1,427 at the 2011 census. According to the United Kingdom Census 2011, the percentage of Welsh language speaker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryngwyn Station
Bryngwyn railway station is a former station which was the terminus for passengers on the Bryngwyn Branch of the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways, and later the Welsh Highland Railway. Beyond the station, an incline climbed the slope of Moel Tryfan to serve a series of slate quarries. Those connected by tramways to the incline head included the Alexandra quarry, Moel Tryfan quarry, Fron quarry, Braich quarry and Cilgwyn quarry. History At Bryngwyn a 1 in 10 balanced incline owned by the Welsh Highland Railway led to an upper plateau from where quarry owned lines radiated to several slate quarries in the Moel Tryfan and Nantlle area. Although slate traffic continued as required until final closure in 1936, passenger trains ceased to operate on the branch in 1914. There is very little left of the original Bryngwyn station today, which would have stood in the middle of fields near a farm where the station takes its name. The station consisted of a typical North Wales Narrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinas, Gwynedd
Dinas is a large hamlet near Bontnewydd, Caernarfon, in Gwynedd, north-west Wales. It is in the ancient parish and modern community of Llanwnda and is served by the parish church of St. Gwyndaf in Llanwnda village, which is about a quarter of a mile to the south. The hamlet developed with the opening of the turnpike Toll roads from Caernarfon first to Pwllheli in 1805, then to Porthmadog in 1810. Two coaching inns were built to serve the roads, Y Mount, which is now an Indian restaurant and Tafarn Hen, which is now a private residence. The Carnarvonshire Railway was built in 1866 on the route of the horse drawn Nantlle Railway. The building in 1878 of the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways (later part of the Welsh Highland Railway) resulted in the opening of Dinas Junction station complete with slate transshipment facilities, which brought the construction of houses for the railway staff. The 20th century saw the development of suburban housing for Caernarfon. The present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the LNWR was the largest joint stock company in the world. Dubbed the "Premier Line", the LNWR's main line connected four of the largest cities in England; London, Birmingham, Manchester and Liverpool, and, through cooperation with their Scottish partners, the Caledonian Railway also connected Scotland's largest cities of Glasgow and Edinburgh. Today this route is known as the West Coast Main Line. The LNWR's network also extended into Wales and Yorkshire. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the ( 9 & 10 Vict. c. cciv), which authorised the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croesor Tramway
The Croesor Tramway was a Wales, Welsh, narrow gauge railway line built to carry slate from the Croesor slate mines to Porthmadog. It was built in 1864 without an act of Parliament and was operated using horse power. The tramway was absorbed into the Croesor and Port Madoc Railway in 1865 and later became the Portmadoc, Croesor and Beddgelert Tram Railway in 1879. Part of its route, from Croesor Junction to Porthmadog, was taken over by the Welsh Highland Railway in 1922, and upgraded to allow the operation of steam locomotives. The remainder of the line continued as a horse-drawn tramway, and operated as such until the mid-1940s. History slate industry, Slate quarrying in the remote Cwm Croesor (Croesor valley) dates back to at least 1846 when the Croesor Quarry opened. Quarrying expanded in the early 1860s and transportation to the shipping wharfs at Porthmadog became a limiting factor. In 1862 discussion began to construct a tramway to connect the valley with the sea. An i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |